The Essential Guide to Master Data Management (MDM)
Vikram Verma
Apr 25, 2024
Understanding Master Data Management
With ever-increasing volumes of data, the ability to harness this data effectively and derive meaningful insights has become a critical factor in business success. This is where Master Data Management (MDM) comes into play. MDM is a comprehensive approach to managing an organization's critical data assets, ensuring data consistency, accuracy, and accessibility across multiple systems and applications.
At its core, MDM is about creating a single, trusted view of an organization's master data. Master data refers to the core data elements essential for business operations, such as customer information, product details, supplier data, and financial data. By establishing a unified and reliable master data source, organizations can streamline their business processes, improve decision-making, and enhance overall data quality.
The evolution of MDM practices has been driven by the increasing complexity of data ecosystems and the need for data-driven decision-making. In the past, organizations often struggled with siloed data spread across multiple systems, leading to inconsistencies, duplication, and inefficiencies. MDM emerged as a solution to these challenges, providing a framework for consolidating, integrating, and managing master data centrally.
The Pillars of Master Data Management
To understand the essence of MDM, it's crucial to grasp what constitutes master data. Master data is the foundational data that represents an organization's core entities, such as customers, products, suppliers, and locations. These data elements are typically shared across multiple systems and applications and are critical for business operations and decision-making.
The core components and objectives of MDM include:
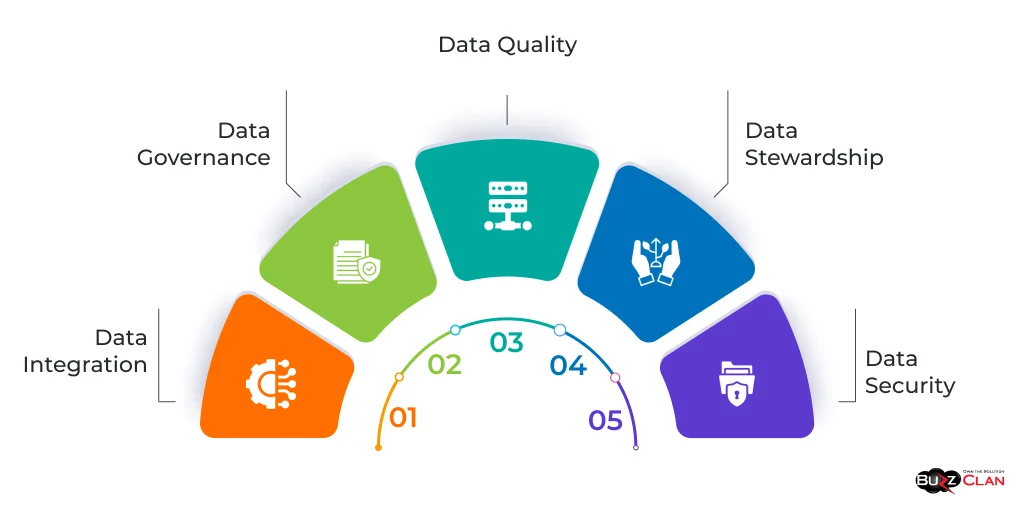
- Data Integration: MDM integrates data from various source systems, such as ERP, CRM, and supply chain management systems, to create a unified view of master data.
- Data Governance: MDM establishes data governance policies and processes to ensure data quality, consistency, and security. This includes defining data standards, ownership, and access controls.
- Data Quality: MDM focuses on improving data quality by identifying and resolving data inconsistencies, duplications, and errors. This ensures that the master data is accurate, complete, and reliable.
- Data Stewardship: MDM assigns data stewardship roles and responsibilities to ensure ongoing maintenance and management of master data. Data stewards are responsible for overseeing data quality, resolving data issues, and ensuring data integrity.
- Data Security: MDM incorporates data security measures to protect sensitive master data from unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance risks.
By addressing these core components, MDM aims to create a trusted and authoritative source of master data that can be leveraged across the organization for various business purposes.
Key Benefits of MDM
Implementing an effective MDM solution offers numerous strategic benefits to organizations. Some of the key advantages include:
- Improved Data Quality: MDM helps enhance data quality by eliminating data silos, resolving data inconsistencies, and establishing data governance processes. This leads to more accurate and reliable data for decision-making.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: By providing a single, trusted source of master data, MDM streamlines business processes and reduces the need for manual data reconciliation. This improves operational efficiency and reduces costs associated with data management.
- Better Customer Experience: MDM enables organizations to gain a 360-degree view of their customers by consolidating customer data from various touchpoints. This allows for personalized interactions, targeted marketing, and improved customer service.
- Faster Time to Market: With a centralized and reliable source of product data, organizations can accelerate product launches, reduce time to market, and ensure consistent product information across channels.
- Regulatory Compliance: MDM helps organizations comply with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, by providing a framework for managing and protecting sensitive master data.
- Improved Business Insights: By providing a unified view of master data, MDM enables organizations to generate valuable business insights, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
MDM empowers organizations to leverage their master data as a strategic asset, driving operational efficiency, enhancing customer experiences, and enabling data-driven decision-making.
MDM Strategies and Frameworks
Developing an effective MDM strategy is crucial for the success of an MDM implementation. An MDM strategy outlines the approach, goals, and roadmap for managing master data within an organization. It considers factors such as data governance, data quality, data integration, and technology architecture.
There are various MDM frameworks and methodologies that organizations can adopt based on their specific needs and goals. Some of the commonly used MDM frameworks include:

- Registry Style MDM: This approach creates a central registry of master data entities, such as customers or products, without physically storing the data. It provides a unified view of master data by linking and referencing data from source systems.
- Consolidation Style MDM: This approach physically consolidates master data from various source systems into a centralized MDM hub. It creates a single, authoritative master data source for downstream applications and processes.
- Coexistence Style MDM: This hybrid approach combines elements of both registry and consolidation styles. It allows for the coexistence of master data in source systems while maintaining a central MDM hub for data governance and synchronization.
- Multidomain MDM: This approach involves managing multiple master data domains, such as customer, product, and supplier data, within a single MDM solution. It enables a holistic view of master data across different business functions.
Organizations should consider their business objectives, data landscape, technology infrastructure, and organizational culture when developing an MDM strategy. The MDM framework should align with the organization's goals and be flexible enough to accommodate future growth and changes.
MDM Tools and Technologies
Various tools and technologies are available in the market to support the implementation of MDM strategies. These MDM tools provide capabilities for data integration, data quality, data governance, and master data management. Some of the market-leading MDM tools include:
- SAP Master Data Governance: SAP's MDM solution provides a centralized platform for managing master data across multiple domains. It offers data consolidation, quality management, and workflow-based data governance features.
- Informatica MDM: Informatica's MDM solution enables organizations to create a single, trusted view of master data. It provides capabilities for data integration, data quality, data governance, and data security.
- IBM InfoSphere MDM: IBM's MDM solution offers a comprehensive platform for managing master data across various domains. It includes features such as data integration, data quality, data governance, and data analytics.
- Oracle Enterprise Data Management: Oracle's MDM solution provides a unified platform for managing master data across the enterprise. It offers capabilities for data integration, data quality, data governance, and data enrichment.
When evaluating MDM tools, organizations should consider scalability, data integration capabilities, data quality features, data governance support, and ease of use. The chosen MDM tool should align with the organization's MDM strategy and integrate seamlessly with existing systems and applications.
Implementing MDM Solutions
Implementing an MDM solution involves a structured approach encompassing various stages and considerations. The key steps in implementing an MDM system include:
| Steps | Description |
| Define MDM Strategy | Develop a clear MDM strategy that aligns with business objectives, identifies master data domains, and outlines the approach for managing master data. |
| Assess Data Landscape | Conduct a thorough assessment of the organization's data landscape, including data sources, data quality, data governance practices, and technology infrastructure. |
| Design MDM Architecture | Design the MDM architecture, including data models, data integration processes, data quality rules, and data governance frameworks. |
| Select MDM Tool | Evaluate and select an MDM tool that aligns with the organization's MDM strategy and requirements. |
| Implement MDM Solution | Implement the MDM solution, including data integration, data quality management, data governance processes, and user training. |
| Maintain and Enhance | Continuously maintain and enhance the MDM solution, including data quality monitoring, data governance updates, and system enhancements. |
During the implementation process, organizations may face challenges such as data quality issues, integration complexities, organizational resistance to change, and lack of skilled resources. To address these challenges, it is essential to establish strong data governance practices, engage stakeholders across the organization, and provide adequate training and support.
MDM in Different Domains
MDM has widespread applicability across various industries and domains. Let's explore how MDM is applied in healthcare, retail, and insurance:
- Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, MDM is critical in managing patient data, provider information, and medical product data. Healthcare organizations can improve patient care, streamline clinical processes, and enhance regulatory compliance by creating a single, accurate view of patient data.
- Retail: In the retail sector, MDM helps manage product data, customer information, and supplier data. By maintaining consistent and accurate product information across channels, retailers can improve customer experiences, streamline supply chain processes, and optimize inventory management.
- Insurance: In the insurance industry, MDM enables managing policyholder data, claims data, and agent information. Insurance companies can improve risk assessment, streamline underwriting processes, and enhance customer service by creating a unified view of customer data.
Real-world case studies highlight the impact of MDM in these sectors. For example, a leading healthcare provider implemented an MDM solution to consolidate patient data from multiple systems, improving care coordination and reducing medical errors. Similarly, a multinational retailer leveraged MDM to create a single product data source, enabling consistent product information across e-commerce and brick-and-mortar channels.
The Role of Data Governance in MDM
Data governance and MDM are closely intertwined. Data governance provides the framework, policies, and processes for managing an organization's data assets, including master data. It establishes the rules, standards, and responsibilities for ensuring data quality, consistency, and security.
MDM, on the other hand, focuses specifically on managing the organization's critical master data. It implements the data governance policies and processes to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of master data across the organization.
MDM is a key component of the larger data governance strategy. It aligns with the overall data governance objectives and ensures that the established data governance framework manages master data. MDM also helps enforce data governance policies, such as data quality rules, data access controls, and data security measures.
Effective data governance is essential for the success of an MDM initiative. It provides oversight, standards, and accountability for managing master data consistently across the organization. Data governance also helps ensure MDM aligns with business objectives and regulatory requirements.
MDM Best Practices
Organizations should adopt best practices for maintaining and scaling their MDM solutions to ensure an MDM implementation's success and long-term sustainability. Some key best practices include:
| Steps | Description |
| Establish Clear Data Ownership | Assign clear data ownership and stewardship roles to ensure accountability for master data quality and governance. |
| Implement Data Quality Processes | Establish robust data quality processes, including data profiling, data cleansing, and data validation, to ensure the accuracy and completeness of master data. |
| Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration | Encourage collaboration among business units, IT, and data governance teams to ensure alignment and buy-in for MDM initiatives. |
| Provide Ongoing Training and Support | Offer continuous training and support to users and stakeholders to ensure effective adoption and usage of MDM solutions. |
| Monitor and Measure MDM Performance | Establish metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor and measure MDM processes' effectiveness and identify improvement areas. |
| Embrace Data Stewardship | Foster a culture of data stewardship, where individuals are empowered to take ownership of master data quality and governance within their respective domains. |
| Conduct Regular Data Audits | Perform regular data audits to assess the quality and consistency of master data and identify any data discrepancies or inconsistencies. |
By adhering to these best practices, organizations can ensure their MDM implementations' long-term success and scalability.
MDM and Data Compliance
MDM is crucial in helping organizations comply with data regulations and privacy laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). These regulations impose strict requirements for collecting, processing, and protecting personal data.
MDM enables organizations to centrally manage and govern sensitive master data, such as customer information, ensuring data privacy regulations handle it. By providing a single, trusted source of master data, MDM helps organizations maintain data accuracy, consistency, and security across systems and applications.
Some key ways in which MDM supports data compliance include:
| Feature | Description |
| Data Access Controls | MDM allows organizations to implement granular access controls, ensuring only authorized individuals can access sensitive master data. |
| Data Privacy and Consent Management | MDM provides mechanisms for managing customer consents and preferences, enabling organizations to respect individuals' privacy rights and comply with data protection regulations. |
| Data Security Measures | MDM incorporates data security measures, such as data encryption, data masking, and data auditing, to protect sensitive master data from unauthorized access and data breaches. |
| Data Lineage and Traceability | MDM maintains data lineage and traceability, allowing organizations to track the origin, usage, and movement of master data, which is essential for compliance reporting and auditing. |
By leveraging MDM for data compliance, organizations can proactively manage and protect sensitive master data, reduce the risk of data breaches, and ensure adherence to data privacy regulations.
Future Trends in MDM
As technology advances and data volumes continue to grow, the future of MDM is poised for exciting developments. Two key trends shaping this future are integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) techniques.
AI and ML can revolutionize MDM by enabling intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and advanced data quality management. Some potential applications of AI and ML in MDM include:
- Automated Data Quality Management: AI and ML algorithms can automatically detect and correct data quality issues, such as data inconsistencies, duplications, and anomalies, reducing manual effort and improving data accuracy.
- Predictive Data Governance: ML models can analyze data usage patterns and predict potential data governance risks, enabling proactive data management and compliance.
- Intelligent Data Matching and Deduplication: AI-powered data matching and deduplication algorithms can accurately identify and merge duplicate master data records, improving data consistency and reliability.
- Personalized Data Views: ML algorithms can analyze user behavior and preferences to provide personalized views of master data, enhancing user experience and productivity.
Other emerging trends in MDM include adopting cloud-based MDM solutions, integrating MDM with big data technologies, and increasing focus on real-time master data management.
As MDM continues to evolve, organizations that stay ahead of these trends and leverage advanced technologies will be well-positioned to derive maximum value from their master data assets.
MDM Career Path and Opportunities
The growing importance of MDM has created exciting career opportunities for professionals interested in data management and governance. MDM professionals are in high demand across industries as organizations seek to leverage their master data for strategic advantage.
MDM roles and responsibilities include:
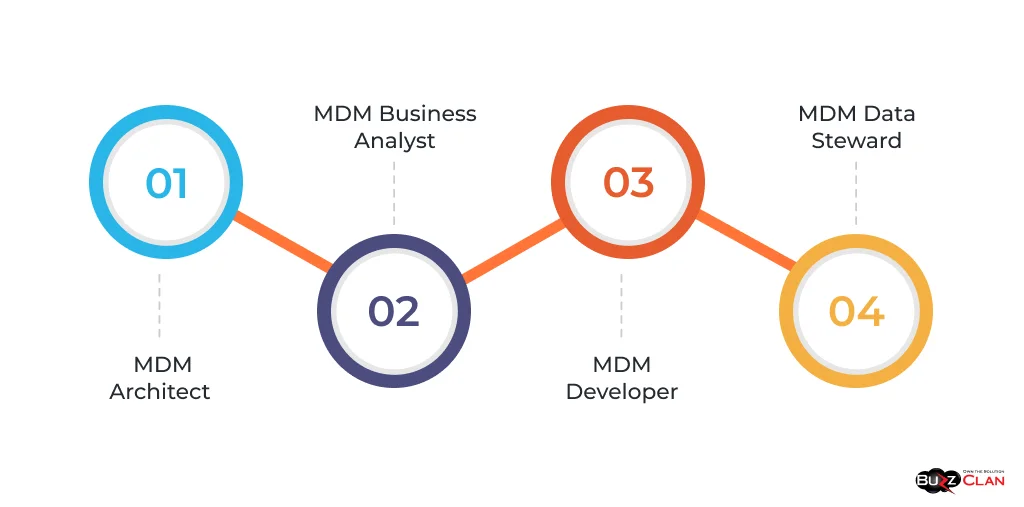
- MDM Architect: Designs and oversees the implementation of MDM solutions, ensuring alignment with business objectives and technical requirements.
- MDM Business Analyst: Collaborates with business stakeholders to identify master data requirements, define data governance policies, and ensure MDM solutions meet business needs.
- MDM Developer: Develops and implements MDM software solutions, integrating data from various source systems and ensuring data quality and consistency.
- MDM Data Steward: This person manages and maintains the quality, accuracy, and consistency of master data within specific domains or business areas.
To pursue a career in MDM, professionals should possess a combination of technical skills, business acumen, and data management expertise.
Some key skills and knowledge areas include:
- Understanding of data management principles and practices
- Knowledge of MDM concepts, frameworks, and methodologies
- Proficiency in data integration, data quality, and data governance tools and technologies
- Strong analytical and problem-solving skills
- Excellent communication and stakeholder management abilities
MDM professionals can expect competitive salaries, with the potential for growth and advancement as they gain experience and expertise. According to industry surveys, the average salary for an MDM Architect in the United States ranges from $120,000 to $180,000 per year. At the same time, MDM Business Analysts and Developers can earn between $80,000 and $120,000 annually.
As the demand for MDM professionals continues to rise, individuals with the right skills and experience can look forward to rewarding and impactful careers in this dynamic field.
MDM Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Let's explore real-world case studies and success stories to illustrate MDM's practical applications and benefits.
- Global Pharmaceutical Company: A leading pharmaceutical company implemented an MDM solution to manage product data across multiple countries and regulatory environments. By creating a single, trusted source of product data, the company streamlined its regulatory compliance processes, reduced time-to-market for new products, and improved overall data quality and consistency.
- Multinational Retail Corporation: A large retail corporation leveraged MDM to create a unified view of customer data across various channels and brands. By consolidating customer data from multiple systems, the company gained a 360-degree view of its customers, enabling personalized marketing campaigns, improved customer service, and increased sales and customer loyalty.
- National Healthcare Provider: A national healthcare provider adopted an MDM solution to manage patient data across multiple hospitals and clinics. The provider improved care coordination, reduced medical errors, and enhanced patient safety and outcomes by establishing a single, accurate view of patient data.
These case studies highlight the tangible benefits that organizations can achieve through effective MDM implementations. By creating a trusted and unified view of master data, organizations can drive operational efficiency, improve decision-making, and deliver better customer experiences.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Nature of MDM
As businesses increasingly rely on data to inform strategic decisions, drive innovation, and deliver exceptional customer experiences, the need for accurate, consistent, and trustworthy master data has never been greater.
Throughout this blog post, we have explored the various facets of MDM, from its core components and benefits to its implementation strategies, best practices, and real-world applications. We have seen how MDM enables organizations to break down data silos, improve data quality, and create a single, unified view of their master data.
As we look to the future, the role of MDM in enabling data-driven success will only continue to grow. With the advent of AI, machine learning, and other advanced technologies, organizations that invest in robust MDM practices will be well-positioned to derive maximum value from their data assets and stay ahead of the competition.
However, implementing MDM is not a one-time project but an ongoing journey that requires commitment, collaboration, and continuous improvement. Organizations must approach MDM as a strategic initiative, involving stakeholders from the business and IT and fostering a culture of data stewardship and governance.
By embracing MDM as a core component of their data management strategy, organizations can lay the foundation for long-term success in the digital age. They can make better-informed decisions, optimize business processes, and deliver exceptional customer experiences, all while ensuring the integrity, security, and compliance of their master data.
In conclusion, we encourage all businesses to recognize the indispensable nature of MDM and invest in the people, processes, and technologies needed to manage their master data effectively. By doing so, they can unlock the full potential of their data assets and thrive in an increasingly data-driven future.
FAQs

Get In Touch