Getting Started with AI and Data Analytics: Business Implementation Guide
Vikram Verma
Mar 21, 2025
Have you ever wondered how your software and hardware usage, known as user data, can be converted into valuable insights or results? Thanks to data analytics, this is possible. Large corporations use these results to create products and services, such as applications, software, processes, etc., to increase customer satisfaction and business market share.
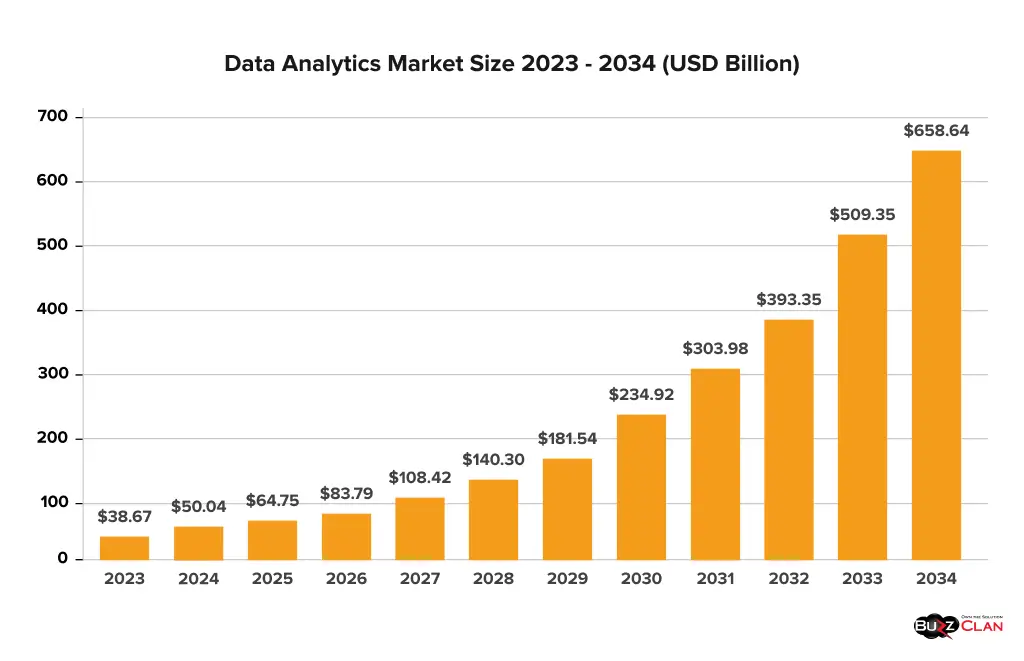
Data analytics (an integral part of data science), which has the potential to reach USD 658.64 billion by 2034, is seeing a recent boom with the integration of artificial intelligence. AI in cybersecurity has established its robust presence in software development and chatbots and is seen to spread its advantages in data analytics. In this guide, let’s understand how AI and data analytics immensely benefit businesses. With the right guide to implementing AI in data analytics, let’s know which tools and tech stack will help.
Understanding AI and Data Analytics
AI includes several components, such as machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, and other advanced models. These components help sort, organize, tag, and process data, maximizing its potential. When integrated with data analytics in a company, AI can lead to rapid operations, enhanced performance, and efficiency. Additionally, it goes one step further and contributes to the advantages of data lakes and virtualization.
Take it as an example of your organization having a big pile of LEGO bricks (data), and you want to build your masterpiece (insights) using the bricks. Here comes artificial intelligence in data analytics that helps you put LEGO bricks quickly, cleanly, and in an organized way, minimizing process duration and maximizing accuracy with automation and without human errors. With AI in data analytics, businesses can create insights and know why it happened and what and when it might happen next.
Benefits of Using AI in Data Analytics
With its tools and technologies, AI supports data analytics in numerous ways, such as explainable AI that helps explain how AI reached its conclusion, building trust and confidence in stakeholders. Similar to this benefit, there are several other benefits such as follows:
Unprecedented Speed & Efficiency
Artificial intelligence, with its learning models and deep learning programs, can analyze and process vast amounts of big data and data quickly. This infusion has helped businesses make timely or ahead-of-time decisions that help them stay ahead of the competition. It also allows companies to cut time, as tasks or projects that used to take days or weeks can now be done in a couple of hours, making AI in data analytics extremely efficient.
Enhanced Accuracy
AI doesn’t make biased decisions. It operates purely on advanced algorithms and reduces the probability and occurrence of human errors. Humans can cause errors due to biased behaviors and other factors, such as fatigue, mental pressure, stress, etc. But with AI, businesses can swiftly enhance accuracy, making operations smoother and more accurate than ever.
Future Predictions
One of the best features of data analytics is predictive analytics. It integrates several high-tech technologies, such as retrieval augmented generation, to help predict future trends by analyzing data from past events and data. This further solves ongoing or upcoming issues in the market or industry and leads to opportunities for higher revenue, market share, and profits.
Personalized Insights
Have you ever wondered how you get personal recommendations on your Netflix, YouTube, or Instagram home page? It’s because of data analytics and AI. Recently, AI has been booming in data science and analytics, advancing and offering personalized insights to improve customer experience and retention by providing what the user wants.
Smooth Data Management
AI has smoothened data management and streamlined data retrieval and utilization. By adequately automating a business’s storage and retrieval processes, AI has helped data analysts. AI has opted to categorize and tag data properly, so data analysts can now access data organizationally.
Components of AI in Data Analytics
AI in data analytics isn’t just a single phenomenon; it comprises several integral parts and elements. Some of these components are as follows:
Machine Learning
Machine learning is like a learning process in which a computer or system teaches from its own experiences or internal and external data. Machine learning utilizes big data to improve decision-making. For example, if you feed a system with an Apple image, it will analyze the image and extract data and details from it. So, if you show another image to it, suppose of an “orange,” then it would compare both pictures and their details to interpret which fruit is an Apple. That’s how machine learning works in full-fledged systems and large databases.
Deep Learning
Deep learning goes one step further than machine learning. It is an advanced part of machine learning that uses neural networks. Neural networks!! Does that ring a bell? Yes, these are the same neural networks that are presented in all of our brains. With the help of these neural networks, the systems and computers are trained to understand objects, photos, audio, videos, etc., for, e.g., self-driving cars. Self-driving cars create neural networks and understand what decisions to make in a fraction of a second by analyzing traffic signs, patterns, and signals.
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing. By its name, it means that by using this processing model, machines and systems can understand human languages. Interesting right? With NLPs, machines can understand languages’ semantics, wordings, and voices. This further helps voice search models like Apple’s Siri, Alexa, and Google Search interpret human language to understand human queries or commands and execute them without disruptions or complications. Where machines only understand and communicate in binary language, with the help of NLP, machines can understand human languages with a streamlined and with no extra effort and ease.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is an integral part of data analytics. It helps predict future trends by analyzing data from past events and records. Predictive analytics allows organizations or individuals to predict what will happen so businesses can make prior decisions and stay ahead of the competition. For example, a store can identify and order only the small amount of inventory that can be used in the upcoming season by looking at the past few particular seasons’ sales. It helps reduce resource wastage and adopt innovation at the same time.
Data Lake vs. Data Warehouse: Key Differences
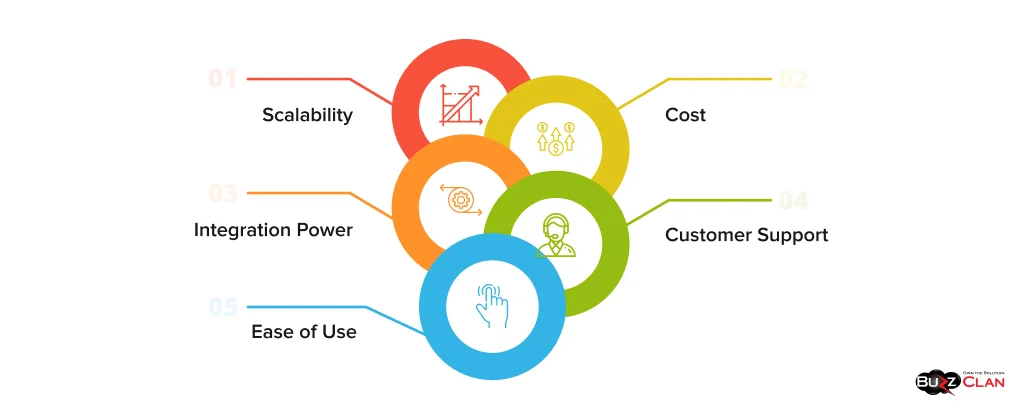
There are several ways by which one can choose the right AI tools and technologies for data analytics, including the tools. Some of them are listed below:
- Ease of Use: The tools and technologies must have an easy and comprehensive UI and UX so they don’t create bottlenecks.
- Integration Power: Before selecting the right tools and tech stack, ensure it integrates well with your existing data infrastructure and analytics workflows. If it creates issues, it can result in downtime and unnecessary technical faults and glitches.
- Scalability: If the tool cannot meet the growing needs of the business, it might not be suitable for your business. Choose a tool that can be scaled according to your business’s needs.
- Cost: Select a tool that matches your budget and doesn’t go out of your budget. Select the tool that has efficient plans and subscription models.
- Customer Support: Customer support is one of the top priorities, as 24×7 technical customer support can help resolve bottlenecks in times of crisis by troubleshooting best practices.
Moreover, there are many other tools available that can help provide AI in data analytics solutions, such as:
- Data Robot
- H2O.ai
- Google Cloud Auto ML
- IBM Watson Studio
- Tableau
Implement AI in Data Analytics in Your Business
Implementing AI in data analytics in your business might be one of the best decisions to keep your business ahead of the competition and offer value to your customers. Let’s learn what are the steps to implementation of the same:
Clear Business Objectives
As a business owner, set clear missions or goals you want to achieve or problems you want to solve using AI and data analytics. Then, check whether the AI and the goals are aligned and can perform as expected.
Robust Data-Driven Infrastructure and Culture
AI cannot work in traditional or low-quality infrastructure. It needs high-tech, data-driven systems to execute its large language models and other algorithms. So, to fulfill your needs and significantly benefit from AI capabilities, build a data-driven infrastructure. Moreover, having a basic understanding of artificial intelligence and its impacts and use cases in every team shortens the gap between technicalities and business perspectives.
Involvement of Pre-trained Models
Why train new AI learning models when you can use pre-trained models? Utilization of pre-trained models helps an organization and its datasets to boost implementation. This, in turn, helps to reduce costs and save resources previously used to train new models.
Use Cases for Better Effectiveness
It is vital to craft scenarios that show AI can be used in multiple applications. Some examples are predictive maintenance and customer segmentation. Doing this will increase effectiveness and demonstrate the results of integrating AI in data analytics.
Measure & Optimize
Your Content Goes HeAMeasuring output helps a business check whether expectations meet the outcomes. If they do, the process continues as it did before. But if the expectations aren’t fulfilled, the AI models and other mathematical and statistical methods are optimized to align correctly with the set KPIs.
Read how BuzzClan helped implement AI in one of the Fortune 500 luxury retailers to achieve immense benefits with its data engineering services.
Common Challenges in AI and Data Analytics Adoption
Some challenges can occur while adopting and implementing AI in data analytics. These challenges are as follows:
Data Quality Issues
- Inaccurate Data: Inaccurate profiling based on poor-quality data is dangerous because it creates false impressions. Due to the complexity of AI systems, the models will only respond appropriately when the data fed to them is up-to-date and of the correct quality.
- Data Silos: The spread of data across multiple systems makes it challenging to access, let alone form an integrated source for AI analytics.
Lack of Skilled Personnel
- Talent Shortage: Today, there is a relatively high demand for data scientists and artificial intelligence specialists, but the number remains relatively limited. Organizations find it difficult to find qualified professionals who can help them adopt AI effectively by applying solutions.
- Training Needs: Current employees may need some orientation on using AI as a tool, which may also take time and be expensive.
Integration Challenges
- Legacy Systems: Some organizations still use old equipment that may not support new deep learning algorithms, making it hard to integrate a new solution.
- Complexity of Implementation: Automating using AI systems cannot be as trivial as it may seem. Current working procedures can always be misconfigured, allowing for mistakes or misconfigurations.
Cost Concerns
- High Initial Investment: Deploying AI solutions entails substantial initial costs, mainly software, hardware, and training.
- Ongoing Maintenance Costs: In addition to one-time installation costs, operating and upgrading AI can incur other expenses, which organizations should consider.
Key Differences Between AI, Machine Learning, and Data Analytics
Several key differences exist between AI, machine learning, and data analytics. It includes different techniques, scope, purpose, etc. Some of them are as follows:
| Aspect | Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine Learning (ML) | Data Analytics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simulation of human intelligence in machines to perform tasks autonomously. | A subset of AI that enables systems to learn from data and improve over time. | The process of examining and interpreting data to conclude. |
| Purpose | To solve complex problems and automate decision-making processes. | To develop algorithms that allow systems to learn from and adapt to data. | To analyze historical data for informed decision-making. |
| Techniques Used | Natural language processing, robotics, computer vision, etc. | Supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. | Descriptive statistics, data visualization, business intelligence. |
| Scope | Broad: It encompasses various applications mimicking human cognitive functions. | Narrower: It focuses on learning patterns from data without explicit programming. | Specific: It aims to answer predefined questions using existing data. |
| Data Types | Handles structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data. | Primarily works with structured and semi-structured data. | Deals with historical datasets for analysis and insights. |
| Outcome | Autonomous systems are capable of reasoning and decision-making. | Models that improve performance through experience with data. | Insights that guide business decisions based on past trends. |
| Real-world Examples | Self-driving cars, virtual assistants (like Siri), fraud detection systems. | Recommendation engines (like Netflix), spam filters, and predictive maintenance. | Business reports, sales forecasting, and customer behavior analysis. |
Key Metrics for Successful AI and Analytics Projects
Some metrics or key aspects represent whether AI and analytics projects go hand-in-hand. Some of these key metrics for successful AI and analytics projects are as follows:
| Key Metrics for Successful AI and Analytics Projects | Description | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Measures how often AI predictions are correct. | Ensures reliability and minimizes errors in decision-making. |
| Precision and Recall | Precision indicates the relevance of optimistic predictions; recall shows the model's ability to identify all relevant instances. | Balances quality of outcomes, reducing false positives and negatives. |
| F1 Score | Combines precision and recall into a single metric. | Helpful in evaluating models on imbalanced datasets, ensuring comprehensive performance assessment. |
| Return on Investment (ROI) | Quantifies the financial benefits gained from AI initiatives relative to costs. | Essential for justifying AI investments and guiding future projects. |
| Customer Effort Score (CES) | Assesses how easy it is for users to achieve their goals with the AI system. | Lower scores indicate better user experience, leading to higher satisfaction and retention. |
| Task Success Ratefor ML | Percentage of tasks completed successfully by users. | Higher rates reflect effective AI solutions that meet user needs efficiently. |
| Latency | Measures response time of the AI system. | Lower latency enhances user experience, especially in real-time applications. |
| User Retention Rate | Indicates the percentage of users who continue using the AI system over time. | High retention suggests satisfaction and ongoing value from the AI solution. |
| Model Deployment Time | The average time taken to deploy new models or updates. | Shorter deployment times improve agility and responsiveness to business needs. |
Future Trends in AI and Data Analytics
Many advancements have been seen in AI, such as ‘Gen AI,’ now let’s discover what future advancements and trends can be seen when AI is integrated into data analytics:
- Storytelling on Automation: AI, with its machine learning models and generative AI capabilities, can narrate a proper data-oriented story if the data is embedded programmatically.
- Conversational Analytics: As elaborated above, regarding NLPs and how they are helpful in a business. AI in data analytics can create chatbots that use NLP models to understand user analysis queries, offering advanced and valuable answers.
- Detecting Issues in Real Time: Since AI can operate at lightning speeds, it can filter out data and make sense of it in real-time, much faster than human speed. When AI scans and organizes data, it filters out issues, such as duplicate data or data errors, in real time, reducing later downtime and complications.
- Embedded Analytics: The automated models reduce the hecticness of manual cognition and offer continuous analysis of products and services for streamlined functioning.
- Cutting-Edge Simulations: AI and data analytics can test numerous simulations for data gathering and utilization.
- Prescriptive Analytics: Prescriptive analytics is part of data analytics. It means that AI, with its algorithms and tools, makes decisions that help businesses achieve their targets and missions. AI can simultaneously evaluate limitless data and determine what has worked well in the past and what needs improvement. By assessing the current state and past data, AI can prescribe what should be done next to address the situation.
Conclusion
Ultimately, AI has increased the potential of data analysis. Businesses can leverage the advantages offered by artificial intelligence and its components in data analytics by implementing detailed steps into their processes. By eradicating possible challenges and taking advantage of their benefits, businesses can uplift innovations and offer more data-oriented products and services. But do you want to infuse your business with AI and data analytics without much trouble and a serene mindset? Do it with BuzzClan.
Businesses must adopt a data engineering strategy that aligns with their project’s budget, timeline, and scope. BuzzClan’s expert data engineering services are the ideal solution for comprehensively analyzing your data needs and the optimal engineering approach. Contact us for unparalleled data engineering solutions that align with your business’s wants and mission.
FAQs

Get In Touch