The Ultimate Guide to Customer Data Platforms (CDPs)
Deepak Desai
May 7, 2024
Introduction to Customer Data Platform (CDP)
A Customer Data Platform is a centralized system that aggregates and unifies customer data from various sources, creating a single, coherent, and actionable view of each customer. By breaking down data silos and integrating data from multiple touchpoints, CDPs empower organizations to gain deep insights into customer behaviors, preferences, and journeys.
The evolution of customer data management has been marked by the proliferation of data sources and the increasing complexity of customer interactions across channels. Traditional data management solutions, such as CRM systems and marketing automation platforms, often need help to keep up with customer data's volume, variety, and velocity. CDPs have emerged as a response to these challenges, providing a more flexible, scalable, and holistic approach to customer data management.
This comprehensive blog post will dive into Customer Data Platforms, exploring their core functionalities, benefits, and real-world applications. We will examine the current market landscape, CDPs' essential features and capabilities, and the steps to implement a CDP solution. Furthermore, we will discuss the future trends shaping the CDP industry and how businesses can leverage CDPs to drive customer-centric strategies and gain a competitive edge.
Understanding Customer Data Platforms
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is software designed to collect, unify, and activate customer data from various sources. CDPs provide a centralized repository that combines data from multiple touchpoints, such as websites, mobile apps, social media, CRM systems, and offline interactions. By integrating and normalizing this data, CDPs create a unified view of each customer, enabling organizations to understand better their customers' behaviors, preferences, and journeys.
CDPs' core functionalities and capabilities revolve around three key areas: data collection, data unification, and data activation.
- Data Collection: CDPs are designed to collect customer data from various online and offline sources. They can ingest data from websites, mobile apps, social media platforms, email campaigns, customer service interactions, and point-of-sale systems. CDPs can handle structured data (e.g., transaction records) and unstructured data (e.g., social media posts) and process data in real-time or batch mode.
- Data Unification: Once the data is collected, CDPs use advanced identity resolution techniques to stitch together data from different sources and create a unified customer profile. This process involves identifying unique individuals across different data points, such as email addresses, phone numbers, or device IDs, and merging their data into a single, coherent record. CDPs can also enrich customer profiles with additional data points, such as demographic information or third-party data, to provide a more comprehensive view of each customer.
- Data Activation: With the unified customer profiles in place, CDPs enable organizations to activate this data for various marketing and customer engagement initiatives. CDPs provide segmentation capabilities, allowing marketers to create targeted audience segments based on specific attributes, behaviors, or preferences. These segments can personalize marketing campaigns, tailor product recommendations, or deliver targeted content across channels.
CDPs differ from other data management solutions, such as CRM systems or Data Management Platforms (DMPs), in several key ways. CRM systems are primarily designed for managing customer interactions and sales processes, while CDPs focus on creating a unified view of the customer across all touchpoints. DMPs, on the other hand, are mainly used for advertising and audience targeting, leveraging third-party data. In contrast, CDPs prioritize first-party data and provide a more comprehensive view of the customer journey.
Benefits of Customer Data Platforms
Implementing a Customer Data Platform offers numerous strategic advantages and benefits for organizations looking to enhance customer experience and drive business growth. Some of the key benefits of using a CDP include:
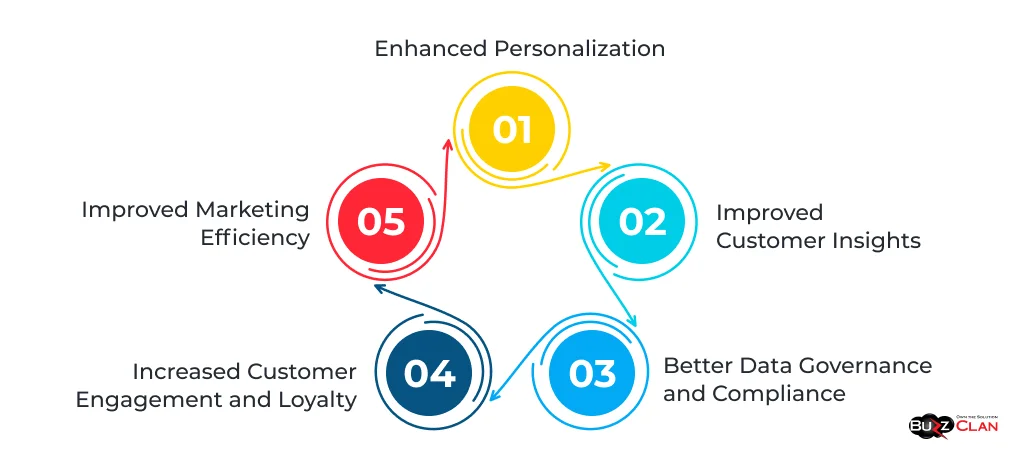
- Improved Customer Insights: By unifying customer data from various sources, CDPs provide a holistic view of each customer, enabling organizations to gain deeper insights into customer behaviors, preferences, and journeys. These insights can inform data-driven decision-making, helping marketers optimize their strategies and deliver more relevant and personalized experiences.
- Enhanced Personalization: CDPs empower marketers to deliver highly personalized experiences across channels by allowing them to create targeted audience segments and access rich customer profiles. Whether tailoring email campaigns, displaying personalized product recommendations on a website, or delivering targeted ads, CDPs enable organizations to engage customers with relevant and timely content.
- Increased Customer Engagement and Loyalty: By leveraging CDPs' insights and personalization capabilities, organizations can foster stronger customer relationships and drive increased engagement and loyalty. Personalized experiences make customers feel valued and understood, leading to higher satisfaction, repeat purchases, and brand advocacy.
- Improved Marketing Efficiency: CDPs streamline marketing processes by providing a centralized platform for managing customer data and executing targeted campaigns. Marketers can reduce manual data integration and segmentation efforts, freeing up time and resources to focus on strategic initiatives. CDPs also enable more effective measurement and optimization of marketing campaigns, allowing organizations to allocate resources more efficiently.
- Better Data Governance and Compliance: CDPs help organizations maintain data quality, consistency, and security by providing a centralized platform for managing customer data. They offer features such as data validation, data cleansing, and data governance controls, ensuring the integrity and accuracy of customer data. CDPs also assist in complying with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, by providing tools for managing customer consent and data access rights.
Real-world case studies demonstrate the tangible benefits of CDP implementations. For example, a leading retail company implemented a CDP to unify customer data from various touchpoints, including in-store transactions, online purchases, and customer service interactions. By leveraging the CDP's segmentation and personalization capabilities, the retailer delivered targeted product recommendations and personalized offers, resulting in a 20% increase in conversion rates and a 15% uplift in average order value.
Similarly, a global financial services firm utilized a CDP to gain a unified view of its customers across multiple business lines and geographies. The CDP enabled the firm to identify high-value customer segments, deliver personalized financial advice, and optimize cross-selling opportunities. As a result, the firm achieved a 25% increase in customer retention and a 30% growth in customer lifetime value.
These examples highlight the transformative power of CDPs in driving business outcomes and delivering exceptional customer experiences.
Customer Data Platform Market Landscape
The Customer Data Platform market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing importance of customer-centric strategies and the need for unified customer data management. A diverse range of vendors characterizes the market, each offering unique features and capabilities to meet the evolving needs of businesses across industries.
Some of the key players in the CDP market include:
- Salesforce: Salesforce CDP, part of the Salesforce Customer 360 platform, provides a unified customer view, AI-driven insights, and real-time personalization capabilities.
- Adobe: Adobe Experience Platform, which includes Adobe Real-Time CDP, offers data unification, audience segmentation, and activation across various channels.
- Oracle: Oracle Unity CDP enables organizations to unify customer data, create audience segments, and orchestrate personalized experiences across touchpoints.
- SAP: SAP Customer Data Platform provides customer data unification, consent management, and personalization capabilities, integrated with SAP's broader customer experience portfolio.
- Segment: Segment CDP focuses on data collection, unification, and activation, with a strong emphasis on data privacy and security.
- Tealium: Tealium AudienceStream CDP offers data unification, segmentation, and activation capabilities, along with a robust ecosystem of integrations.
Other notable vendors in the CDP market include Treasure Data, ActionIQ, mParticle, and BlueConic, each offering unique value propositions and specializations.
The CDP market is expected to continue growing in the coming years. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global CDP market size is projected to grow from USD 3.5 billion in 2021 to USD 15.3 billion by 2026 at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 34.6% during the forecast period.
Several trends are shaping the future of the CDP market, including:
- Increased Adoption Across Industries: While CDPs have been widely adopted in industries such as retail, e-commerce, and media, their usage is expanding to sectors like healthcare, financial services, and telecommunications as businesses recognize the value of unified customer data.
- Integration with Other Marketing Technologies: CDPs are increasingly integrating with other marketing technologies, such as marketing automation platforms, customer service systems, and analytics tools, to provide a more seamless and holistic customer experience.
- AI and Machine Learning Enhancements: CDP vendors incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities to provide advanced analytics, predictive modeling, and personalization recommendations.
- Focus on Data Privacy and Compliance: With the growing importance of data privacy regulations, CDP solutions are evolving to provide robust consent management, data governance, and compliance features.
As the CDP market matures, organizations have a wide range of options when selecting a CDP solution that aligns with their specific business needs and objectives.
Features and Capabilities of CDPs
Customer Data Platforms offer comprehensive features and capabilities to empower organizations to effectively manage and activate customer data. Let's explore some of the essential features and functionalities provided by CDPs:
| Steps | Task |
|---|---|
| 1. | Data Collection and Integration |
| CDPs offer connectors and APIs to collect customer data from various sources, such as websites, mobile apps, CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, and offline channels. | |
| They support the ingestion of structured and unstructured data, enabling the capture of customer interactions, transactions, and behaviors across touchpoints. | |
| CDPs can handle data in real-time or batch mode, ensuring that customer profiles are up-to-date and actionable. | |
| 2. | Data Unification and Identity Resolution |
| CDPs employ advanced identity resolution algorithms to match and merge customer data from different sources into a single, unified customer profile. | |
| They use deterministic and probabilistic matching techniques to identify unique individuals based on attributes like email addresses, phone numbers, or device IDs. | |
| CDPs can handle data quality issues, such as duplicates or inconsistencies, to maintain a clean and reliable customer database. | |
| 3. | Segmentation and Audience Building |
| CDPs provide powerful segmentation capabilities, allowing marketers to create targeted audience segments based on demographic attributes, behavioral patterns, or engagement levels. | |
| They support the creation of dynamic segments that automatically update based on real-time customer interactions and behaviors. | |
| CDPs enable the creation of lookalike audiences, helping marketers identify and target prospects similar to their high-value customers. | |
| 4. | Real-Time Data Processing and Activation |
| CDPs can process and analyze customer data in real time, enabling marketers to respond to customer actions and triggers promptly. | |
| They support real-time segmentation and personalization, allowing organizations to deliver relevant and timely experiences based on customer behavior and preferences. | |
| To orchestrate personalized communications, CDPs integrate with various activation channels, such as email, SMS, push notifications, and advertising platforms. | |
| 5. | Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning |
| Advanced CDPs incorporate predictive analytics and machine learning capabilities to uncover deeper insights and make data-driven predictions. | |
| They can analyze customer data to identify patterns, predict future behaviors, and estimate customer lifetime value. | |
| CDPs can provide propensity scoring, helping marketers identify customers most likely to convert, churn, or respond to specific offers. | |
| 6. | Data Privacy and Compliance |
| CDPs provide features to ensure data privacy and compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. | |
| They offer consent management tools, allowing customers to control their data preferences and opt-in or opt-out of data collection and processing. | |
| CDPs provide data governance capabilities, enabling organizations to define data access rights, auditing, and data retention policies. | |
| 7. | Reporting and Analytics |
| CDPs offer reporting and analytics capabilities to help marketers measure the effectiveness of their campaigns and customer engagement strategies. | |
| They provide dashboards and visualizations to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and monitor customer journey performance. | |
| CDPs can integrate with external analytics tools and business intelligence platforms for advanced reporting and data exploration. |
By leveraging these features and capabilities, CDPs empower marketers and businesses to comprehensively understand their customers, deliver personalized experiences, and drive measurable business outcomes.
Customer Data Platform Use Cases
Customer Data Platforms find applications across various industries and business scenarios, enabling organizations to drive personalized customer experiences, optimize marketing strategies, and improve operational efficiency. Let's explore some real-world use cases of CDPs:
- Retail and E-commerce:
- A retail company uses a CDP to unify customer data from online and offline channels, creating a single view of each customer's purchase history, preferences, and interactions.
- The CDP enables the retailer to create targeted segments based on customer behavior, such as frequent buyers or high-value customers, and deliver personalized product recommendations and promotions.
- By leveraging the CDP's real-time data processing capabilities, the retailer can trigger personalized emails or push notifications based on customer actions, such as cart abandonment or product views.
- Financial Services:
- A bank implements a CDP to gain a holistic view of its customers across various products and services, such as checking accounts, credit cards, and loans.
- The CDP helps the bank identify cross-selling opportunities and deliver personalized financial advice based on customer profiles and transaction data.
- By analyzing customer data, the bank can proactively detect potential churn risks and initiate targeted retention campaigns to improve customer loyalty.
- Healthcare:
- A healthcare provider uses a CDP to unify patient data from electronic health records (EHRs), claims systems, and patient portals.
- The CDP enables the provider to create comprehensive patient profiles, including demographics, medical history, and treatment preferences.
- By leveraging the CDP's segmentation capabilities, the provider can identify patient cohorts for targeted outreach programs, such as preventive care reminders or chronic disease management initiatives.
- Media and Entertainment:
- A streaming platform leverages a CDP to collect and unify viewer data from multiple devices and channels, such as web, mobile, and connected TVs.
- The CDP helps the platform understand viewer preferences, viewing habits, and engagement patterns, enabling personalized content recommendations and targeted advertising.
By analyzing viewer data, the platform can optimize content production and licensing decisions based on audience demand and preferences.
- Travel and Hospitality:
- A hotel chain uses a CDP to create a unified view of its guests across properties, booking channels, and loyalty programs.
- The CDP enables the hotel chain to deliver personalized experiences based on guest profiles and past interactions, such as room preferences, dining recommendations, and special offers.
- By leveraging the CDP's data activation capabilities, the hotel chain can orchestrate seamless omnichannel experiences, such as mobile check-in, personalized in-room services, and post-stay follow-ups.
These use cases demonstrate the versatility and applicability of CDPs across diverse business domains. By leveraging unified customer data, organizations can gain deeper insights into customer behaviors, preferences, and journeys, enabling them to deliver exceptional experiences and drive business growth.
Implementing a Customer Data Platform
Implementing a Customer Data Platform involves several key steps to ensure a successful deployment and integration with existing systems. Here's a guide to help organizations navigate the CDP implementation process:
| Steps | Task |
|---|---|
| 1. | Define Business Objectives and Requirements |
| Clearly define the business objectives and goals for implementing a CDP, such as improving customer insights, enhancing personalization, or optimizing marketing campaigns. | |
| Identify the specific use cases and requirements the CDP should address, considering data sources, customer touchpoints, and desired outcomes. | |
| 2. | Assess Data Landscape and Quality |
| Conduct a thorough assessment of the organization's current data landscape, including existing data sources, systems, and silos. | |
| Evaluate the quality and consistency of customer data across different sources, identifying gaps or challenges that must be addressed. | |
| 3. | Select the Right CDP Solution |
| Evaluate various CDP solutions available in the market based on the organization's specific requirements, budget, and technology stack. | |
| When selecting a CDP solution, Consider data integration capabilities, scalability, ease of use, and vendor support. | |
| 4. | Plan Data Integration and Migration |
| Develop a detailed plan for integrating the CDP with existing data sources and systems, including customer databases, CRM platforms, marketing automation tools, and analytics platforms | |
| Determine the data migration strategy, considering data volume, data format, and data cleansing requirements. | |
| 5. | Establish Data Governance and Privacy Policies |
| Define data governance policies and procedures to ensure data quality, consistency, and security within the CDP. | |
| Implement data privacy and consent management mechanisms to comply with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA, ensuring customer data is collected, stored, and processed promptly. | |
| 6. | Configure and Customize the CDP |
| Configure the CDP based on the organization's requirements, including data schema definition, mapping, and transformation rules. | |
| Customize the CDP's user interface, dashboards, and reporting capabilities to align with the organization's branding and user preferences. | |
| 7. | Train and Onboard Users |
| Provide comprehensive training to relevant teams on using the CDP effectively, such as marketing, customer service, and analytics. | |
| Develop user guides, documentation, and support resources to ensure smooth onboarding and adoption of the CDP platform. | |
| 8. | Test and Validate |
| Conduct thorough testing and validation of the CDP implementation to ensure data accuracy, integration stability, and system performance. | |
| Perform user acceptance testing (UAT) to validate that the CDP meets the defined business requirements and delivers the expected functionalities. | |
| 9. | Deploy and Monitor |
| Deploy the CDP into the production environment, following a phased approach if necessary, to minimize disruption to existing systems and processes. | |
| Establish monitoring and alerting mechanisms to identify and resolve any issues or performance bottlenecks proactively. | |
| 10. | Measure and Optimize |
| Define key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to measure the success and impact of the CDP implementation. | |
| Continuously monitor and analyze CDP performance, user adoption, and business outcomes, identifying areas for improvement and optimization. |
Engaging stakeholders from various departments, including marketing, IT, data governance, and legal, throughout the implementation process, is crucial to ensuring alignment and support for the CDP initiative. Effective communication, change management, and project management practices are essential for a successful CDP deployment.
Common challenges and pitfalls to be aware of during CDP implementation include data quality issues, data integration complexities, resistance to change, and lack of clear ownership and governance. To mitigate these challenges, organizations should:
- Establish a dedicated CDP implementation team with clear roles and responsibilities.
- Foster a data-driven culture and secure executive sponsorship for the CDP initiative.
- Prioritize data quality and invest in data cleansing and standardization efforts.
- Develop a robust data integration strategy and work closely with IT teams to address technical challenges.
- Provide adequate training and support to users to drive adoption and maximize the value of the CDP.
By following these best practices and addressing potential challenges proactively, organizations can successfully implement a CDP and unlock the full potential of their customer data.
Customer Data Platform vs Data Management Platform
While Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) and Data Management Platforms (DMPs) deal with customer data, they serve distinct purposes and cater to different needs. Understanding the key differences between CDPs and DMPs is crucial for organizations to decide which solution best fits their requirements.

- Data Focus:
- CDPs primarily focus on first-party data collected directly from an organization's channels and touchpoints, such as websites, mobile apps, and CRM systems.
- DMPs, on the other hand, mainly deal with third-party data, which is data acquired from external sources, such as data providers, ad networks, and data exchanges.
- Data Persistence and Freshness:
- CDPs store and manage customer data persistently, creating a unified and historical view of each customer over time.
- DMPs typically store data for a limited period, usually 90 days or less, as the focus is on real-time audience targeting and ad serving.
- Identity Resolution:
- CDPs employ advanced identity resolution techniques to stitch together data from various sources and create a single, unified customer profile based on deterministic and probabilistic matching.
- DMPs rely on anonymous identifiers, such as cookies or device IDs, to create audience segments for ad targeting without necessarily resolving individual customer identities.
- Data Activation:
- CDPs enable activation of customer data across various channels and touchpoints, such as email, social media, customer service, and personalization engines.
- DMPs primarily focus on activating data for advertising purposes, such as programmatic ad buying, retargeting, and audience targeting.
- Data Ownership and Control:
- CDPs give organizations full control and ownership over their customer data, which is collected and managed within the organization's systems.
- DMPs often involve data sharing and aggregation across multiple parties, and the ownership and control of the data may be distributed among different stakeholders.
- Use Cases:
- CDPs are used for many customer-centric use cases, such as personalization, customer journey orchestration, customer insights, and omnichannel marketing.
- DMPs are primarily used for advertising and media-related use cases, such as audience segmentation, ad targeting, and media optimization.
Organizations should choose between CDPs and DMPs based on their needs and priorities. A CDP would be the most suitable if the primary focus is leveraging first-party data for customer engagement, personalization, and customer-centric strategies. On the other hand, if the main objective is to optimize advertising efforts and leverage third-party data for audience targeting, a DMP may be the better fit.
It's important to note that CDPs and DMPs are not mutually exclusive, and some organizations may benefit from using both solutions. CDPs can provide a unified and persistent view of customer data, while DMPs can enhance advertising effectiveness by leveraging third-party data and enabling targeted ad campaigns.
Ultimately, the decision between a CDP and a DMP should be based on a thorough assessment of the organization's data management requirements, marketing objectives, and technology ecosystem.
Regulatory Compliance and Customer Data Platforms
In the era of heightened data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), organizations must ensure that their customer data management practices, including the use of Customer Data Platforms (CDPs), are compliant with these regulations.
CDPs are crucial in helping organizations navigate the complexities of data privacy compliance. Here's how CDPs can assist in ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements:
- Data Collection and Consent Management:
- CDPs provide mechanisms to capture and manage customer consent for data collection, processing, and sharing.
- They allow organizations to create granular consent options, enabling customers to specify their preferences for data usage and communication channels.
- CDPs can track and record consent history, providing an audit trail of customer permissions and preferences.
- Data Access and Portability:
- CDPs enable organizations to fulfill data subject access requests (DSARs) by providing a centralized view of customer data across various systems and touchpoints.
- They can facilitate the extraction and portability of customer data, allowing organizations to respond to customer requests for data access or data transfer to another service provider.
- Data Deletion and Retention:
- CDPs assist in managing data deletion and retention policies by regulatory requirements.
- They can automate the deletion of customer data based on predefined retention periods or customer requests for data erasure.
- CDPs can also help maintain data minimization by ensuring that only necessary data is collected and retained for the specified purposes.
- Data Security and Protection:
- CDPs provide security features and controls to protect customer data from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse.
- They can implement data encryption, access controls, and audit logging to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of customer data.
- CDPs can also assist in detecting and responding to data security incidents, helping organizations meet breach notification requirements.
- Privacy by Design and Default:
- CDPs can be designed and configured with privacy principles, incorporating features like pseudonymization, minimization, and privacy-enhancing technologies.
- They can enforce privacy settings by default, ensuring that customer data is collected, processed, and shared in a manner that respects privacy rights and complies with regulatory requirements.
To ensure compliance with data privacy regulations when using a CDP, organizations should:
- Conduct a thorough assessment of their data collection and processing practices to identify any gaps or risks related to regulatory requirements.
- Develop and maintain comprehensive privacy policies and notices that inform customers about data collection, usage, and rights.
- Implement robust consent management processes, ensuring customer consent is obtained and recorded for all relevant data processing activities.
- Establish clear data retention and deletion policies and configure the CDP to enforce these policies automatically.
- Regularly review and update their CDP configuration and practices to align with evolving regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
By leveraging CDPs' compliance capabilities and following best practices for data privacy, organizations can build trust with their customers and mitigate non-compliance risks.
Future Trends in Customer Data Platforms
As customer expectations evolve and technology advances, the Customer Data Platform (CDP) market is poised for significant growth and innovation in the coming years. Let's explore some of the emerging trends and predictions that will shape the future of CDPs:
- AI-Driven Insights and Personalization:
- CDPs will increasingly leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies to derive deeper insights from customer data.
- AI-powered algorithms will enable CDPs to identify complex patterns, predict customer behavior, and generate highly personalized recommendations and experiences.
- CDPs will incorporate natural language processing (NLP) capabilities to analyze unstructured data, such as customer reviews and social media interactions, providing richer context and sentiment analysis.
- Real-Time Data Activation and Decisioning:
- CDPs will focus on enabling real-time data activation and decision-making, allowing organizations to respond to customer actions and triggers immediately.
- Advancements in streaming data processing and edge computing will enable CDPs to process and analyze data in near real-time, facilitating instant personalization and dynamic customer experiences.
- Customer Journey Orchestration:
- CDPs will evolve to provide more sophisticated customer journey orchestration capabilities, enabling organizations to design, execute, and optimize multi-channel customer journeys.
- They will offer visual journey mapping tools, allowing marketers to create and test different journey paths and automate personalized interactions across touchpoints.
- Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs):
- As data privacy concerns continue to grow, CDPs will incorporate privacy-enhancing technologies to ensure secure and compliant data management.
- Data anonymization, differential privacy, and homomorphic encryption will be integrated into CDPs to protect customer data while enabling valuable insights and personalization.
- CDP Ecosystems and Integrations:
- CDPs will expand their ecosystems and integrations with a wider range of marketing, sales, and customer service technologies.
- They will provide seamless connectivity with CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, customer support tools, and analytics solutions, enabling a more holistic view of the customer and facilitating data-driven actions across the organization.
- Industry-Specific CDPs:
- The CDP market will see the emergence of industry-specific solutions tailored to the unique needs and challenges of different sectors, such as healthcare, financial services, and e-commerce.
- These specialized CDPs will offer pre-built data models, connectors, and compliance features specific to each industry, accelerating implementation and delivering targeted insights.
- CDP as a Service (CDPaaS):
- Cloud-based CDP solutions will gain prominence, offering the flexibility and scalability of a software-as-a-service (SaaS) model.
- CDPaaS will enable organizations to quickly deploy and scale their CDP initiatives without the need for extensive in-house infrastructure and resources.
- CDP Democratization and Self-Service:
- CDPs will prioritize user-friendly interfaces and self-service capabilities, empowering business users to access and leverage customer data without heavy reliance on IT teams.
- Visual drag-and-drop interfaces, pre-built templates, and low-code/no-code functionalities will enable marketers and business users to create segments, build campaigns, and generate insights independently.
As these trends shape the future of CDPs, organizations must stay agile and adapt their strategies to leverage these platforms' full potential. By staying informed about the latest CDP advancements and aligning their customer data management practices with emerging trends, businesses can stay ahead of the curve and deliver exceptional customer experiences in the digital age.
Conclusion: The Role of Customer Data Platforms in Driving Customer-Centric Strategies
Throughout this blog post, we have explored the key aspects of CDPs, including their core functionalities, benefits, and real-world applications. We have seen how CDPs differ from traditional data management solutions and how they empower organizations to break down data silos, enhance customer insights, and drive data-driven decision-making.
The CDP market is evolving rapidly, with various vendors offering solutions tailored to different industries and use cases. As organizations navigate the complex landscape of customer data management, choosing a CDP solution that aligns with their specific needs and goals is crucial.
Implementing a CDP requires careful planning, stakeholder alignment, and a focus on data governance and compliance. By following best practices and proactively addressing potential challenges, organizations can successfully deploy a CDP and unlock the full value of their customer data.
As we look to the future, the role of CDPs in driving customer-centric strategies will only continue to grow. Emerging trends such as AI-driven insights, real-time data activation, and privacy-enhancing technologies will shape the next generation of CDPs, enabling organizations to deliver even more personalized and engaging customer experiences.
To stay competitive in the digital age, organizations must embrace the power of customer data and invest in the right tools and strategies to harness its potential. By adopting a CDP and putting customer data at the heart of their decision-making processes, businesses can foster deeper customer relationships, improve operational efficiency, and drive sustainable growth.
As a final thought, it is important to remember that a CDP is not a silver bullet solution but rather an enabler of customer-centricity. To truly succeed in delivering exceptional customer experiences, organizations must cultivate a data-driven culture, break down organizational silos, and continuously iterate and optimize their strategies based on customer insights.
By combining the power of a CDP with a customer-centric mindset and agile processes, organizations can unleash the full potential of their customer data and build lasting competitive advantage in the ever-evolving business landscape.
FAQs

Get In Touch
