Cloud Computing: The Guide to Powering Modern Business
Ravinder Kumar
Mar 7, 2025
Did you know that by 2026, the world will have produced 200 zettabytes of data, and global cloud computing spending is expected to reach $947.3 billion?
While the numbers are enormous, the potential of cloud is far broader. 84% of companies in the US use private cloud for their business. Do you also look forward to migrating your business to the cloud? If yes, you are at the right place. Before planning, you must know about all cloud computing aspects in detail. We will discuss all that and the solutions to challenges that may come along the way. But before that, let’s define cloud computing.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing allows access to computing resources like software, databases, storage, and networks over the internet. The catch is that you only pay for the resources you use and can save a ton by not investing in hardware. All you need to do is partner with a cloud provider, and they will help you fulfill your requirements with ease. From handling high traffic during online sales to running your favorite Netflix and ensuring sustainability, the cloud has made the technological revolution possible.
Brief History of Cloud Computing
Do you remember the time when floppy disks were used for storage? The worst part was that you could only use your data on the machine it was saved. There was no way you could access it from different locations. A solution to centralizing data was required, and hard drives and local networks came in handy. However, the problem was solved only partially.
With the advent of the internet, the idea of cloud computing began to see daylight. Businesses demanded a solution where they could make the best use of infrastructure, software, and development tools without the hassles of managing them. With these parameters in mind, Amazon launched its Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) in 2006. Since then, cloud computing has influenced all industries by making technology accessible and facilitating seamless application development.
Cloud Computing Importance in the Digital World
Cloud computing has enabled the digital world to expand its services across borders while maintaining security and flexibility.
- Keep Up With the Market: Cloud services let you scale your operations according to business demands and better adapt to market changes.
- Efficient Innovation: With the necessary tools, you can deploy applications faster, test new applications, and sell them faster.
- Worldwide Access: You can easily access data anywhere and look forward to seamless remote work environments where you can collaborate in real-time with your peers.
- Easy Access To Tools: You no longer need to spend months developing applications. Instead, you can depend on cloud applications to fulfill your requirements at minimal costs.
- Data Security and Backup: The cloud has multiple security features and layers, which allow you to maintain data integrity and back up faster during disasters.
Types of Cloud Deployment Models
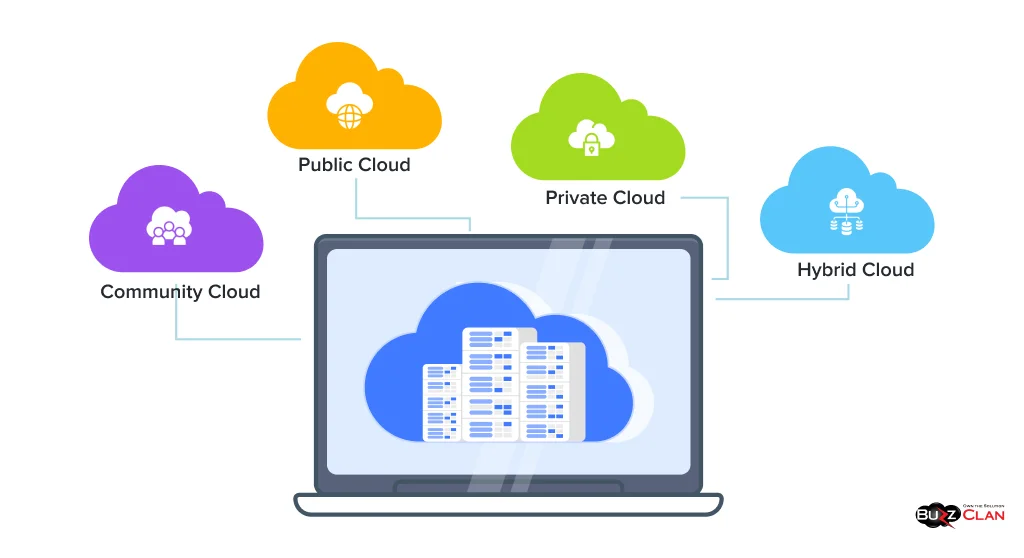
Cloud computing offers multiple choices. Here’s a closer look at the main cloud deployment models.
Public Cloud
These cloud environments are owned by third-party providers and are shared between multiple organizations. The best part is that you require minimal technical expertise to run your business operations on the public cloud. You can access their services anytime and anywhere with a good internet connection.
However, these environments have shared resources, which may put your sensitive data at risk. Moreover, you can not do much about the features offered by your provider as customization capabilities are limited. More importantly, you must always rely on the provider to guarantee uptime and availability.
Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
Private Cloud
These cloud environments are ideal for organizations that want top-notch privacy and security. You can choose to manage them on-premise or by a third-party provider. The best part about these solutions is that you get exclusive access and control over the infrastructure and can customize them to meet your needs.
Moreover, with added privacy and security, meeting industry standards in such environments is easier. However, maintaining their hardware requires heavy investments, and scaling these solutions is a major challenge. Furthermore, you must spend a fortune on in-house experts to manage private cloud operations.
Examples: VMware’s vCloud and OpenStack.
Hybrid Cloud
If you wish to leverage the power of private and public clouds, hybrid clouds can be your pick. Not only do you get access to a vast pool of resources, but you also get access to top-notch security and data protection.
Leveraging both environments allows you to scale your resources and ensure the best backups quickly. However, everything is not rosy with these cloud environments. You will need to be extra cautious when integrating both of these environments. Also, the costs can add up quickly with additional features.
Examples: Netflix, AWS Outposts, Azure Hybrid Benefit, IBM, Azure Arc
Community Cloud
Companies with similar technological needs often prefer to invest in a community cloud, which helps them establish smooth collaboration and share costs. The best part about these environments is that they address diverse compliance needs, allowing companies to ensure data privacy and security easily. However, these environments have significant drawbacks. They offer limited scalability and are not ideal for fulfilling extensive demands.
Examples: Cisco, Cloud4C, Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE)
You may like to read “Public Cloud vs Private Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud.“
Cloud Services Explained (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
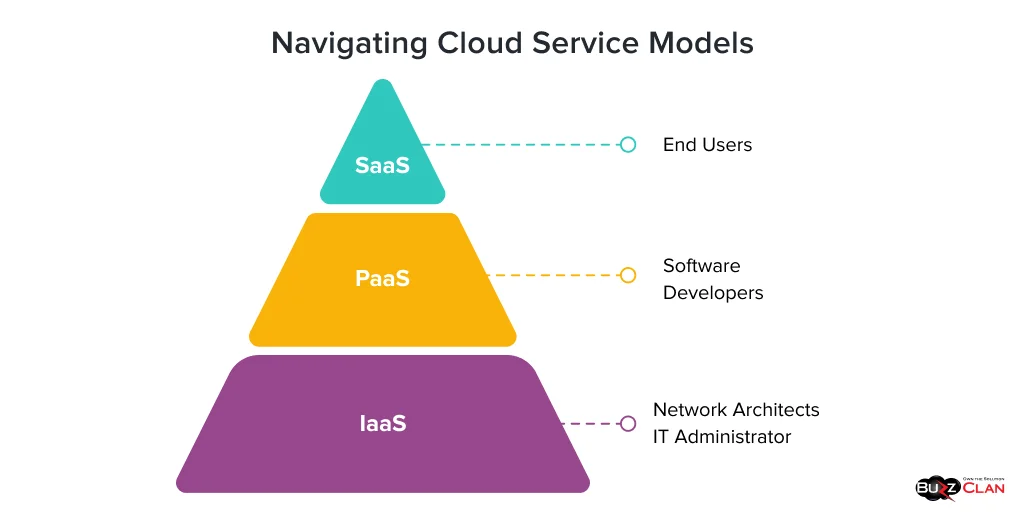
Here are the cloud service models used in cloud computing.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
What if you could access computing resources without managing infrastructure? Well, IaaS does that and much more! The list is endless, from simplifying operations to building virtual environments! All you need to do is take care of the setup and maintenance while your provider handles the storage, networking, and infrastructural needs.
Characteristics of IaaS
- Pay-as-you-go pricing
- Complete control over applications, operating systems (OS), and applications.
- Scales as per your needs
Best IaaS Tools
- Amazon EC2 (AWS)
- Linode
- Alibaba Cloud
- Rackspace
- Google Compute Engine (GCP)
- Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS is your savior if you want a platform that lets you build and deploy applications minus the hassles of infrastructure management. You get access to a platform that provides tools, middleware, and database management, letting you focus entirely on building applications. All these functionalities have made it a common denominator among developers worldwide.
Characteristics of PaaS
- You get access to built-in tools like databases, APIs, and development environments.
- Simplifies app development by handling OS, runtime, and middleware.
- You can look forward to faster development cycles.
Best PaaS Tools
- Google App Engine
- Cloud Foundry
- Engine Yard
- IBM Cloud
- Dokku
- Heroku
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Are you tired of developing apps to fulfill your business demands? Wait for a second, as the universe just heard your demand! Jokes apart, SaaS tools let you achieve on multiple fronts with enhanced ease. Whether managing your projects on a management tool, onboarding your clients, watching your favorite shows on Netflix, or studying for a prestigious exam, SaaS brings the best of the world to your fingertips with the simple demand of a good internet connection and zero hassles of maintenance, installation, or updates.
Characteristics of SaaS
- Cloud providers manage these solutions
- They are accessible anywhere with internet connectivity.
- You can take their subscriptions for a desired duration.
Best SaaS Tools
- ProofHub
- Zapier
- Basecamp
- Calendly
- Netflix
- Slack
- Salesforce
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is ideal for business owners or IT teams that wish to run code but don’t want to manage servers. This model’s best feature is that you no longer need to configure settings manually; it automatically scales based on changing demands. Due to its multiple benefits, developers working on lightweight, scalable, and event-driven applications prefer this cloud model.
Characteristics of Serverless Computing
- It is an ideal solution for developers as they can solely focus on code
- The perfect model for microservices and event-driven tasks
Top Serverless Computing Tools
- Genezio
- Google Cloud Functions
- Azure Functions
- AWS Fargate
- Vercel Functions
- Cloudflare Workers
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
There are two sides to the coin; the same applies to cloud computing. Let’s have a look at the advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| You will save a lot on energy costs, hardware, and maintenance. | The long-term costs can be high as subscriptions and usage fees can add up quickly. |
| Small businesses can benefit as the initial investment is low. | Large-scale transfers can be costly and time-consuming. |
| You can look forward to the rapid deployment of new tools and techniques. | Performance may witness a dip due to shared resources and network latency. |
| You can work on shared projects in real time, irrespective of location. | You will have less control over infrastructure and software configurations. |
| You can use resources efficiently and reduce your carbon footprint with ease. | However, you must pay additional charges for storage, data transfers, and premium features. |
Cloud Computing Usage Across Industries
Here is how industries make the best of cloud services.
Finance and Banking
The financial sector has made remarkable improvements in the cloud. Here’s how they use the cloud to their advantage.
- Detecting fraudulent transactions with ease
- Supporting mobile banking apps and digital payment processing
- Enabling secure API integration with fintech partners
- Securing data storage and meeting multiple regulatory requirements
- Providing built-in encryption and access controls
Manufacturing
The world of manufacturing owes its innovative spirit to the cloud. This is how they have made the best use of cloud computing.
- Leveraging predictive maintenance to maintain sound machine health
- Real-time production monitoring and tracking
- Demand forecasting and maintenance planning
- Creating virtual replicas of physical assets
Retail and E-commerce
Thanks to cloud computing, the retail and e-commerce industry has impacted every corner of the world. Here are some ways in which the cloud has impacted the industry.
- Seamless inventory management and demand forecasting
- Personalized marketing with customer behavior analysis
- Handling seasonal demand with elastic computing
Media and Entertainment
The media industry has grown exponentially, which would have been impossible without cloud computing. Here is how it made the best use of the cloud.
- Cloud-based video editing for extraordinary experiences
- Distributing content globally
- Offering personalized recommendations
- Providing live service operations
Key Components of Cloud Computing
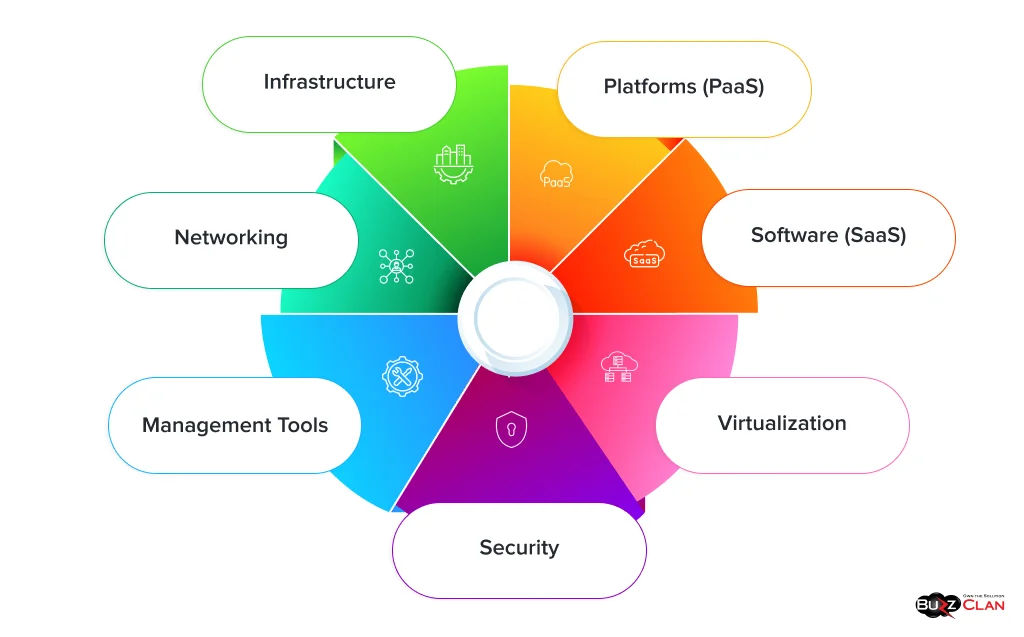
Let’s understand the main components of cloud computing.
- Infrastructure: All physical and virtual resources required to deliver cloud services are managed in this component.
- Platforms (PaaS): This component ensures that you get the tools and environment for building applications without the hassles of managing hardware.
- Software (SaaS): With SaaS, you can access multiple applications over the internet without the need to install or maintain them.
- Virtualization: This is a technique by which you can easily create virtual versions of physical resources, and it helps you manage your cloud resources efficiently.
- Networking: This component greatly ensures sound communication between users, resources, and devices.
- Security: One key aspect of the cloud is ensuring your infrastructure is safe from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Management Tools: These comprise all services and software required to ensure optimal performance in the cloud.
Challenges and Risks in Cloud Computing
The cloud is not risk-free. Before you jump on the train, here is what you need to know.
Lack of Knowledge and Expertise
Due to the complex nature of cloud management, working on it becomes tedious. You need to ensure that your employees are constantly updating and upgrading themselves. While multiple opportunities exist to build in the cloud, the knowledge gap must be covered first. As a business owner, you can conduct training and urge your employees to invest in suitable courses, develop an in-depth understanding, and then manage cloud applications with minimum issues and maximum reliability.
Cost Management
While cloud service providers offer the “Pay As You Go” model, the setup costs can be sky-high. For the same, you must ensure that you use the resources to their maximum capacity. Also, overall costs can increase with a sudden spike in usage. Managing all these aspects can be time-consuming. Lastly, if you turn on services and forget to turn them off, you will also pay for them.
Interoperability and Flexibility
Let’s be honest. You cannot be switching cloud providers every month. However, if you need to switch one after a few years, you must ensure clarity on multiple fronts. Often, cloud providers have set data management and security metrics. This is why applications written with one cloud in mind must be rewritten for another. Managing the entire process requires attention to detail and careful planning, which can be time-consuming.
Multi-Cloud Environments
Close to 84% of enterprises depend on multiple cloud providers. This can increase the load on the infrastructure team and make management difficult. While many cloud providers offer automated management, you must be careful when signing collaboration agreements. Make sure to keep your customer needs at the forefront when you invest your stakes in multi-cloud environments.
Data Security and Privacy
Data security is a significant concern when switching to cloud platforms. While a cloud provider assures data integrity, you are responsible for verifying their claims. You need to speak with their customers and carefully review their testimonials. Dealing with the cloud requires sending and receiving vast amounts of data, which is vulnerable to leaks. Identity thefts, data breaches, and malware infections can damage your brand reputation.
Performance Challenges
Even minimal latency can lead to a huge percentage drop in users and declined profit margins. This is due to inefficient load balancing, which is responsible for poor user experience. Thus, there is an emerging need to ensure top-notch performance and a robust disaster recovery strategy. If you do not work on these aspects, you will lose customers and damage your reputation.
High Dependence on Network
Since resources are provisioned in real time, high-speed networks are necessary for cloud computing. While these data and resources are exchanged over the network, a sudden outage can harm your business. This is why many companies invest in multi-cloud environments, as seldom would two providers fail simultaneously. Thus, you must ensure that internet bandwidth is always high and your cloud service provider guarantees 99.9% uptime.
How To Select A Cloud-Based Service Provider?
Security and performance must be your top priorities when choosing a cloud service provider. Also, ensure you have answers to all these questions before making a final decision.
- Scout reviews, read testimonials, and connect with existing customers to get a clear picture.
- Choose a cloud provider that offers free trials, training support, and a dedicated knowledge base. Also, check their customer support. Are they willing to support you with queries 24/7?
- Check how well your cloud service provider scores regarding scalability, security, and compliance. Do they offer comprehensive audit and logging services? Also, if they face a security breach or an issue, how do they report it?
- Does the cloud provider fit your budget needs? Are there any hidden costs you need to be aware of? Also, make sure to compare multiple providers before you finalize them.
- How are their report generation features? Do they have well-defined communication channels?
- Does their list of tools support your existing technology stack? If not, do they have APIs to help you easily maintain a sync?
- Do they have a clear exit strategy in place? If you want to shift to another platform in the future, are there any costs or procedures you need to be aware of?
Comparison of Top Cloud Service Providers
What makes the top cloud service providers different and yet a favorite of tech giants? Let’s find out!
| Cloud Service Providers | Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Microsoft Azure | Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | IBM Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Founded in | 2006 | 2010 | 2008 | 2016 |
| Key Strengths | AWS boasts the largest ecosystem among the top cloud providers and offers the best and widest range of services. | Azure offers top-notch enterprise integration capabilities, making it a favorite among businesses. | GCP is known for providing advanced AI/ML tools and data analytics. | You can say goodbye to all your security concerns with the IBM cloud. |
| Pricing | Pay-as-you-go model | Pay-as-you-go model | Flexible pricing with user discounts. | Competitive pricing for enterprise-grade users. |
| Global Data Centers | 100+ availability zones in 30 regions | 60+ regions globally. | 35+ regions globally. | 20+ regions globally. |
| Customer Support | Multiple tiers with 24/7 support. | 24/7 support with enterprise-level SLAs. | Multiple tiers, including AI-driven support. | Dedicated support for enterprise clients. |
| Market Share (Q4 2024) | 30% | 21% | 12% | 2% |
Future Trends in Cloud Computing
The future of Cloud Computing is bright. With businesses working day and night to make it more secure and robust, it would be interesting to note the future developments. Here is a list of future trends in cloud computing.
Widespread Adoption of AI and ML
While GCP is known for its advanced AI and ML functionalities, more businesses will follow suit. These tools will improve decision-making, speed implementations, and customer service and design ease. Many industries have already jumped on the train to fine-tune their operations, and others will soon follow suit.
Rise In Use of Cloud-Native Technologies
Microservices, Kubernetes, and Docker will continue to dominate all industry needs. These technologies are gaining importance because they are lightweight and offer low latency. The best part is that they are super fast to execute and provide much-needed scalability, portability, and resilience in cloud-native applications.
Cloud-Powered Quantum Computing
Quantum computing will no longer be a challenging scientific term. Jokes apart, the top cloud service providers will work on developing quantum computing as a service (QCaaS), paving the way for solving complex problems in materials science and cryptography.
Global Adoption of Zero Trust Architecture
With cyber threats evolving faster than the speed of light, it becomes all the more important to have advanced security solutions. Hackers no longer rely on usual techniques but use advanced evasion to tamper with your systems. As a result, there is an emerging need for security measures that can foil breach attempts and provide comprehensive security. Zero trust models will help ensure that on a wide scale and leave no room for faulty systems.
Top Cloud Capabilities to Learn About
While scalability, security, and transparency are critical components of cloud infrastructure, the cloud has revolutionized data management, zero-trust, sustainability, and cost optimization. Let’s learn more about the top cloud capabilities.
Cloud Storage
Cloud storage involves storing digital data on an off-site location server. Usually, third-party providers maintain these and are responsible for managing and securing infrastructure data. However, you should not trust them blindly. Ensure you understand their processes in-depth before letting them handle your data. Once you have done that, you will be saved from the hassle of owning and operating your data centers. Furthermore, you can expand and reduce your data footprint on demand.
Cloud Networking
Traditionally, organizations used their private network hardware components to create an isolated environment. However, setting up and managing them became complicated over time. Fret not; the cloud is there to your rescue! Cloud networking solves these challenges by letting your organization use virtual network components instead. All you need to do is focus on efficiency and optimizing configuration, and your cloud service provider will manage the hardware and infrastructure.
Cloud Migration
Cloud migration involves moving data, infrastructure, applications, and other objects to a cloud computing environment. If you are working on legacy applications and are willing to modernize them, moving them to the cloud is wise, as you can use multiple functionalities to make your business operations seamless. Companies usually move data from on-premises servers to the public cloud. Once migrated, the systems undergo optimization and modernization. Thus, choose the proper techniques; the right cloud migration strategies will make your transitions smoother.
Cloud Data Management
Cloud data management involves maintaining data across cloud platforms. With cloud data management, you can look forward to optimized resource allocation and seamless data sharing and enjoy the best of both worlds. Many businesses choose to work with multi- and hybrid cloud providers, as they can keep sensitive data on the private cloud and others on the public cloud to save costs.
Cloud Security
Cloud security comprises best practices, technologies, and cybersecurity policies for securing applications, data, and infrastructure in cloud environments. It provides storage and network protection against internal and external threats. While cloud computing is a common choice for companies globally, migrating to dynamic cloud environments requires new approaches to security. This ensures data remains secure across online infrastructure, applications, and platforms. Usually, cloud service providers follow a shared responsibility model. This implies that security is a joint responsibility and depends on your model. The more a provider manages, the more they can protect.
Cloud Governance and Compliance
Cloud compliance ensures that your environment follows one or more specific security and privacy standards. These requirements vary from region to region, and you must thoroughly understand them to avoid penalties and fines. These standards could be established by the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) or the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). You can also set internal standards for your organization to stay ahead of competitors.
Cloud Sustainability
Cloud sustainability defines how organizations tailor their decision-making to meet organizational and environmental goals. Customers are more willing to work with organizations that follow these practices. With cloud sustainability, your IT department can ensure minimal environmental damage when architecting, optimizing, and deploying workloads in the cloud.
Cloud Cost Optimization
Ensuring the perfect balance of cloud resources for each application takes work. You need to monitor costs as each workload is unique and the requirements evolve. Cloud cost optimization can reduce costs while ensuring zero compromise on performance. It also ensures that your cloud investments are aligned with organizational requirements.
Cloud Performance Optimization
Performance is a crucial factor in cloud computing. Cloud performance optimization reduces cost, minimizes resource wastage, and adjusts workloads. This lets you identify and work on the most effective infrastructure setups for multiple scenarios. Moreover, you get a better return on investment by leveraging application metrics to guide resource usage.
Transform Your Business Landscape With BuzzClan’s Cloud Expertise
The team of experts at BuzzClan understands that customization is the key to cloud computing. No two businesses have the exact needs. This is why we conduct a thorough infrastructural analysis and document your needs to build the best solutions. We use tools and techniques that help you stay consistent with monitoring and logging. This way, you stay ahead of competitors and enjoy top-notch security. Here is what you can look forward to with BuzzClan.
- Providing 99.99% uptime
- ROI- focused implementation
- Cloud-native development expertise
- Industry-specific compliance expertise
- Seamless application modernization
- Reduced deployment time
One of our significant achievements has been supporting Levernie Corp. in successfully mitigating a disaster. One of our financial sector customers was affected by a natural disaster. Luckily, it had a solid recovery plan and could return online in a few hours without data loss or downtime.
Summing Up
Are you still wondering whether to integrate the cloud into your business? If you wish to stay ahead of competitors, the choice is yours! However, jumping on the trainer is a no-brainer if you want to achieve operational excellence like never before. Before you place your unwavering faith in cloud functionalities, thoroughly analyze your cloud providers and their security settings.
If you play it casually there, you will compromise your data security and customer trust. Thus, investigate and select a provider that can offer customized plans and scale per your requirements. This will help you experience the full influence of the cloud and take your business to higher echelons of success.
FAQs

Get In Touch






