The Future Unclouded: Navigating Tomorrow’s Cloud Computing Trends
Ronak Sharma
Jan 16, 2025
Introduction
Over the past decade, cloud computing has transitioned from an emerging innovation to the fundamental backbone underpinning enterprise information technology today. Cloud platforms now supply the computational power driving everything from mobile apps to billion-user social platforms and AI breakthroughs expanding human potential.
While cloud adoption continues accelerating across industries, the technology itself maintains relentless momentum – with new paradigms like multicloud, serverless computing, and edge delivery gaining traction. This fluidity demands awareness and strategic readiness to harness the latest cloud advancements confidently.
This comprehensive guide explores the current cloud landscape and market trajectory while spotlighting pivotal emerging trends set to redefine cloud computing usage and upside in the 2020s. Let’s peer into the future unclouded by uncertainty!
The Current State of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has entered mainstream enterprise IT budgets and roadmaps. Public cloud spend crossed $500 billion in 2022 growing over 15% year-over-year, as more workloads move from private data centers to leverage cloud’s flexibility, savings and innovation pace.
Market Share Distribution
The cloud market bifurcates between infrastructure / platform services and software solutions on top. Amazon Web Services dominates the IaaS/PaaS segment with 33% market share, trailed by Microsoft Azure at 22% and Google Cloud Platform with 11%, per Canalys.
SaaS leaders include ubiquitous platforms like Microsoft Office 365, Google Workspace and Salesforce. Niche clouds focus on vertical needs – telehealth, genomics, engineering simulation, and advertising.
Overall Growth Trajectory
Total cloud spend is estimated to reach $1.3 trillion by 2025 compounding annually by 16%, reports Gartner. While early stages saw smaller productivity apps migrate, strategic system modernization underway mid-decade targets core legacy HR, ERP, supply chain and customer relationship management to cloud through 2030 with sustained enthusiasm.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Computing
Multiple pivotal technology and market forces promise to further the cloud computing trajectory over the coming decade:
Technological Advancements
Several architectural platforms and paradigms gaining adoption will expand cloud possibilities:
- Multicloud and hybrid cloud combining private infrastructure with multi-vendor public resources suit specialized needs. Organizations also avoid vendor lock-in through diversification.
- Microservices and containerization allowing workloads to be composed modularly from independent components – then deployed across clusters speeding lifecycles through granular changes.
- Serverless computing simplifying event-driven data and application logic execution without provisioning full-stack servers. Automated scalability and usage-based pricing amplify attractions.
- Edge computing pushes storage and compute closer to data sources and usage locales – improving responsiveness. This suits applications from retail to automation with sensitivity to network latency.
Industry Market Directions
Equally pivotal are go-to-market and consumption model evolutions entering the mainstream:
- As-a-service consumption grows prevalent allowing near-instant project acceleration by consuming building blocks like analytics, governance and data preparation fully managed – without platform skill mastery. Flexibility and time-to-value matter more.
- Industry verticalization increases with purpose-built capabilities for healthcare, communications, manufacturing, and transportation sectors. Meeting specialized needs outpaces horizontal generalizations.
- Partner ecosystem traction gains momentum on leading clouds as validated third-party capabilities fill gaps in mapreduce, streaming, quantum machine learning and IoT applications using tools like AWS Marketplace and Azure Arc. Community multiplicity fosters choice.
Enterprise Cloud Journeys
Lastly, from the standpoint of user migration and adoption trends – these directionalities gain prominence:
- Beyond basic productivity apps, mission-critical workload mobilization momentum rises inside enterprises desperate to escape legacy constraints. Evaluating the degree of cloud readiness and pragmatic migration pathways now lead planning.
- Multi-year roadmaps shepherd incremental transition balancing agility ambitions and pragmatism given current team skills, cultural readiness for change plus operational and technical debt limiting options.
- Cloud-first application modernization initiatives set directives to replatform existing assets while ensuring new capabilities get conceived natively for cloud service consumption rather than on-premise deployment fallbacks. Cloud fluency training expands.
The Cloud Computing Market Players and Their Domains
Horse races fuel cloud vendor comparisons, but specialization also warrants highlighting unique strengths:
Cloud Generalists and Market Share Leaderboard
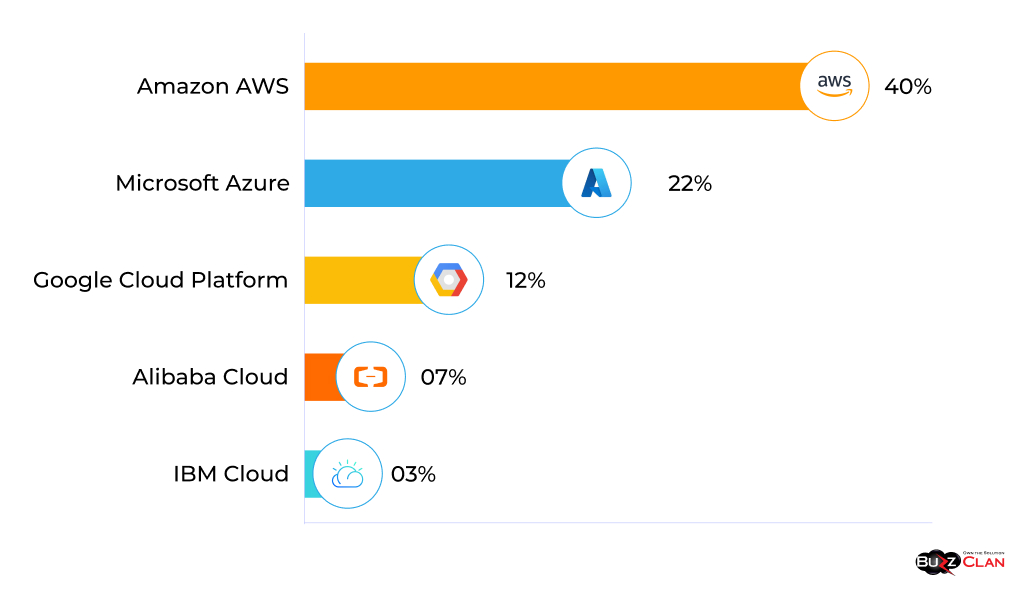
The major public IaaS and PaaS operators battle for enterprise wallet share. Latest worldwide market share standings as of mid-2023:
- Amazon AWS – 40%
- Microsoft Azure – 22%
- Google Cloud Platform – 12%
- Alibaba Cloud – 7%
- IBM Cloud – 3%
AWS maintains market leadership with the broadest, deepest cloud services portfolio covering over 200 categories from foundational IaaS offerings to specialist AI, blockchain, satellite data capabilities and developer-centric PaaS tooling fuelling web scale startups.
Azure counters with tight integration into Microsoft’s ubiquitous SaaS productivity stack – Office365, Dynamics, Power Platform – and on-premise workload interoperability bridging legacy environments to cloud through hybrid interconnect options.
Meanwhile Google Cloud strategically focuses on open source appeal, sustainability positioning and leveraging databricks for machine learning appeal – though scale lags considerably.
Secondary IaaS combatants operate successfully in geographic niches – Oracle for US government agencies, Tencent Cloud in China, Naver Cloud in Korea and local operators across Eastern Europe, Latin America and Southeast Asia.
Cloud Services Spectrum
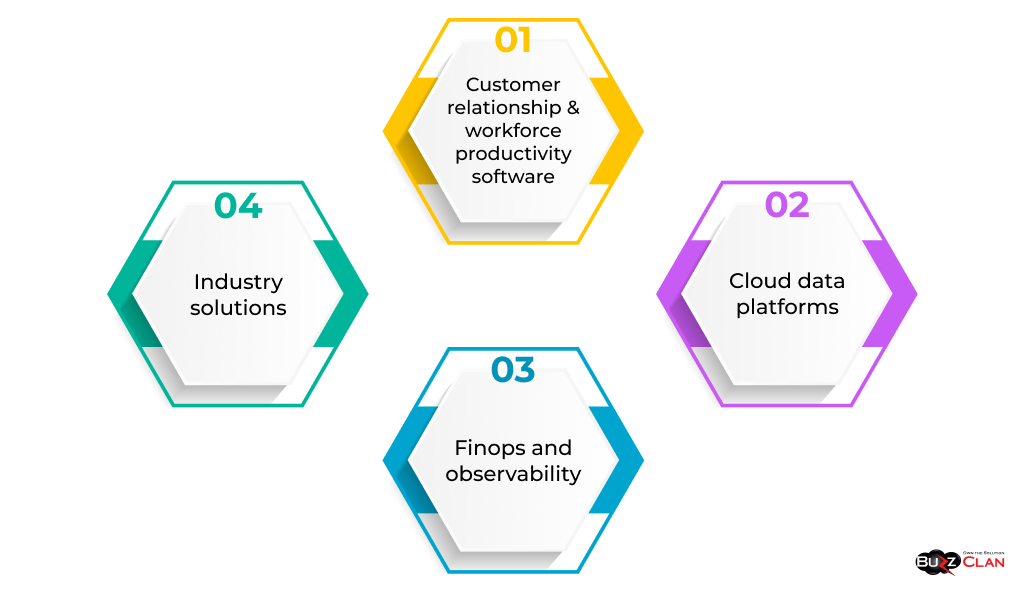
Drilling down into specific workload categories reveals vibrant specialization across pioneers despite commoditization of basic building blocks -servers, storage and networking:
- Customer relationship & workforce productivity software – Salesforce, Workday and ServiceNow command respect with market-leading SaaS capabilities earning recurring revenues and healthy margins. Slack, Atlassian and Dropbox lead horizontal niches.
- Cloud data platforms – Modern analytics and data warehousing offerings from Snowflake, Databricks, Confluent and Starburst surpass legacy options in performance, flexibility and TCO for processing petabytes. AWS Redshift maintains market strength while Azure Synapse competes.
- Finops and observability – Monitoring and optimizing cloud spending explode as complexity obscures visibility. CloudHealth, Datadog, and Dynatrace lead APM. Mongo Atlas leads managed databases.
- Industry solutions – Healthcare (Epic, Cerner, Teladoc), life sciences (Veeva, IQVIA), agriculture (ADAM), automotive (Aerospike), financial (Mambu, ThoughtMachine) and manufacturing verticals each adopt tailored platforms addressing niche needs standardized horizontal clouds miss.
Future Predictions for Cloud Computing
Based on adoption barriers faced by customers presently, analysts anticipate enterprise cloud directions will emphasize:
Cloud Market Growth Forecasts
International Data Corporation (IDC) predicts worldwide spending on public cloud to reach $1.3 trillion by 2025 – representing 16% CAGR often coming at the expense of traditional outsourcers.
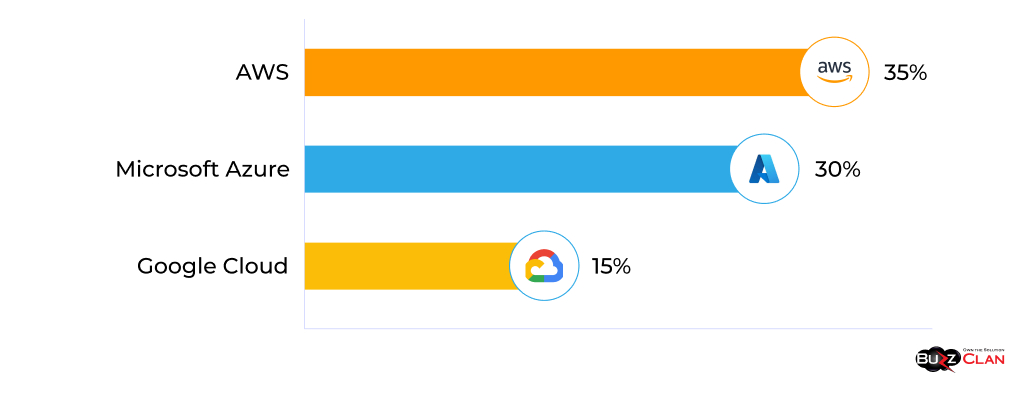
Assuming patterns witnessed in the past persist through the decade, IDC projects market share by 2030 as:
- AWS – 35%
- Microsoft Azure – 30%
- Google Cloud – 15%
This implies Azure continues gaining larger enterprise spend through turnkey integration with essential Microsoft software-as-a-service offerings – Dynamics CRM, Sharepoint, Exchange Online – embedded into day-to-day business processes.
Technological Augmentation Trajectories
Advances across the core cloud delivery chain aims to simplify adoption spanning:
Automated cloud management – AIops platforms via applications like DigitalOcean App Platform and InfoScitex Wize automate manual tasks – provisioning, scaling, uptime monitoring – through workflow orchestration and predictive analytics.
Global decentralized infrastructure – Using blockchain mechanisms to coordinate resource delivery enables edge computing location independence from centralized clouds while maintaining economies of scale.
Confidential secure computing enclaves – Multi-party computation using encrypted data processing eliminates risks of exposing proprietary algorithms or sensitive datasets to any cloud.
Hybrid cloud turnkey appliances – Converged hardware solutions like Dell EMC Cloud PowerEdge C2 rapidly standup infrastructure, virtualization management, storage capacity and disaster recovery natively across distributed environments on-demand without deep operator skills.
Challenges and Considerations
Still, these enterprise struggles adopting cloud computing remain roadblocks needing mitigation:
Evolving Cloud Security and Compliance Standards
Managing hostile threats and meeting fast-changing regulatory compliance remains challenging, requiring constant investment:
- Nation state cyberattacks pose digital sovereignty threats from data persistence in unauthorized international regions or topological domains outside enterprise control.
- Exact data lineage and residency confirmation demands increase importance given explosion of regulations – like GDPR, CCPA around personally-identifiable information (PII) encryption, plus industry edicts in finance and healthcare safeguarding records.
- Edge computing shifts from centralized security controls to localized distributed mechanism brings risks akin to the mobile era.
Key Cloud Security Trends will encompass:
- Multi-factor authentication using biometrics becoming default access patterns moving beyond easily phished tokens and passwords persistently
- Granular attribute and policy-based access controls instead of blanket permissions to entire resources leading to incidents
- End-to-end encrypted workflows and storage preventing malicious activities or surveillance further growing manifold
Revamping Enterprise Integration and Change Management
Migrating mission-critical legacy systems-of-record into cloud persistently struggles from economic constraints and inadequate skillsets. Common snags include:
- Integrating tightly coupled legacy applications secured investment given high risks. Breaking dependencies risks outages disrupting operations.
- Limited cloud fluency across infra and middleware administrator teams to overhaul toolchain adoption including provisioning, deployment scripts, and monitoring workflows safely.
- Platform compatibility shortcomings require running legacy virtual machines on IaaS longer than desired temporarily even while new cloud-native apps get engineered given code surgery barriers.
Best practices combatting hurdles cover sustainable re-education campaigns, setting quality bars preventing shadow IT emergence and prioritizing integration modernization across domains with the highest user friction.
Preparing for the Cloud Computing Future
Based on the evolutionary cloud landscape explored above- here is guidance for technology leaders seeking to leverage cloud advances rather than be disrupted by industry shifts:
Strategic Planning for Future of Cloud
- Embrace multi-cloud adoption for select workloads to de-risk from infrastructure failures, regional jurisdictional changes or technology platform obsolescence risks concentrated into one mega-vendor.
- Align architecture leadership with specialization as generalist skills get commoditized – prioritizing emerging domain expertise in Kubernetes, distributed ledgers, blockchain infrastructure operations and low code workflow orchestration.
- Allow decentralized autonomy between teams balancing alignment tradeoffs using product management hierarchy above while nurturing team accountability below for customer outcomes.
- Encourage teams to assess moot alternatives with market maturity, incent experimentation separate from legacy constraints and obsolete practices through innovation days and hackathons exploring pre-release capability horizons quarterly if not faster.
- Enable practitioners to avail loose coupling in existing tight legacy application estates through APIfication layers, exposing core functions using modern interfaces for emerging channels based on pragmatism.
The Next Destination Beyond Cloud Computing
Current episodic pressures – economic volatility, energy crises, supply chain turbulence -mandate pragmatism for most IT groups rather than chasing supposedly utopian innovations disconnected from reality.
However, the perennial quest for maximizing autonomy, mastery and purpose continues inspiring exploration into emerging paradigms each holding revolutionary potential once achieving fruition:
- Reversible computing using quantum principles promises massive energy efficiency gains executing calculations by uncomputation – discarding intermediate states.
- Autonomic systems capable of self-management via integrated monitoring, analytics and control loops render human oversight optional by learning operational envelopes safely first.
- Democratized full-stack infrastructure abstraction liberates worldwide talent through simplified no/low code environments where intent translates into collateral (code, configurations, orchestrations) transparently.
Conclusion
In closing, cloud computing remains firmly entrenched as the predominant mechanism powering digital transformation across institutional and consumer technology landscapes for the next decade at least.
Core focus areas for enterprises encompass migration prioritization balancing rapid modernization needs with pragmatic integrations, talent realignment and optimizing multi-cloud leverage sustaining leverage.
Meanwhile, the next frontiers look set to massively expand access and exponentially improve provisioning economics as cloud increasingly becomes the primary conduit for technological self-actualization at scale.
FAQs

Get In Touch
Follow Us
Table of Contents
- Perkenalan
- Kondisi Terkini Komputasi Awan
- Tren-Tren Baru dalam Komputasi Awan
- The Cloud Computing Market Players and Their Domains
- Cloud Services Spectrum
- Future Predictions for Cloud Computing
- Challenges and Considerations
- Preparing for the Cloud Computing Future
- Kesimpulan
- Pertanyaan yang Sering Diajukan (FAQ)