Implementing Enterprise Data Backup and Recovery: Strategies and Solutions
Neha Nair
Jul 4, 2025
Data backups and recoveries are among the most effective ways to secure data. However, only 54% of organizations have a well-defined and documented disaster recovery plan. These plans protect organizations from detrimental breaches and help them recover faster when their systems are compromised.
Moreover, 30% of organizations have poorly documented disaster recovery plans, and 41% don’t upgrade and update them. Worse, 51% of SMBS don’t have an incident response plan in place.
Consequently, if you don’t regularly back up your data, you’re setting your business up for failure and inviting cyber attacks. Luckily, everything is not lost; we’re here to support you.
This blog will discuss the multiple aspects of data backup and recovery to help your organization stay current on the best strategies and solutions.
What is Data Backup and Recovery?
When discussing data backup and recovery, we refer to a system where you create copies of your data and store them securely. This is done knowing that your data can be restored quickly and stays usable in the event of data loss, corruption, cyber attacks, or a system failure.
While backups prevent accidental data deletion, recovery helps you restore it and maintain business continuity. Likewise, you must use the best tools and techniques and comply with industry best data retention and security practices. Shockingly, only 10% of IT users take backups daily, whereas less than 20% do it weekly and monthly. 26% of users do it in less than a year, and 20% never do it!
Importance of Backup and Recovery
With the average cost of a data breach reaching a whopping $4.45 million, inadequate data protection and financial risks come crawling in. Above all, these make data backup and recovery a must for modern data management strategies. As a business owner, you cannot wait for attacks to materialize and then take action. One of the best examples is the attack on the Colonial pipeline that disrupted fuel supplies across the U.S. East.
In an ideal world, businesses fulfill all customer needs and work 24/7. However, you can still ensure 99.99% of that with robust backup and recovery solutions. While reduced downtime is a significant advantage, these solutions also ensure regulatory compliance. Meanwhile, test them regularly and update them according to the latest trends, considering real-world scenarios. As a result, this will help you build organizational resilience and keep your assets safe amidst uncertainty.
Types of Data Backup Methods
Multiple types of backup are essential for seamless protection and disaster recovery. Let’s understand each one.
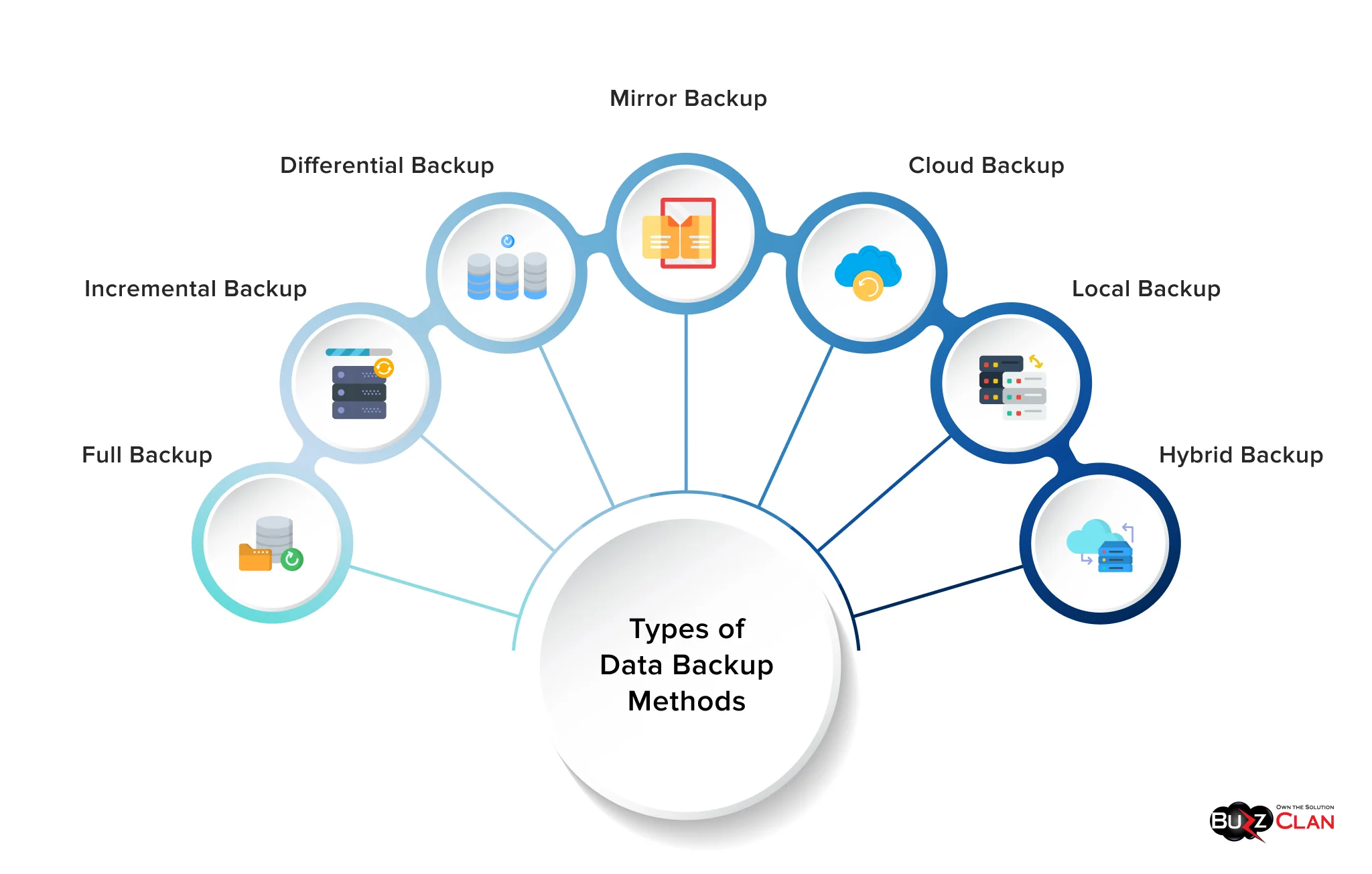
Full Backup
While full backups are time-consuming and take longer than other types, they are also the easiest to manage and restore. A copy is made regardless of when it was last modified, files, folders, or other data. Moreover, the best part is that they are not dependent on backups. All you need to do is ensure significant storage. You can do a full backup either weekly or monthly with other backups.
Incremental Backup
Data is subject to multiple changes, and this backup type takes care of that. And what does that mean? It only copies the data that has changed/added since the last backup. These backups are faster and help you save more storage than full backups. However, restoration can be complex as you must sequentially restore the previous and other incremental backups. Lastly, there is an increased risk of data loss if an incremental backup is corrupted or missing.
Differential Backup
A differential backup ensures all data has changed since the last full backup was copied. So, when you restore your data, you only need the last full backup, the last differential backup. Moreover, the restoration speed is high, and you can quickly build a balance between storage efficiency and the former. It is a better option than incremental backups, as only two are required. However, all that glitters is not gold. Besides, differential backups can grow in size and are slower than incremental backups for regular creation.
Mirror Backup
If you wish to have a replica of the source data, then mirror backup is your ideal choice. This data is copied as is, without encryption or compression. Thus, the best thing about this backup type is that it is updated in real time. Moreover, you can easily access and restore data without any hassles. However, there are a few drawbacks to mirror backups. It doesn’t provide a version history, so you will not have a backup if the lost data is deleted, as changes are made in real time. In addition, significant storage is required due to no compression.
Cloud Backup
These backups are stored on a remote cloud-based infrastructure provided by cloud service providers. Most importantly, you can easily automate and scale them per your organizational demands. All you need is a good internet connection. However, you must handle cloud storage costs, which can increase over time.
Local Backup
All you need are hard drives for these backups. Yes, you read that right! You don’t even need an internet connection for these backups. Similarly, you only need to shell out some money for hardware costs and get going. While they are much faster than cloud backups, they can be ruined if a local disaster occurs. Subsequently, all these aspects make them challenging to maintain at certain times.
Hybrid Backup
The perfect blend of local and cloud backups, these backups ensure that your data is available in off-site and regional locations. Additionally, it is a favorite among businesses as the recovery times are faster, and cloud backups offer much-needed resilience. However, you must balance management and infrastructure, as local and cloud backup systems are involved.
Further Reading
Key Strategies for Effective Data Backup
Did you know that only 28% of organizations back up their research and development data? Still, the multiple backup times don’t get the security they deserve. Here is a list of strategies that will help you guarantee adequate data backups.
Follow the 3-2-1 Backup Rule
This strategy is followed by organizations worldwide. Thus, you must maintain three copies of your data in this document. The first is the primary copy, whereas the other two are backups. The practice is to store your backups on two kinds of media. They can be hard drives for cloud storage. This will significantly reduce the risk of hardware failure. At the same time, you must ensure that one backup is stored off-site or in the cloud to protect against fires, theft, or local disasters. Besides, doing all this will ensure maximum reliability and accessibility in emergencies.
Automate Your Backups
Manual backups are often prone to inconsistencies and human error. Thus, automation is the key here. So, you need to set a time to schedule your backups- daily, weekly, or monthly. This way, you can heave a sigh of relief that your data is backed up without human intervention. Moreover, multiple backup tools and cloud services will help you automate the process and reduce the risk of missed backups.
Make Use of Versioning and Incremental Backups
Your data will keep changing over time, so keeping multiple versions of your files is a must. With versioning, you can store several iterations of the same file, and this will come in handy when you restore previous versions in case of accidental deletions. You can even use incremental backups, where only the data that has changed since the last backup is saved. As a result, you can save time and storage compared to performing full backups.
Prioritize Critical Data
Not all data is essential, so you need to analyze which data should be backed up. However, databases, financial records, and business applications must be backed up frequently. Doing so will ensure that critical data is protected in the best possible way.
Establish Clear Backup Retention Policies
It is a must to lay down clear backup retention policies. They will decide how long backups should be kept and when they should be deleted or archived. However, if you retain too many backups, you will only waste storage space. On the other hand, if you don’t maintain them long enough, you will lose precious data. Thus, make sure that your retention policy is aligned with business needs.
Steps to Restore Data Backup and Recovery
Before you restore your data backup and recovery, you must check that critical information is also being restored. These steps will help you ensure that you are on the right track.
- Before you restore your data backup and recovery, you must check that critical information is also being restored. These steps will help you ensure that you are on the right track.
- Likewise, gauge the situation and understand the nature of the data loss or system failure before you begin the process. Is a single file corrupted, or is it a complete system failure? Knowing this information will help you determine which kind of backup is most suitable for restoration.
- Now that you understand the situation, you must select the most appropriate backup. You can choose a full, incremental, or versioned backup depending on your needs.
- The next step is to ensure your storage device is ready for restoration. Is there enough storage space for the data? Are your external drives prepared for the process? Also, check your network connections to see if you need to restore them from the cloud.
- Access your backups and check if you have proper credentials and access permissions.
- Navigate through the storage and select the files or folders you wish to restore. At the same time, some systems allow you to perform specific files, while others let you restore entire systems.
- Kickstart the restoration process. The time required for cloud and remote backups depends on the size of the data and your internet speed. Meanwhile, the time needed for local backups is less. However, it still depends on whether the data is restored. Moreover, ensure you don’t interrupt the process.
- Once the process is complete, verify the integrity of the restored data. Then, test any applications or systems that rely on it to ensure they function correctly.
- Lastly, thoroughly check and monitor for any performance issues in the restoration process.
Modern, Comprehensive vs. Traditional Backup and Recovery
While traditional systems are low-cost and utterly independent of network connectivity, modern solutions reduce the risks of human errors and can easily handle growing data volumes.
| Aspect | Modern, Comprehensive Backup and Recovery | Traditional Backup and Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | These solutions leverage cloud-based or hybrid systems. | Often rely on physical storage media like DVDs or local hard drives. |
| Storage Location | Data is stored in multiple locations for redundancy. | Data is stored in a single remote location or on-site. |
| Frequency of Backups | Real-time backups. | Backups are scheduled daily, weekly, or monthly. |
| Automation | Backups are automated with AI/ML tools, detecting suspicious activities and recovery. | Manual processes are more commonly used while there is limited automation and scheduling. |
| Recovery Speed | The recovery times are faster as snapshots, replication, and failover tools are used. | The recovery times are slow due to manual handling. |
| Recovery Point Objective (RPO) | Data loss is minimal due to frequent and incremental backups. | There is a higher risk of data loss as the backups are less frequent. |
| Recovery Time Objective (RTO) | The recovery is super fast, and granular recovery options are available. | The recovery is slower because traditional methods require more time. |
| Data Volume Management | It is ideal for larger data volumes. | The scalability offered is limited, making managing extensive data volumes difficult. |
| Data Security | Advanced encryption, compliance features, and robust access controls are standard. | Unauthorized access is common as there are limited encryption and security features. |
| Redundancy | Built-in redundancy using multi-cloud or geographically distributed backups. | Minimal redundancy as they rely on physical copies or local systems. |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective in the long run as they run on the cloud. | High upfront costs for hardware and ongoing costs for maintenance and storage. |
| Monitoring and Alerts | Offers real-time monitoring, proactive alerts, and predictive analysis. | Limited monitoring and manual alert systems. |
| Disaster Recovery (DR) | Integrated disaster recovery tools with automated failover and testing. | Disaster recovery requires additional time and effort to implement. |
Tools and Solutions for Enterprise Backup and Recovery
Here is a list of tools and solutions for enterprise backup and recovery.
| Category | Tool/Solution |
|---|---|
| Data Backup and Recovery |
|
| Cloud Solutions |
|
| Data Management |
|
| Cloud Backup |
|
Offsite Servers vs. Independent Drives
Let’s understand the differences between offsite servers and independent drives.
| Aspect | Offsite Servers | Independent Drives |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | They are located in data centers or cloud infrastructure and can easily be accessed online. | These include physical storage devices like SSDs, USB drives, and external hard drives. |
| Accessibility | Accessible anytime and anywhere with an internet connection. | Accessible only when physically connected to a compatible device. |
| Storage Capacity | Scalable storage options are available depending on your provider. | The size of the drive limits these solutions. |
| Data Security | Cloud providers offer security measures like encryption and firewalls. | Practices like multi-factor authentication and encryption are used. |
| Risk of Data Loss | The loss is minimal as the service provider maintains backups. | The risk is higher as drives can be damaged, lost, or stolen. |
| Cost | You are charged monthly or annually based on the storage and usage. | There is a one-time cost for purchasing the drive unless maintenance is needed. |
| Maintenance | Service providers maintain servers, which include patches, updates, and hardware repairs. | You are responsible for maintaining drives. |
| Speed | Dependent on internet speed; high-speed internet enables fast access and uploads | Offers high-speed access locally (e.g., USB 3.0, Thunderbolt). |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; users can increase or decrease storage as needed. | Limited scalability; requires buying a new drive for additional storage. |
| Portability | It is not physically portable, as it exists in remote locations. | While they are portable and easy to carry, they are prone to physical damage. |
| Customization Capabilities | Limited by the options provided by the service provider. | It is fully customizable based on the user’s preferences for setup and use. |
| Examples |
|
|
Best Practices for Data Backup and Recovery
Following these practices will help you implement data backup and recovery for your business.
Establish Clear Objectives and Policies
You must be clear on your objectives before implementing a backup strategy. Meanwhile, you need to understand the data that needs to be backed up, its frequency, and the level of protection required. Post that creates a policy that outlines them and gives a clear idea of retention strategies (how long backups should be kept before they are archived/deleted). Lastly, the responsibilities for backup tasks should be defined, and they should be tracked regularly.
Automate Backups
Manual backups are full of errors and inconsistencies. Thus, automating them is a must to ensure smooth functioning. So, you must set a schedule update frequently and use software that gives timely alerts if anything goes wrong. Lastly, you will need to ensure that backups are taken outside peak working hours to avoid any disruption in workflow.
Use Incremental and Differential Backups
Working in a stepwise manner is the key to getting good results. Similar is the case with backups. We read in the blog that full backups are time-consuming and take a long time to complete. Thus, it is best to use incremental or differential backups. These strategies will help you reduce time and storage while ensuring top-notch data integrity and ease of recovery.
Encrypt Data Backups
Cybercriminals would be utterly disappointed when they cannot understand your data. Thus, it is a must to use encryption algorithms like AES-256 to ensure that your sensitive data is always safe. You can choose a solution offering built-in encryption or consider encrypting backup files individually if stored in cloud environments or shared networks. Just make sure to encrypt backups during storage and transmission. Also, don’t think your job is done once you have implemented encryption. Lastly, you will still need to use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to limit access to your backup and storage systems.
Regularly Test Backup and Recovery Procedures
We all have heard that prevention is better than cure. This also holds for data backup and recovery. When you regularly test these processes, you will have nothing to worry about in the event of a disaster. How can I do that? Test if your backup files can be restored and read without errors. Another thing you must do is to simulate data loss scenarios and see how quickly and effectively you can recover your data. Ensure you do this once every 3-6 months or if you have made any significant changes to your system. Doing so will help you deal with potential issues before they become big problems.
Ensure Scalability of Backups
You cannot expect miracles from the same backup strategy you started with. They must scale with your business. Thus, only invest in a backup solution that accommodates increasing data loads. Meanwhile, you can use cloud-based or hybrid backups, depending on your business needs.
Documentation To Rescue
Documentation is the key to seamless data backup and recovery. Thus, document all your schedules, processes, and associated information. This will help your team take the right actions and serve as handy training material. The second thing you need to do is use monitoring tools to track backup health and address any performance issues. How will this help you in the long run? Well, not only will this help you resolve issues faster, but it also ensures seamless backups and recovery.
Fulfill Data Backup Compliance and Legal Requirements
All industries have diverse regulatory requirements that drive data retention and backup practices. So, ensure the backup solutions you use comply with industry requirements. And how do you ensure that? To do so, you must regularly review and update your backup strategies. Also, you must understand how to implement retention schedules or get help from an expert. Subsequently, this will help you analyze how long you can retain backups and when to archive or destroy them.
Ensure Backups Are Physically Secure
Where you store your backups is a combined business decision. However, physical security must be a given. This means that whether you use on-premise or cloud backups, you must protect the devices from unauthorized access or theft. At the same time, double-check with your cloud provider about how they secure their data centers. This way, you can also prevent data from tampering and maintain its integrity.
Build A Disaster Recovery (DR) Plan
You might wonder why you need a disaster recovery plan when working on your backups. Well, it will only make it simpler to recoup if your organization faces a data loss or a system failure. The process to follow is simple. Moreover, ensure you have outlined the steps to take if such an event occurs. After that, decide the maximum time data must be recovered and limit the acceptable data loss per your backup frequency. As a result, you can minimize downtime and maintain your customers’ trust.
Further Reading
Data Backup Strategies for SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS Environments
Data backup and recovery strategies in cloud environments are tailored to each model’s characteristics and service requirements. Let’s examine the backup plan for each environment.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
While cloud providers manage the infrastructure and application updates in the SaaS model, you will still need to bear data protection responsibility. Here are some strategies that will come in handy.
- First, understand your cloud provider’s data retention policies and backup features. Few offer limited data backup and recovery for defined time frames, and you may need to invest in additional tools.
- Secondly, automated backup scheduling should be used to ensure that essential data is backed up regularly. This will minimize the risk of data loss due to attacks or unintentional human errors.
- Thirdly, check if your chosen SaaS platform integrates with other systems to ensure seamless data exchanges and backup.
- Suppose you are dealing with a SaaS application that doesn’t offer sufficient backup capabilities. In that case, you can schedule regular data exports to on-premise systems to create a separate and secure archive.
PaaS (Platform as a Service) Backup
In PaaS environments, you are responsible for handling application data and ensuring its integrity, whereas your cloud provider will handle the hardware, storage, and networking requirements. Here are some backup strategies that will come in handy.
- The first step is to use Paas-specific tools to ensure your data is regularly backed up and can be restored.
- Secondly, managed database and storage services will help you automate processes. To manage the entire process, use version control systems.
- Thirdly, when planning a backup strategy, you must ensure that your code and configurations are backed up. Also, document all your processes and dependencies. They will help you restore your systems to a working state in case of failure.
- Lastly, ensure you have distributed backup copies in multiple regions to stay up and running during an outage.
PaaS (Platform as a Service) Backup
The best thing about IaaS environments is that you have great control over your applications, data, and operating systems. However, you are also responsible for handling backup and disaster recovery. Here are some strategies that will come in handy.
- First, use IaaS-specific tools to back up the state of your virtual machines.
- Secondly, leverage snapshots for guaranteed protection against deletion or corruption. They are a powerful tool for protection against accidental deletions.
- Thirdly, all the critical data stored in block storage must be backed up.
- Moreover, you must use automation tools to schedule backups of configurations, databases, and virtual machines.
- While IaaS offers excellent backup, store backups in a different location and region for an added layer of protection.
- Lastly, multiple network settings and security configuration backups are needed for seamless restoration during recovery.
Security Considerations in Backup and Recovery
Cybercriminals always look to take advantage of poor security measures in your data backup and recovery systems. However, you need to keep these factors in mind to keep them at bay.
- Use strong encryption algorithms to ensure secure backups and protect them from lurking cyber threats. This will also help prevent unauthorized access and data tampering.
- Ensure only authorized personnel have access to backup systems. Not all your employees must be able to access backups. Thus, you should enable audit logging features to track who accessed backup systems and suspicious activity.
- Make sure the backups’ physical and virtual locations are secure. If you depend on a cloud provider, check whether they have the necessary security certifications. Also, check that your data is stored at multiple locations to ensure disaster readiness.
- Use hash functions to ensure backup data integrity and check for tampering. You can even use Write-Once, Read-Many (WORM) storage to ensure the data cannot be modified or deleted once the backup is complete.
- Conduct regular audits of your data backup and recovery processes to ensure they align with the best practices and foil unauthorized access attempts. Moreover, you must set automated alerts to inform you of any issues or anomalies with the backup process.
- Understand how you can securely dispose of backups when they are no longer needed.
- Ensure that remote workers back up data only with encrypted web portals or Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to prevent data interception. Also, endpoint security measures should be implemented on devices to avoid data breaches.
In addition to these measures, ensure you take care of these aspects. They will help you protect your systems from threats.
Air-Gapped and Immutable Backups
These backups are logically isolated from your network to prevent cyber threats. This is why they are stored offline on external hard drives, tape drives, and on-premise cloud storage with advanced access controls. Thus, keep your weekly backups offline after completion. At the same time, immutable backups cannot be altered or deleted once they have been written. Consequently, they are a must-have to protect against cyber attacks or encrypt backup data.
Ransomware Protection in Backups
Ransomware has led to many companies losing millions. It is time to realize that traditional security systems will not suffice. Subsequently, to have robust protection against backups, ensure you have implemented multi-layered security strategies. They will help you identify suspicious activity quickly and alert administrators before the damage spreads. Similarly, you should also use network segmentation to ensure your backups are isolated and there is a lesser attack surface for cybercriminals.
Backup Validation Techniques
Imagine depending on your backups with a blind eye, and they decide to ditch you at the last moment. You don’t want that to happen! Thus, it is necessary to use backup validation techniques and ensure that your backed-up data is accurate, complete, and recoverable whenever needed. Likewise, techniques like checksum verification, synthetic full backups, and automated test restores are necessary. Most importantly, hospitals with electronic health records (EHRs) must implement automated restores as they recover sample data from backups and compare it to the source. Lastly, they flag discrepancies so that you can take action before actual disasters occur.
Backup Metadata Management
Backup metadata is a must-have as it contains all the information about backed-up files, including storage locations, timestamps, versions, and retention policies. Thus, you must ensure you can retrieve data quickly and stay on top of compliance needs. Therefore, e-commerce companies handling vast customer transaction data use metadata tagging in their backup systems. This makes it easier for them to locate specific datasets without scanning the entire backup repository. Ultimately, this streamlines their workflow significantly.
Industry-Specific Applications of Data Backup and Recovery
Let’s understand how different industries use data backup and recovery methods.
| Industry | Applications of Data Backup & Recovery | Compliance Standards | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare |
|
|
Data backup and recovery are necessary to prevent the loss of sensitive medical data and aid faster recovery. |
| Finance & Banking |
|
|
Data backup and recovery will help you prevent fraud, ensure compliance, and maintain the integrity of your data. |
| Government |
|
|
Protects sensitive government data, unauthorized access, and cyberattacks. |
| Education |
|
|
Safeguards student and faculty data while ensuring seamlessness in digital learning environments. |
| Retail & E-commerce |
|
|
Protects customer payment information, ensures business continuity, and prevents data breaches. |
| Manufacturing |
|
|
It prevents downtime in manufacturing processes and protects intellectual property from cyber threats. |
Data Backup and Recovery in Small Businesses vs. Enterprises
While small businesses focus on affordability and simplicity, enterprises invest in robust, scalable solutions to ensure compliance and business continuity.
| Aspect | Small Business | Enterprises |
|---|---|---|
| Budget | The budgets are limited. | The budget is comparatively larger to accommodate advanced solutions and specialized teams. |
| Infrastructure | Small businesses rely on external drives or essential cloud backups. | The solutions are complex and multi-layered, with dedicated data centers and cloud solutions. |
| Flexibility | Systems are smaller, and you will need to scale them manually. | The solutions are highly scalable and leverage automation to handle growing data volumes. |
| Data Volume | The data volumes are in the range of a few GB to TB. | The data volume goes up to petabytes as it is distributed across multiple locations. |
| Complexity | The focus is on system backups, and the solutions are relatively straightforward. | The solutions are multi-layered and often require orchestration. |
| Backup Frequency | Backups can be scheduled manually, weekly, or daily as fewer critical systems exist. | Continuous and real-time backups to meet organizational objectives. |
| Recovery Time | The recovery times are longer and may take days. However, they are used due to simpler setups and fewer criticalities. | Recovery times range from minutes to hours as they are essential to meet operations and SLAs. |
| Automation | Manual methods are used to schedule and manage backups. | Enterprise-grade tools are used, and minimal manual intervention is required. |
| Backup Storage | Local storage with limited redundancy. | The storage is distributed across multiple locations for seamless disaster recovery. |
| Compliance | Small businesses must only follow a few regulatory requirements unless operating in a regulated industry. | Must abide by strict compliance standards. |
| Disaster Recovery (DR) | Disaster recovery plans are informal and only focus on backups. | The comprehensive recovery plans include testing, failover mechanisms, and regular audits. |
| Staffing Needs | No dedicated staff is required. | Dedicated IT teams are required for this. |
| Testing and Validation | Backup testing is often overlooked. | Regular and automated testing of backups and recovery processes are standard practices. |
Modern Technology Integration
Let’s see how modern technology enhances the ability of data backup and recovery methods.
Container Backups
Containers are short-lived and created dynamically, rendering traditional methods ineffective. In addition, to ensure your backup strategies are robust, snapshot-based backups and stateful container protection are necessary. For example, Kubernetes-based applications use tools like Kasten K10 to restore settings quickly, even if a container crashes. As a result, the prowess of these tools is increasing fast among businesses.
Microservices Architectures and Backup Considerations
Microservices architectures are a must-have for your data backup and recovery strategies if you must distribute your application components across multiple services. Not only will this add an extra layer of protection, but it will also minimize downtime in the long run. In short, this is why online streaming services often separate user authentication services and content recommendation engines.
Backup Strategies for Edge Computing
Edge computing helps you operate in remote locations, even with limited connectivity. Therefore, make sure you use incremental backups and have robust local storage options. For example, a smart city’s IoT network will generate massive real-time data that needs to be backed up locally before syncing to a central cloud. Moreover, tools like AWS Snowball or Azure IoT Edge will help efficiently transfer backup data from edge devices to the cloud, ensuring resilience against local failures. Consequently, this helps businesses maintain operational continuity even in unpredictable environments.
AI/ML in Backup Optimization
AI enhances the efficiency of backups by helping you deal with failures, optimize storage, and detect anomalies in backup data. At the same time, ML enables you to reduce backup times, identify redundant data, and detect ransomware faster. Subsequently, enterprises use AI-powered backups to detect unusual file modifications and prevent data corruption.
Cost Analysis of Implementing Data Backup and Recovery
It is time to discuss the costs involved in data backup and recovery and how you can make the most of your investment. To prevent your costs from going haywire, use a mix of strategies such as cloud backups, automation, tiered storage, and deduplication. These techniques will not only help you save costs but also access data faster.
Similarly, with data deduplication, you can quickly reduce your storage needs by 70%. At the same time, automation will help you reduce the workload of IT staff and monitor operational costs. Let’s understand with an example.
For instance, you must shift 50 TB of archival data from on-premise to cloud cold storage at $0.01/GB per month. Exercise can help you save.
50,000×0.01×12=6,000 USD per year
The numbers can be higher depending on the locations in which your business is spread.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in Data Backup and Recovery
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) in data backup and recovery includes all direct and indirect expenses over the system’s lifecycle. Let’s say you invest in a backup solution with an initial cost of $50,000, annual software licensing of $10,000, maintenance at $5,000 per year, and operational costs of $15,000 per year over 5 years; the TCO can be calculated as follows:
TCO= Initial Investment+(Recurring Costs×Years)
TCO=50,000+[(10,000+5,000+15,000)×5]
50,000 + 150,000 = 200,000 $
Return on Investment (ROI) in Data Backup and Recovery
If you are implementing a backup solution and it prevents an annual loss of $80,000 due to downtime and data loss, while the total cost over five years is $200,000, the ROI can be calculated as:
ROI= (Total Benefits – TCO) X 100
TCO
ROI= (80,000 X 5- 200,000) X 100
200,000
= 100%
A 100% ROI indicates that the backup solution recovers costs over five years and doubles its value in prevented losses.
How BuzzClan Supports Backup & Recovery?
Disasters never come announced. Above all, we understand that and help you manage your backups and recovery strategies. Subsequently, our team of experts will first analyze your requirements and technological landscape to suggest the best possible solution. In addition, we follow security best practices and ensure your systems are safe from all threats. Moreover, we use advanced and automated tools to ensure nothing slips through the cracks- making our cybersecurity services one of a kind. Here is what you can look forward to.
- Automated compliance and monitoring
- Real-time cost monitoring
- Predictive scaling capabilities
- ROI-focused implementation
- Automated backup and recovery
- 24/7 monitoring and support
- Advanced auditing and logging functionalities
Conclusion
By 2031, ransomware attacks will occur every 2 seconds. Yes, you read that right! So, having resilient data backups and recovery in place is critical. Moreover, organizations prioritizing recovery and data backup will bounce back faster and not falter on customer trust. All you need to do is leverage the right tools and follow the 3-2-1 backup rule to secure your business’s future and stay ahead of your competitors. Lastly, you can rope consultants to develop a solid data backup and recovery framework.
FAQs

Get In Touch
