Difference Between Public Cloud vs Private Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud
Gururaj Singh
Jan 18, 2024
In today's digital landscape's ever-evolving tapestry, cloud computing emerges as a trend and a cornerstone of modern business technology. Its ascent from a mere buzzword to a fundamental business tool mirrors the rapid pace at which technology is reshaping our world. The terms Public, Private, and Hybrid Cloud have become more than just technological jargon; they are the pathways to digital transformation and operational efficiency.
But what do these models truly entail, and more importantly, how do they fit into your unique business narrative? Each model - Public, Private, and Hybrid Cloud - has distinct characteristics, advantages, and considerations.
Our focus here is to demystify these cloud environments. We aim to offer a clear, comparative view of Public, Private, and Hybrid Cloud models. This exploration is about understanding what each model brings and discerning which cloud strategy aligns best with your business objectives. Whether you're a startup stepping into the cloud arena or an established enterprise reevaluating your cloud strategy, this guide will help you make an informed, strategic decision in your cloud journey.
Comparison of Computing Deployment Models
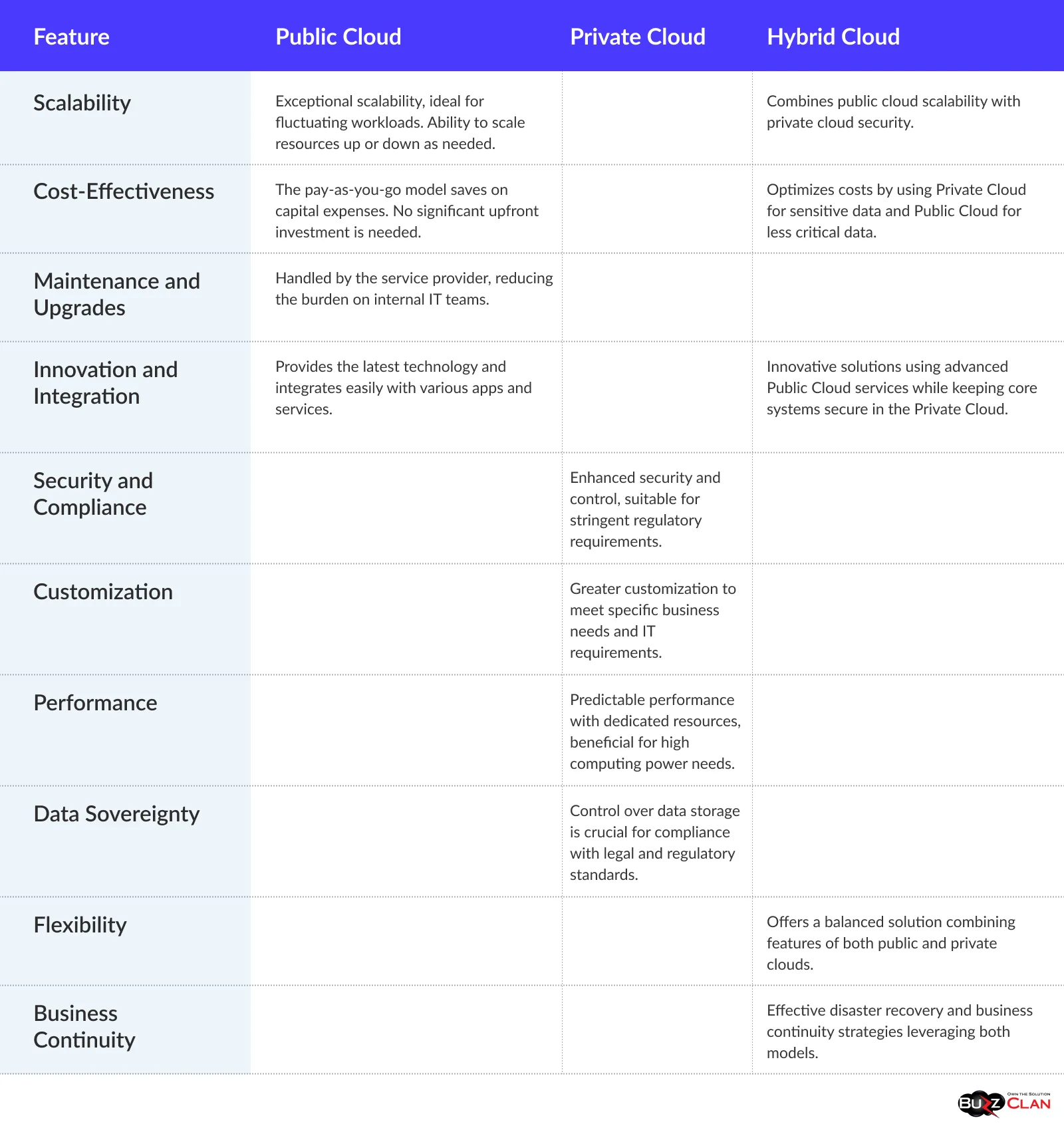
Benefits: Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud vs. Hybrid Cloud
Public Cloud
Public Clouds are shared resources that offer vast scalability and flexibility. They are cost-effective, eliminating the need for significant capital investments in infrastructure. Businesses benefit from the latest innovations and easy integration with various services. However, they may need help in terms of security and compliance for sensitive data.
Private Cloud
Private Clouds provide a dedicated environment, offering enhanced security and control, ideal for businesses with stringent compliance requirements. They allow for greater customization and consistent performance. While offering superior control and security, the trade-off comes in higher costs and the need for in-house expertise for maintenance.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Clouds offer the best of both worlds, blending the flexibility and scalability of the Public Cloud with the security and control of the Private Cloud. They provide a versatile environment that optimizes costs and enhances business continuity. This model is ideal for businesses balancing innovation with stringent security and compliance requirements.
Each cloud model has unique advantages, and the choice depends on your business needs, goals, and constraints.
The Basics of Cloud Computing
At its heart, cloud computing delivers computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. It's akin to renting versus owning a house; with cloud services, you're essentially renting digital space and capabilities, often resulting in cost savings, advanced performance, and the flexibility to scale as needed.
One of the most significant advantages of cloud computing is its scalability. It allows businesses to adjust resources based on their current needs, which is especially beneficial for coping with fluctuating workloads. Imagine having the power to upscale or downscale your IT resources with just a few clicks – that’s the agility cloud computing offers.
Another key element is cost efficiency. Cloud computing eliminates the capital expense of buying hardware and software, setting up and running on-site data centers—the racks of servers, the round-the-clock electricity for power and cooling, and the IT experts for managing the infrastructure. It adds up fast and can be a hefty burden for businesses.
Moreover, the cloud offers enhanced performance. The most significant cloud computing services run on a worldwide network of secure data centers, regularly upgraded to the latest fast and efficient computing hardware generation. This offers several benefits over a single corporate data center, including reduced application network latency and more significant economies of scale.
Public Cloud: An Overview
The Public Cloud is often the most recognized model when discussing cloud computing. It’s the epitome of what cloud computing promises: vast, scalable, and accessible to all. So, what exactly is a Public Cloud?
Definition and Basic Understanding
The Public Cloud is a model of cloud computing where a service provider makes resources available to the public over the Internet. These resources include storage, applications, and virtual servers. Think of it as a gigantic, shared digital space where various users can rent as much or as little of the service as they need. The beauty of this model lies in its sheer scale and accessibility—anyone with internet access can use these services.
Key Features
- Resource Sharing: The Public Cloud operates on a multi-tenant architecture, sharing the same physical resources among multiple users. This is similar to renting an apartment in a large building; you have space, but the underlying infrastructure is shared.
- Scalability: Perhaps the most standout feature, scalability, ensures that as your business grows, your cloud capacity can grow with it. Need more storage or computing power? Simply scale up your cloud services without the need for physical hardware upgrades.
- Cost-Effectiveness: With a pay-as-you-go model, you only pay for what you use. This eliminates the need for significant upfront investment in infrastructure.
- Accessibility and Flexibility: Public Cloud services are available anywhere, anytime, with an internet connection. This global accessibility makes it a flexible option for businesses operating in multiple locations.
Major Public Cloud Providers

Several key players dominate the Public Cloud landscape.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): A frontrunner in the cloud arena, AWS offers a comprehensive range of services, including computing power, storage options, and networking capabilities.
- Microsoft Azure: Known for its seamless integration with Microsoft's software products, Azure is a favorite among businesses looking for a robust cloud solution compatible with existing Microsoft tools.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): With its stronghold in data analytics and machine learning, GCP is a go-to for organizations looking to leverage cloud computing for advanced data processing and insights.
Benefits of Public Cloud
The Public Cloud isn't just popular; it's a powerhouse of benefits tailored to meet the needs of a diverse range of businesses and industries. Here's why many are opting for this model:
Cost-Effectiveness and Pay-As-You-Go Model
One of the most compelling draws of the Public Cloud is its cost structure. The pay-as-you-go model allows businesses to pay only for the resources they use, which can significantly reduce upfront and ongoing costs. This is akin to only paying for the electricity and water you use in your house rather than a flat rate regardless of consumption. This model is particularly appealing for startups and small businesses as it eliminates the need for hefty initial investments in hardware and infrastructure.
High Scalability and Flexibility
The Public Cloud provides an unmatched level of scalability. Whether you're experiencing a sudden spike in traffic or expanding your business operations, the Public Cloud can scale up or down to accommodate your needs. This flexibility is a game-changer, ensuring that businesses can react quickly to market demands without the burden of over-provisioning resources.
Wide Range of Services and Applications Available
The Public Cloud offers an extensive catalog of services and applications, from basic storage and computing services to advanced AI, machine learning, and data analytics capabilities. This wide array ensures businesses can find the tools to innovate and grow. Providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP continually update and expand their service offerings, keeping businesses at the forefront of technological advancements.
Challenges and Considerations for Public Cloud
While the Public Cloud offers numerous benefits, it has challenges. Understanding these hurdles is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions and strategize effectively to mitigate risks.
Security Concerns in a Shared Environment
In the Public Cloud, data from different organizations is stored on the same hardware, albeit virtually segregated. This shared environment raises concerns about data breaches and cyber threats. While cloud providers implement robust security measures, the inherent nature of shared resources can be a deal-breaker for businesses with susceptible data. It's like living in a gated community; while security protocols are in place, the shared space might still concern some.
Potential for Limited Customization
The Public Cloud operates on a standard architecture to serve a broad customer base. This can limit the scope for customization as compared to a Private Cloud. Businesses with specific, unique requirements for their IT infrastructure may find this one-size-fits-all approach restrictive. It's akin to renting an apartment where you can't knock down walls or change the building's external structure.
Data Governance and Compliance Issues
Navigating data governance and compliance in the Public Cloud can be complex, particularly for businesses operating under stringent regulatory frameworks. Compliance issues arise due to the multi-tenant nature of the Public Cloud and the fact that data centers may be located in different geographical regions with varying legal implications. Ensuring compliance in such a scenario is like playing a game where the rules change depending on your location.
Private Cloud: An Overview
The Private Cloud stands out for its exclusivity and control in the spectrum of cloud computing models. It's a model where cloud infrastructure is solely dedicated to a single organization. This could be managed internally or by a third party and hosted on-premises or off-site. Picture a gated estate instead of a public park; your space is operated and maintained according to your needs
Definition and Unique Characteristics
The Private Cloud is defined by its single-tenant environment, where the services and infrastructure are maintained on a private network. Key characteristics include enhanced security and control, as the resources are not shared with any other organization. This dedicated environment allows for customized configurations and adaptations to specific business needs.
Customization and Control
In a Private Cloud, the organization has complete control over the virtualized environment, offering higher security and privacy. This is particularly advantageous for businesses that handle sensitive data, require strict data governance, or operate in industries with stringent regulatory requirements. It’s like having a personal home theater; you control the movie playlist, the seating arrangement, and who gets an invite.
Enhanced Performance and Reliability
Since resources in a Private Cloud are not shared, organizations benefit from consistent performance and reliability. This setup can be tailored to match the business's needs, ensuring critical applications run smoothly and efficiently.
Cost and Infrastructure Considerations
While Private Clouds offer numerous benefits in terms of security and control, they do come with higher costs compared to Public Clouds. Setting up a Private Cloud requires significant investment in infrastructure, technology, and manpower. Additionally, maintaining and upgrading this environment is solely the organization's responsibility, which can add to the operational costs.
The Private Cloud is a compelling option for businesses prioritizing security, control, and customization. However, this model requires a careful assessment of costs and infrastructure capabilities to ensure it aligns with the organization's objectives and resources.
Benefits of Private Cloud
The Private Cloud is more than just a secluded digital environment; it's a powerhouse of benefits tailored for businesses seeking greater control and customization. Here are the key advantages:
Enhanced Security and Control
The standout feature of the Private Cloud is its enhanced security. Operating in a single-tenant environment means the infrastructure is dedicated solely to one organization, significantly reducing the risk of external breaches. This heightened security level is especially crucial for industries dealing with sensitive data, like finance and healthcare. It's akin to having a personalized security system for your home tailored to your specific needs and risks.
Greater Customization and Tailored Solutions
One size does not fit all in IT infrastructure, and the Private Cloud embraces this notion. Organizations can tailor their cloud environment to their exact specifications, from the network configurations to the storage and computing resources. This level of customization allows businesses to optimize their IT environment according to their operational requirements and goals.
Predictable Performance and Dedicated Resources
In the Private Cloud, resources are not shared with other organizations, leading to more predictable and consistent performance. This mainly benefits applications with high computing power or specific performance requirements. With dedicated resources, businesses can ensure that their critical operations run smoothly and efficiently without the fear of resource contention often seen in shared environments.
With enhanced security, customization capabilities, and reliable performance, the Private Cloud presents an attractive option for businesses prioritizing control over their IT environment. It offers a tailored solution that aligns closely with individual business needs, providing a solid foundation for growth and innovation.
Challenges and Considerations for Private Cloud
While offering distinct advantages, the Private Cloud has challenges that businesses must consider. These challenges can impact both the short-term implementation and long-term operational strategy.
Higher Costs and Resource Requirements
One of the most significant considerations of the Private Cloud is the cost. Unlike the Public Cloud, where the service provider manages the infrastructure, the organization is responsible for the capital and operational expenses of setting up and maintaining the cloud infrastructure in a Private Cloud. This includes costs associated with hardware, software, and the technical staff required to manage and support the environment. These costs can be prohibitive for smaller businesses or those with limited IT budgets.
Complexity in Setup and Maintenance
Setting up a Private Cloud infrastructure requires expertise and a sophisticated understanding of cloud technologies. This complexity extends to ongoing maintenance and management. Keeping the cloud environment secure, efficient, and up-to-date demands constant vigilance and skilled resources, which can be challenging for organizations without a robust IT department.
Scalability Limitations
While Private Clouds offer dedicated resources, they can't match the near-infinite scalability of Public Clouds. Expanding a Private Cloud often involves purchasing additional physical hardware, which can be time-consuming and expensive. This limitation can be critical for businesses anticipating rapid growth or experiencing fluctuating demand.
While the Private Cloud offers enhanced security, control, and customization, these benefits come at the cost of higher financial investment, complexity in management, and scalability limitations. Businesses must weigh these challenges against their specific needs and capabilities to determine if a Private Cloud is the right fit.
Hybrid Cloud: Combining the Best of Both Worlds
In the dynamic world of cloud computing, the Hybrid Cloud emerges as a harmonious blend of the Public and Private Clouds, integrating their strengths while mitigating their limitations. It's like having the best of both worlds – the robust security of the Private Cloud and the vast scalability of the Public Cloud.
Introduction to Hybrid Cloud and Its Concept
A Hybrid Cloud is a computing environment combining a Private Cloud with one or more Public Cloud services, with proprietary software enabling communication between each service. This fusion creates a unified, automated, and well-managed computing environment. The critical aspect of a Hybrid Cloud is its ability to allow data and applications to intermingle across private and public clouds.
Integrating Public and Private Cloud Features
The beauty of the Hybrid Cloud lies in its flexibility. It allows businesses to store protected or privileged data on a Private Cloud while still enjoying the expansive computational resources of a Public Cloud for everyday applications. Think of it as a hybrid car that can switch between gas and electric power – using each for what they do best. For instance, a company might use a Private Cloud for sensitive, business-critical operations like financial reporting while relying on a Public Cloud for high-volume, less-sensitive tasks like email.
Ideal Scenarios for Hybrid Cloud Adoption
The Hybrid Cloud model is particularly beneficial in several scenarios:
- Businesses with Dynamic Workloads: For companies that experience fluctuating demands, the Hybrid Cloud offers the elasticity to scale up or down, leveraging Public Cloud resources during peak periods.
- Organizations with Big Data Processing: Companies that handle large-scale data analytics can use the Public Cloud's vast resources for processing while keeping sensitive data sets secure in a Private Cloud.
- Regulatory Compliance and Data Sovereignty: Businesses subject to regulatory compliance can keep sensitive data in a Private Cloud or a specific geographic location while utilizing the Public Cloud for other tasks.
The Hybrid Cloud model offers a versatile and strategic approach for businesses seeking both the security of a Private Cloud and the scalability and cost-effectiveness of a Public Cloud. It represents a sophisticated cloud strategy that can be tailored to suit specific business needs and scenarios.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
With its blend of Public and Private Clouds, the Hybrid Cloud model brings many benefits, making it an increasingly popular choice for businesses striving for a balanced cloud strategy.
Flexibility and Balanced Approach
The most significant advantage of the Hybrid Cloud is its unparalleled flexibility. Businesses are not restricted to the binary choice of public or private but can enjoy the benefits of both. This flexibility allows for a more balanced approach to cloud computing. Depending on their specific needs at any given time, companies can shift workloads between cloud solutions—offering a customized blend of scalability, cost-efficiency, and security. It's like having a versatile toolkit; you use the tool that best fits the job.
Optimal Resource Utilization
With the Hybrid Cloud, organizations can optimize their resource utilization. By leveraging the Public Cloud for less sensitive, scalable tasks and the Private Cloud for critical, sensitive workloads, businesses ensure that they use the right resources for the right jobs. This not only maximizes efficiency but also can result in significant cost savings. The Hybrid Cloud model enables businesses to operate more efficiently by aligning their computing needs with the most suitable cloud environment.
Strategic Deployment for Sensitive and Non-Sensitive Data
The Hybrid Cloud provides a strategic advantage when it comes to data deployment. The Private Cloud offers a secure environment with enhanced controls for sensitive data. At the same time, the Public Cloud is an ideal choice for less sensitive data that can benefit from the scale and power of public resources. This strategic segregation ensures that all data is stored in the most appropriate and secure environment, catering to compliance requirements and business policies.
In summary, the Hybrid Cloud offers a flexible, resource-optimized, and strategically sound approach to cloud computing. It empowers businesses to tailor their cloud environment to their precise requirements, striking the perfect balance between operational efficiency, security, and cost-effectiveness.
Challenges and Considerations for Hybrid Cloud
Despite its numerous advantages, the Hybrid Cloud comes with a unique set of challenges. These considerations are crucial for businesses to address for a successful Hybrid Cloud strategy.
Complexity in Deployment and Management
One of the primary challenges of the Hybrid Cloud is the complexity involved in its deployment and ongoing management. Juggling between two cloud environments means dealing with different interfaces, tools, and management strategies. This complexity requires higher expertise and may necessitate advanced training for IT staff or hiring specialists. It's akin to mastering two musical instruments; each has nuances and demands proficiency.
Ensuring Seamless Integration and Interoperability
For a Hybrid Cloud model to function efficiently, seamless integration between Public and Private Cloud components is essential. This integration ensures data and applications can move freely and securely between the two environments. However, achieving this level of interoperability can take time and effort, especially when dealing with different cloud providers or legacy systems. It requires careful planning and often sophisticated technical solutions.
Balancing Security Across Diverse Environments
Security in a Hybrid Cloud environment is complex, as it must encompass the varying security protocols of both Public and Private Clouds. Ensuring consistent security policies and measures across these diverse environments is challenging. There's a need for vigilant monitoring and management to protect against vulnerabilities, especially when data is in transit between different cloud platforms.
These challenges – from deployment complexity and integration to security management – make the Hybrid Cloud a sophisticated model that requires thoughtful consideration and strategic planning. Businesses must weigh these factors against the potential benefits to determine if the Hybrid Cloud is the right approach for their needs.
Challenges and Considerations for Hybrid Cloud
Choosing between Public, Private, and Hybrid Cloud models is a significant decision that hinges on various factors. It’s not just about the size or sector of your business but about aligning your specific needs and goals with the right cloud solution.
Key Factors to Consider
- Business Needs and Requirements: Start by assessing what you need from the cloud. Are you looking for flexibility and scalability, or is security your primary concern? For instance, a startup looking to scale rapidly might find the Public Cloud more beneficial, while a financial institution might prioritize the security of a Private Cloud.
- Compliance and Data Security: Consider your industry's legal and compliance requirements. If you're in a highly regulated industry, like healthcare or finance, data security and compliance will be paramount, possibly swaying you towards a Private or Hybrid Cloud solution.
- Budget Constraints: Be realistic about what you can afford. Public Clouds are generally more cost-effective and have lower upfront costs, while Private Clouds require a significant investment in infrastructure and maintenance.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Evaluate your need for scalability. If your business experiences fluctuating workloads or rapid growth, the Public Cloud's scalability or a Hybrid Cloud's flexibility might be more suitable.
- Technical Expertise: Consider your in-house IT capabilities. Deploying and managing a Private or Hybrid Cloud requires a certain level of expertise. If your team doesn’t have this, a Public Cloud, which the provider governs, might be more appropriate.
Assessing Long-Term Strategy
Your decision should align with your long-term business strategy. Consider where you see your business in the next five to ten years and how your cloud choice will support this vision. The right cloud environment can fuel growth and innovation, but choosing the wrong one can lead to unnecessary complexity and costs.
Examples of Business Cloud Strategies
- A global retail chain might opt for a Hybrid Cloud to keep sensitive financial data secure in a Private Cloud while using the Public Cloud for their e-commerce platforms.
- A small tech startup might choose a Public Cloud for its low upfront costs and scalability, allowing it to focus on rapid growth and innovation.
Conclusion
Navigating the cloud landscape can be akin to charting a c ourse through uncharted waters – exciting but filled with crucial decisions. The choice between Public, Private, and Hybrid Cloud models is more than a technical decision; it's a strategic one that can significantly impact your business's efficiency, scalability, and bottom line. As we've explored, each model has its unique strengths and challenges tailored to different business needs and goals.
The journey to the cloud should start with a deep dive into your organization's specific requirements, aspirations, and constraints. Whether it's the agility and cost-effectiveness of the Public Cloud, the security and control of the Private Cloud, or the balanced approach of the Hybrid Cloud, the right choice aligns with your business strategy, both for today and the future.
Remember that such decisions don't have to be made alone. Partnering with cloud experts like BuzzClan can illuminate the path forward. With their expertise, you can tailor a cloud solution that fits your unique business landscape, ensuring a smooth and successful transition into the cloud.
Stayng informed and agile will be critical as the cloud continues to evolve. The suitable cloud model is about more than just where your business is now but where it can go.

Get In Touch
Follow Us
Table of Contents
- Comparison of Computing Deployment Models
- Benefits: Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud vs. Hybrid Cloud
- The Basics of Cloud Computing
- Public Cloud: An Overview
- Major Public Cloud Providers
- Benefits of Public Cloud
- Benefits of Private Cloud
- Challenges and Considerations for Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud: Combining the Best of Both Worlds
- Introduction to Hybrid Cloud and Its Concept
- Integrating Public and Private Cloud Features
- Ideal Scenarios for Hybrid Cloud Adoption
- Benefits of Hybrid Cloud
- Challenges and Considerations for Hybrid Cloud
- Challenges and Considerations for Hybrid Cloud
- Conclusion
- Get In Touch
