Data Fabric vs. Data Mesh: Choosing the Right Architecture for Your Organization
Deepak Desai
Apr 11, 2024
Introduction
As data environments become more complex and heterogeneous, effective data management and governance have never been more tricky. Two emerging architectural approaches, Data Fabric and Data Mesh, have gained significant attention as potential solutions to these challenges. In this blog post, we will explore the concepts of Data Fabric and Data Mesh, compare their key features, and explore how they can help organizations unlock the true value of their data.
What is Data Fabric?
Data Fabric is an architectural approach that provides a unified, integrated view of an organization's data across multiple systems and platforms. It leverages various technologies like data integration, management, and governance to create a seamless and consistent data experience.

- Data integration: Connecting and integrating data from various sources, such as databases, applications, and cloud services.
- Data management: Ensuring data quality, reliability, and security through robust data governance practices.
- Data discovery: Enabling users to easily find, access, and understand relevant data across the organization.
Data Fabric is particularly useful for organizations with complex data landscapes, where data is scattered across multiple silos and systems. By providing a unified data view, Data Fabric enables faster decision-making, improved data analytics, and enhanced operational efficiency.
What is Data Mesh?
Data Mesh is a decentralized architectural approach that treats data as a product and empowers domain teams to own and manage their data. It is based on four core principles:
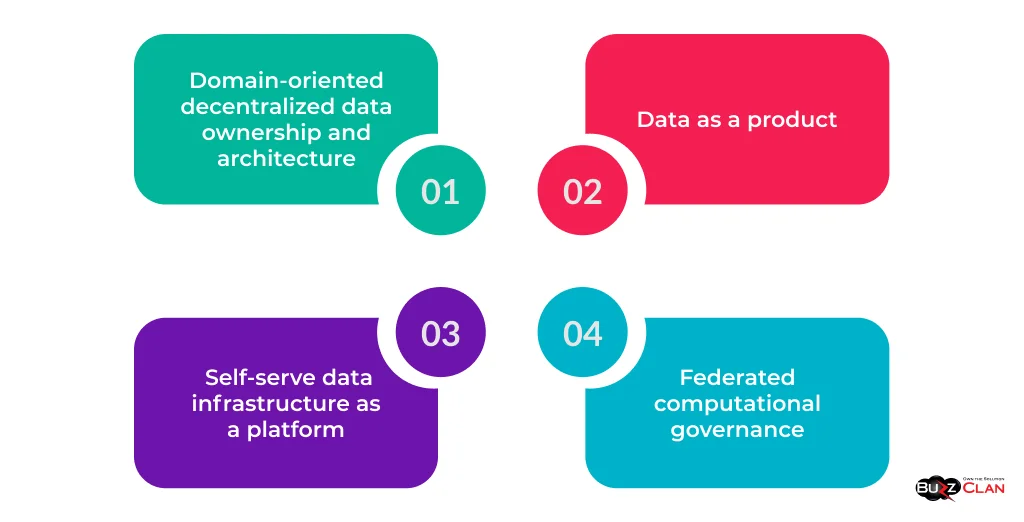
- Domain-oriented decentralized data ownership and architecture
- Data as a product
- Self-serve data infrastructure as a platform
- Federated computational governance
In a Data Mesh architecture, data is organized around business domains, with each domain team responsible for creating, managing, and serving their data products. This approach promotes data autonomy, agility, and scalability, enabling organizations to deliver value faster and more efficiently.
Choosing the right data architecture is crucial for organizations to manage and leverage their data assets effectively. The choice between Data Fabric and Data Mesh depends on various factors, such as organizational structure, data strategy, and business goals, which we will explore further in this blog post.
Data Fabric and its Key Components
Now, let's look at Data Fabric and its key components.
Technology Stack and Integrations
Data Fabric relies on a robust technology stack that includes data integration tools, data management platforms, and data governance solutions. Some of the key technologies used in a Data Fabric architecture include:
- Data integration platforms: Tools like Talend, Informatica, and Apache NiFi enable seamless data integration across various sources and systems.
- Data management platforms: Solutions such as Cloudera, Hortonworks, and MapR Data Platform provide a unified platform for managing and processing data.
- Data governance tools: Platforms like Collibra, Alation, and IBM Data Governance help ensure data quality, security, and compliance.
Data Fabric integrates these technologies to create a unified data environment that enables organizations to manage, govern, and utilize their data effectively.
Data Management and Integration
One of the core capabilities of Data Fabric is its ability to handle data management and integration. It provides a centralized approach to managing data across the entire organization, ensuring data consistency, quality, and security.
Data Fabric enables organizations to:
- Connect and integrate data from various sources, including on-premises systems, cloud platforms, and external data providers.
- Ensure data quality through data profiling, cleansing, and enrichment techniques.
- Enforce data governance policies and standards across the organization.
- Enable data discovery and self-service access to data for business users.
By providing a unified view of data and streamlining data management processes, Data Fabric helps organizations overcome data silos, improve data quality, and accelerate data-driven decision-making.
Benefits and Challenges of Data Fabric
| Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Improved data accessibility and discovery | Complexity in integrating disparate data sources and systems |
| Enhanced data quality and consistency | Ensuring data security and compliance across the data fabric |
| Faster time-to-insights and decision-making | Addressing data governance and data ownership issues |
| Reduced data management complexity and costs | Managing the scalability and performance of the data fabric architecture |
Organizations need a well-defined data strategy, a skilled data team, and a technology stack to overcome these challenges.
Data Mesh and its Key Components
Let's shift our focus to Data Mesh and explore its core principles and benefits.
Domain-Oriented Decentralized Data Ownership
One of the key principles of Data Mesh is domain-oriented decentralized data ownership. In a Data Mesh architecture, data is organized around business domains, with each domain team responsible for managing and serving their data products.
This approach promotes data autonomy and agility, enabling domain teams to make data-driven decisions faster and more efficiently. It also reduces the burden on central data teams, allowing them to focus on providing the necessary infrastructure and governance framework.
Data as a Product
Another core principle of Data Mesh is treating data as a product. In a Data Mesh architecture, data is not just a byproduct of business processes but a valuable asset that is carefully designed, developed, and delivered to meet the needs of data consumers.
Each domain team is responsible for creating and managing their data products, ensuring that they are:
- Discoverable: Easily findable and accessible to data consumers
- Addressable: Uniquely identifiable and referenceable
- Trustworthy: Reliable, accurate, and up-to-date
- Self-describing: Accompanied by metadata that describes the data product's content, quality, and usage
By treating data as a product, Data Mesh enables organizations to create a data-driven culture where data is valued, managed, and consumed effectively.
Data Mesh: Advantages and Drawbacks
Implementing a Data Mesh architecture offers several advantages, including:
- Increased data agility and autonomy for domain teams
- Faster time-to-value for data products
- Improved data quality and trust
- Scalability and flexibility to accommodate new data sources and use cases
However, Data Mesh also has some potential drawbacks, such as:
- Complexity in implementing and managing a decentralized data architecture
- Ensuring data consistency and interoperability across different domains
- Addressing data governance and compliance challenges in a decentralized environment
- Requiring a significant cultural shift and upskilling of domain teams
To mitigate these drawbacks, organizations must have a clear data strategy, a well-defined governance framework, and the tools and platforms to support a Data Mesh architecture.
Data Lake Considerations
Data Lakes have become popular for organizations that store and process large volumes of structured and unstructured data. In the data fabric and mesh context, data lakes can play a crucial role as a centralized repository for raw data.
In a Data Fabric architecture, Data Lakes can serve as a source for data integration and processing, feeding into the unified data view provided by the fabric. Data Fabric can help ensure data quality, governance, and security across the Data Lake and other data sources.
Data Lakes can be a shared infrastructure platform in a Data Mesh architecture, providing domain teams with the tools and resources to store, process, and serve their data products. The Data Mesh principles of self-serve data infrastructure and federated computational governance can be applied to the Data Lake to ensure data quality, security, and compliance.
Comparative Analysis of Data Fabric and Data Mesh
Now that we understand Data Fabric and Data Mesh let's compare them across different dimensions.
Architecture
- Data Fabric follows a centralized approach, providing a unified view of data across the organization.
- Data Mesh follows a decentralized approach, with domain teams owning and managing their data products.
Scalability
- Data Fabric can scale well for moderate to large-scale data environments but may face challenges with vast and complex data landscapes.
- Data Mesh is designed to scale horizontally, accommodating the growth of data sources and use cases across different domains.
Governance
- Data Fabric provides a centralized governance framework, ensuring consistent data quality, security, and compliance across the organization.
- Data Mesh relies on federated computational governance, with domain teams responsible for governing their data products within a shared governance framework.
Performance
- Data Fabric can perform well for data integration and processing tasks but may face challenges with real-time data processing and complex data transformations.
- Data Mesh enables domain teams to optimize the performance of their data products based on their specific requirements and use cases.
Scenarios and Case Studies
According to Gartner reports, organizations across various industries, including healthcare, finance, and retail, have adopted Data Fabric and Data Mesh. Some notable case studies include:
- A large healthcare organization uses Data Fabric to integrate data from multiple sources and enable real-time patient care and research analytics.
- A global financial institution adopting Data Mesh to empower domain teams and accelerate the delivery of data products for risk management and compliance.
Data Virtualization
Data Fabric and Data Mesh can leverage Data Virtualization as a complementary technology. Data Virtualization enables organizations to create a unified view of data across different sources without physically moving or replicating the data.
In a Data Fabric architecture, Data Virtualization can create a logical data layer that abstracts the complexity of underlying data sources and provides a unified data access interface.
In a Data Mesh architecture, Domain Teams can use data virtualization to create virtual data products that combine data from multiple sources and serve them to data consumers in a self-serve manner.
Industry Insights
Gartner, a leading research and advisory firm, has provided insights on Data Fabric and Data Mesh in their reports and publications. According to Gartner:
- Data Fabric is a key technology trend that enables organizations to create a unified data management and integration framework across multiple data sources and platforms.
- Data Mesh is an emerging architectural approach that enables organizations to scale their data management and analytics capabilities by empowering domain teams to own and manage their data products.
The Data Fabric and Data Mesh solutions market is multiplying, with vendors such as IBM, Informatica, Talend, and Atlan offering products and services in this space. As organizations grapple with the challenges of managing and leveraging their data assets, adopting data fabric and data mesh is expected to increase in the coming years.
Choosing What's Best for Your Organization
Choosing between Data Fabric and Data Mesh depends on various factors specific to your organization, including:
Organizational Structure
- Data Fabric may be a good fit if your organization has a centralized data team and a relatively simple data landscape.
- Data Mesh may be a better choice if your organization has a decentralized structure with domain teams that understand their data and its usage well.
Data Strategy and Business Goals
- Data Fabric may align well with your goals if your organization's data strategy focuses on creating a unified view of data and enabling centralized data management and governance.
- Data Mesh may be better if your organization's data strategy emphasizes data agility, autonomy, and faster time-to-value for data products.
Technical Expertise and Resource Availability
- Implementing a Data Fabric requires a skilled central data team with data integration, management, and governance expertise.
- Adopting a Data Mesh requires domain teams with the technical skills and resources to own and manage their data products.
Ultimately, the choice between Data Fabric and Data Mesh should be based on thoroughly assessing your organization's data landscape, business goals, and available resources.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we have explored the concepts of Data Fabric and Data Mesh. These two architectural approaches address the challenges of managing and leveraging data in complex and heterogeneous environments.
Data Fabric provides a unified view of data across the organization, enabling centralized data management, governance, and integration. On the other hand, Data Mesh follows a decentralized approach, empowering domain teams to own and manage their data products and enabling data agility and scalability.
Both approaches have their benefits and challenges, and the choice between them depends on various factors specific to your organization, such as organizational structure, data strategy, and technical expertise.
Organizations must stay informed about emerging architectural patterns and best practices as the data landscape evolves. By understanding the concepts of Data Fabric and Data Mesh, organizations can make informed decisions about their data architecture and set themselves up for success in the data-driven future.
In the comments section below, we encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with Data Fabric and Data Mesh. If you have any questions or want to explore how these approaches can benefit your organization, please contact our team for a consultation.
FAQs

Get In Touch
