What is Business Intelligence?
Sanjay Sharma
Jan 5, 2024
Overview of Business Intelligence
Business Intelligence (BI) is like the Swiss Army knife of the corporate world—a versatile tool designed to help businesses make informed decisions. At its core, BI encompasses the technologies, practices, and applications that collect, analyze, and present business data. Far from being a single tool or system, BI is an evolving concept that continues to grow with the advent of big data, machine learning, and other technological advancements.
Importance of BI in Modern Business
In today's hyper-competitive business landscape, making decisions based on gut feelings or outdated reports is as risky as crossing a busy street with your eyes closed. BI acts as the traffic light and crosswalk, providing real-time insights that guide decision-making and strategy. Companies leveraging BI can enjoy benefits such as:
- Improved Decision-Making: Businesses can make more informed decisions with accurate and timely data.
- Operational Efficiency: BI can streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve productivity.
- Competitive Advantage: Insights derived from BI can help companies stay one step ahead of competitors.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Understanding customer behavior and preferences enables a more personalized user experience, which can lead to increased loyalty and revenue.
What Readers Can Expect to Learn from This Guide
Consider this pillar page your ultimate guide to Business Intelligence. Whether you're a seasoned executive looking for advanced BI strategies or a newcomer wanting to understand the basics, this guide covers you. We will walk you through:
- The history and evolution of BI
- Different types of BI and their applications
- The benefits and challenges of implementing BI solutions
- Real-world case studies
- The future trends shaping the BI landscape
So, buckle up as we embark on this enlightening journey through the multifaceted universe of Business Intelligence. Whether you're looking to make smarter business decisions, optimize your operations, or outwit your competitors, this guide will give you the knowledge you need to succeed.
The Evolution of Business Intelligence
The transition from Traditional Data Analytics to BI
Fast forward to the 1990s and early 2000s, and we witness the adolescence of BI. The internet and increasing computational power led to the emergence of more sophisticated data analytics. Businesses started moving from merely descriptive analytics, which told them what had happened, to diagnostic analytics, which started to explain why things happened.
However, traditional data analytics could have been more convenient and required specialized interpreting skills. Enter the new age of BI, where analytics tools have become more integrated, user-friendly, and accessible to non-technical users. It's like going from riding a tricycle to driving a sports car—suddenly, you have power, speed, and agility at your fingertips.
Modern BI Tools and Technologies
Welcome to the present day, where BI has matured into an intelligent, real-time, dynamic toolset. Modern BI is characterized by the following:
- Self-Service BI: Empowering users to generate reports and insights without requiring technical expertise. It's DIY analytics at its best.
- Data Visualization: Tools that convert complex data into graphs, charts, and other visual formats, making it easier to glean insights at a glance.
- Real-Time Analytics: The capability to analyze data as it's generated, offering businesses timely insights.
- AI and Machine Learning: Integration of machine learning algorithms to predict future trends and make recommendations.
- Cloud-Based BI: Offering flexibility and scalability, cloud BI solutions enable access to insights anytime, anywhere.
And there you have it—the fascinating journey of Business Intelligence from its humble beginnings to its current superstar status. If BI were a person, it would be the nerdy kid who grew up as a tech mogul. The following section will explain what Business Intelligence entails and how it can be categorized. Stay tuned as we continue to explore the ever-evolving world of BI.
What Exactly is Business Intelligence?
Ah, the million-dollar question: What exactly is Business Intelligence (BI)? It's a term you've probably heard thrown around boardrooms and business articles, often hailed as the secret sauce to business success. Let's peel back the layers and dig into what BI truly entails.
Definition and Core Components
Business Intelligence is the art and science of collecting, storing, analyzing, and transforming data into actionable insights that inform an organization's strategic and tactical business decisions. It's like the GPS for your business, offering direction and clarity in a complex landscape. The core components of BI are:
- Data Collection: Harvesting data from various sources, databases, sensors, or user activities.
- Data Storage: Safely storing this collected data in a manner that's both secure and easily accessible.
- Data Analysis: Employing various tools and algorithms to sift through this data and draw meaningful insights.
- Data Visualization: Presenting these insights in an understandable and actionable format, such as dashboards, reports, or graphs.
Types of BI Analysis
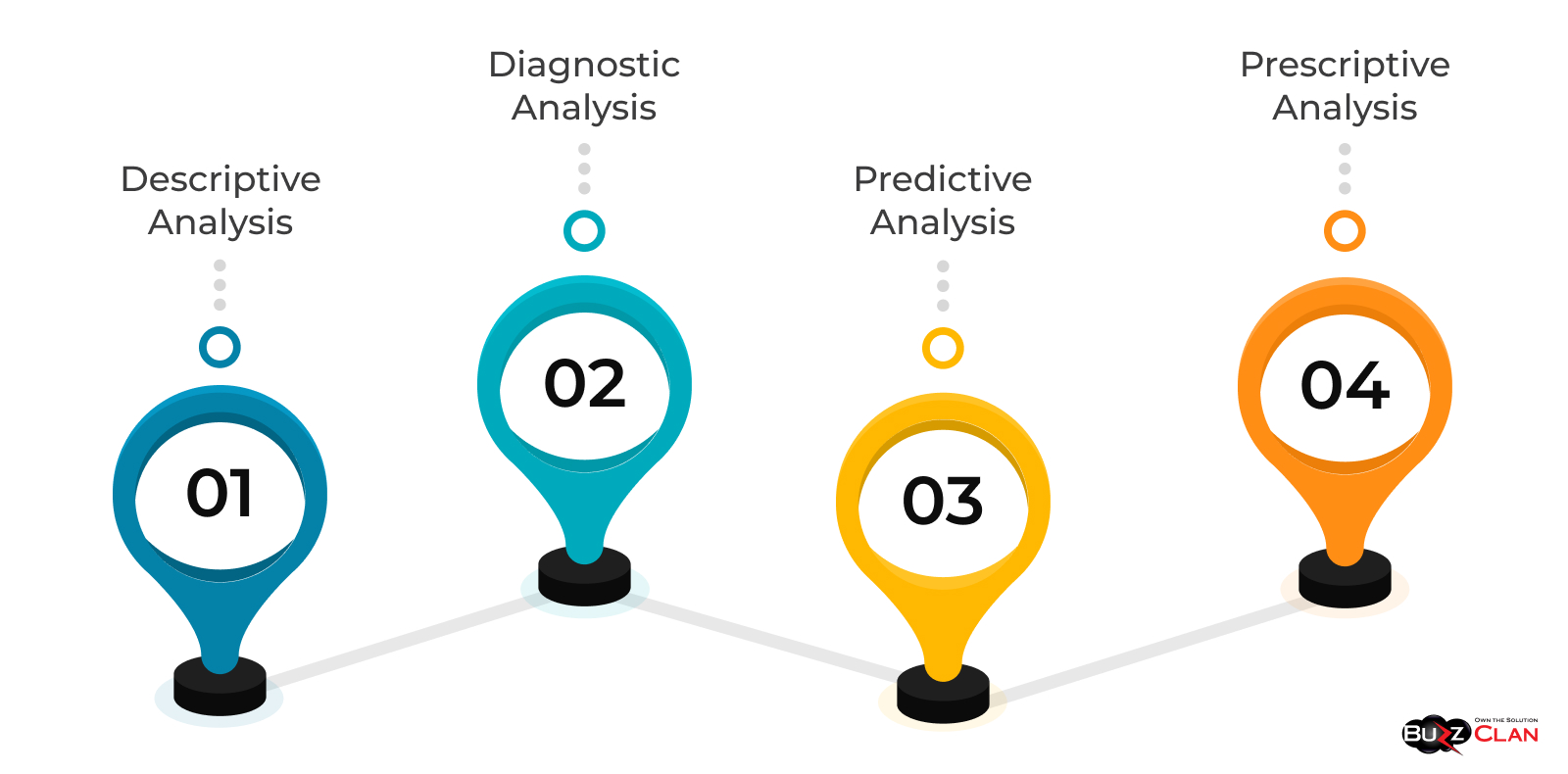
Descriptive Analysis:
- What it is: This is the most basic form of BI and involves analyzing historical data to identify patterns or trends.
- Use-case: Understanding last quarter's sales performance.
Diagnostic Analysis:
- What it is: Diagnostic analysis seeks to understand the causes behind observed outcomes.
- Use-case: Identifying the reason for a sudden drop in sales in a particular region.
Predictive Analysis:
- What it is: This form delves into future possibilities based on existing data.
- Use-case: Forecasting sales for the upcoming holiday season.
Prescriptive Analysis:
- What it is: This is the most advanced form of analysis, offering specific recommendations for handling potential future scenarios.
- Use-Case: Advising on inventory levels to maintain for anticipated sales increases.
Advantages and Disadvantages of BI
Advantages:
- Informed Decision-Making: BI tools process data to provide actionable insights, aiding in more informed decision-making.
- Operational Efficiency: By identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and other operational issues, BI can help streamline operations.
- Cost Savings: With data-backed insights, businesses can reduce wastage and optimize resource allocation.
- Competitive Advantage: Knowledge is power, and BI gives you a significant advantage over competitors not leveraging data effectively.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: BI platforms can be expensive regarding initial setup and ongoing maintenance.
- Complexity: Some BI systems require specialized skills to use effectively, which can be a barrier for smaller organizations.
- Data Accuracy: BI tools are only as good as the data they analyze. Quality data can lead to correct insights.
- Security Risks: Data breaches can expose sensitive information, making robust security measures necessary.
BI Platforms
Several BI platforms have gained popularity for their robust features and user-friendly interfaces. Some notable ones include
- Tableau: Known for its data visualization capabilities, Tableau is a favorite among data analysts.
- Microsoft Power BI: A versatile platform offering deep integration with other Microsoft products.
- SAP Business Intelligence: Offers a range of analytics and reporting tools and is particularly strong in enterprise-level applications.
- Oracle BI: Known for its scalability, Oracle BI is another enterprise favorite.
- QlikView: Offers associative model that allows complex data discovery and preparation.
Each platform has its own set of strengths, weaknesses, and unique features, making the choice dependent on specific business needs and existing infrastructure.
BI and Big Data
The advent of big data has been a game-changer for BI. With the enormous amount of data generated every second, BI tools have become more sophisticated to handle this influx.
- Data Lakes: BI tools can now integrate with data lakes, enabling organizations to analyze unstructured data alongside traditional data sources.
- Real-time Analytics: Big data capabilities have enabled real-time analytics, providing businesses with immediate insights.
- AI and Machine Learning: The complexities of big data often require the predictive capabilities of AI and machine learning algorithms, which are increasingly being integrated into BI platforms.
Key Functionalities: Data Mining, Reporting, Performance Metrics, etc.
BI offers a myriad of functionalities, each a cog in the well-oiled machine of intelligent business decision-making:
- Data Mining: The act of discovering patterns and relationships in large data sets.
- Reporting: Generating structured data summaries to monitor different business aspects.
- Performance Metrics: Using KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) to measure the effectiveness of various business processes.
- Data Visualization: Transforming raw data into visual formats like charts, graphs, and heat maps for easier interpretation.
The BI Ecosystem
Welcome to the bustling metropolis of the Business Intelligence (BI) ecosystem. Think of it as a dynamic cityscape where data sources are the buildings, BI software serves as the infrastructure, and the users are the bustling citizens. Let's take a guided tour of this fascinating landscape.
Data Sources:
Data sources are like the rivers and reservoirs that nourish the BI ecosystem. They come in various forms and sizes:
- Databases: The foundational pillars of the BI world, databases store structured data that can be easily queried and analyzed.
- Spreadsheets: The workhorses of small businesses and departments, spreadsheets are often the starting point for many BI processes.
- Cloud Storage: Cloud storage solutions offer scalable and flexible storage options for the celestial vaults of the digital age.
- APIs and Web Services: These pipelines connect external services, bringing in data from social media, web analytics, or other third-party sources.
BI Software:
BI software acts as our metaphorical city's roads, highways, and public transportation, helping data move smoothly and efficiently.
- Dashboard Software: Consider this the BI control center, where various metrics and KPIs are displayed in real-time.
- Data Visualization Tools: These are the artists of the BI world, turning raw data into visually appealing and easily digestible formats.
- Analytics Platforms: The libraries and research centers these platforms offer advanced capabilities like predictive modeling and machine learning algorithms.
Users:
Ah, the inhabitants of our BI city—the people who give meaning to all this infrastructure and data.
- Analysts: The architects and city planners analysts dive deep into the data to extract valuable insights.
- Managers: The administrators and mayors use BI to monitor team performance, set goals, and make tactical decisions.
- Executives: The governors and presidents, these high-level decision-makers use BI to guide overall strategy, mergers, and market expansions.
Benefits of Implementing BI
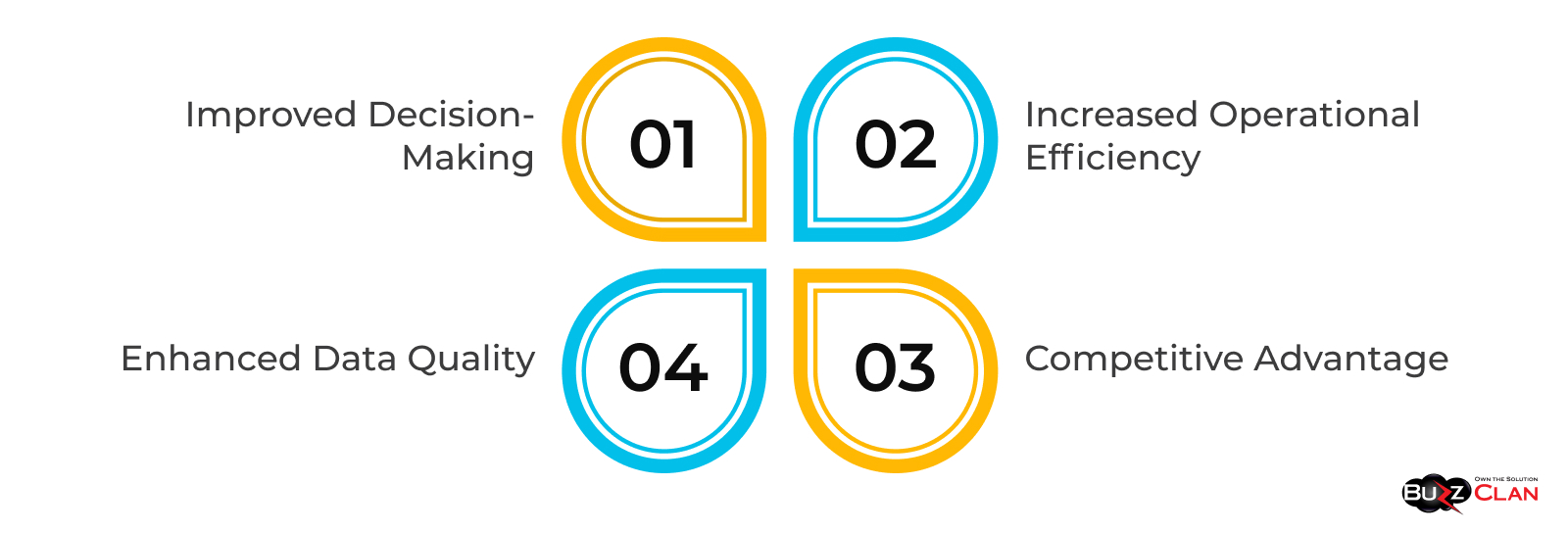
Ah, the sweet fruits of labor—when implemented correctly, Business Intelligence (BI) can deliver a smorgasbord of benefits that make the initial investment feel like buying a winning lottery ticket. Let's unpack these rewards and understand why they're crucial for modern businesses.
Improved Decision-Making
BI is the wise oracle that helps you make more informed decisions. By providing real-time insights and historical data analysis, BI allows businesses to
- Make data-driven decisions rather than relying on gut feelings or instinct.
- Prioritize strategic initiatives by understanding what's working and what's not.
- Identify market trends and consumer behaviors, helping to tailor products and services.
Improved decision-making is like a GPS guiding you through complicated business challenges.
Enhanced Data Quality
Garbage in, garbage out—or so the saying goes. With BI, data quality is enhanced through
- Data cleaning and normalization to ensure your database is as clean as a whistle.
- Integrating multiple data sources provides a more comprehensive view of business operations.
- Implementation of data governance policies, ensuring accuracy and compliance.
Better data quality means more reliable insights, akin to having a well-tuned orchestra instrument—it makes everything sound better.
Increased Operational Efficiency
Time is money, and efficiency is the fast lane to saving both. BI contributes to operational efficiency by
- Automating routine data collection and reporting tasks, freeing up human resources.
- Offering real-time performance metrics that help identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies in the system.
- Facilitating better resource allocation through demand forecasting.
- Think of it as upgrading from a bicycle to a jet plane. The time and effort saved can be channeled into more strategic activities, propelling the business forward.
Competitive Advantage
BI is your ace in the hole in the high-stakes poker game of business. It offers a competitive advantage by
- Giving you insights into market trends before competitors catch on.
- Facilitating a more agile response to market changes.
- Enabling personalized marketing strategies that resonate with target audiences.
In short, BI helps you know your cards and what's likely in everyone else's hands, giving you the upper hand in strategic planning and execution.
Business Intelligence in Different Industries
Business Intelligence (BI) is like a blockbuster movie—it's a hit across various genres (or in this case, industries). From healthcare to retail, BI has proven its versatility and indispensability. Let's look at how BI plays a starring role in different sectors.
Healthcare
In an industry where decisions can be life-altering, BI is the diagnostic tool healthcare professionals never knew they needed.
- Patient Data Analysis: BI helps analyze patient data to identify trends, improve treatments, and predict outcomes.
- Resource Allocation: Through BI, hospitals can optimize the allocation of resources like staff, beds, and medical equipment.
- Compliance and Reporting: BI tools can automate the process of data collection and reporting, ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations.
In a nutshell, BI in healthcare is like a skilled surgeon—precise, reliable, and crucial.
Retail
In the fast-paced world of retail, BI is the personal shopper that helps businesses tailor their offerings and optimize customer experiences.
- Inventory Management: BI tools can predict inventory needs based on historical data and seasonal trends.
- Customer Behavior: Through BI, retailers can understand buying patterns and preferences, enabling personalized marketing.
- Sales Forecasting: BI can predict future sales trends, helping retailers make informed stock levels and promotions decisions.
Think of BI in retail as the ultimate sales associate—always one step ahead and ready to assist.
Finance
In the finance sector, BI is the risk analyst and portfolio manager rolled into one, minus the fancy suits.
- Fraud Detection: Advanced BI algorithms can detect irregular transactions that may signify fraudulent activity.
- Risk Assessment: BI tools can analyze market trends and historical data to assess investment risks.
- Customer Segmentation: Through BI, financial institutions can segment customers based on behavior, enabling more targeted services.
BI is your most trusted financial advisor in finance, minus the exorbitant fees.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, BI is the quality control inspector and efficiency expert.
- Supply Chain Optimization: BI provides insights into the supply chain, helping to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Quality Assurance: BI tools can monitor product quality in real-time, triggering alerts for anomalies.
- Operational Efficiency: Through BI, manufacturers can optimize machine allocation, labor distribution, and other operational aspects.
Imagine BI in manufacturing as a well-oiled machine—reliable, efficient, and indispensable.
Marketing
Last but not least, in marketing, BI is the creative director and market analyst combined, helping to craft strategies that resonate and convert.
- Campaign Analysis: BI can track the performance of marketing campaigns in real-time, offering insights for optimization.
- Customer Segmentation: Through BI, marketers can segment their audience for more targeted and effective campaigns.
- ROI Measurement: BI tools can accurately measure the ROI of various marketing channels, helping to allocate budgets more effectively.
BI is like the genius ad campaign everyone discusses in marketing—it simply steals the show.
Features to Look for in a Business Intelligence Tools
When choosing your BI tool, it's essential to have a checklist of features that align with your business goals. Here are some to consider:
- Data Integration: Can it easily integrate with your existing data sources, such as databases, spreadsheets, and CRM systems?
- Real-Time Analytics: Does it offer real-time data analysis for timely decision-making?
- Data Visualization: How robust are its data visualization capabilities? Can you create custom charts and graphs?
- Collaboration: Are there features that allow team members to collaborate, such as shared dashboards or report commenting?
- Mobile Accessibility: Can you access your BI dashboards on various devices, including mobile?
Budget Considerations
The elephant in the room—budget. As with any significant business investment, it's crucial to consider the upfront costs and the long-term value. Some budgetary considerations:
- Subscription vs. One-Time Fee: Some BI tools operate on a subscription model, while others require a one-time license fee. Weigh the pros and cons of each.
- Scalability: Consider the costs of scaling up, especially as your business grows.
- Hidden Costs: Be wary of additional costs like training, implementation, and data overage fees.
- ROI: Always consider the potential return on investment. A more expensive tool may offer features that significantly boost your business's efficiency and revenue.
Steps to Implement a BI Solution
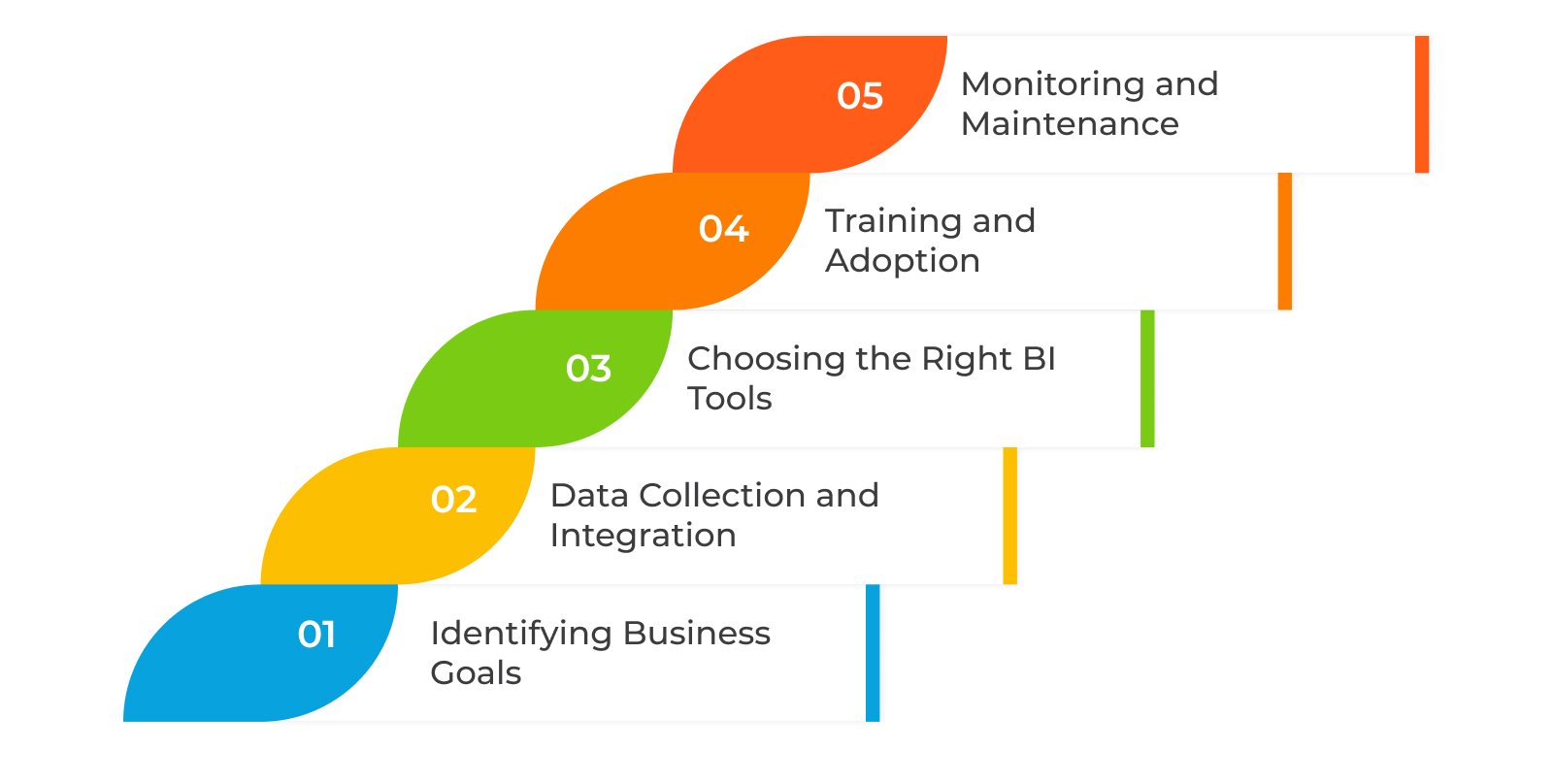
The honeymoon is over, and now it's time to move in together—metaphorically speaking. Implementing a Business Intelligence (BI) solution is like setting up a new home; you must plan, collaborate, and perhaps deal with a few bumps. Let's explore the essential steps to make this cohabitation as smooth as possible.
Identifying Business Goals
Before you jump headfirst into the BI pool, you need to know how deep it is. In other words, what are you hoping to achieve with your BI implementation?
- Strategic Goals: Are you looking to improve your business strategy, such as entering new markets or optimizing existing ones?
- Operational Goals: Is the focus on streamlining operations, like reducing costs or improving supply chain efficiency?
- Analytical Goals: Are you looking to perform in-depth data analysis for customer behavior, sales trends, or market research?
Identifying clear goals is like laying the foundation for your new home—it sets the stage for everything that follows.
Data Collection and Integration
With your goals in place, it's time to gather your building materials, aka your data.
- Data Sources: Identify where your data will come from. This could be existing databases, CRM systems, or even spreadsheets.
- Data Quality: Ensure the data is clean, accurate, and up-to-date.
- Data Integration: Use BI tools to integrate these disparate data sources into a unified view.
Think of this step as the framework of your house; it holds everything together.
Choosing the Right BI Tools
Now, for the fun part—choosing your fixtures and fittings, or in this case, your BI tools.
- Feature Match: Ensure the chosen tools align with your business goals.
- User-Friendliness: Consider the technical skill level of the users and opt for a tool that matches.
- Budget: Consider your budget, considering upfront and ongoing costs.
This is where your home starts to look like a home, filled with everything that makes it functional and comfy.
Training and Adoption
A home is a little if no one knows how to live in it. Training and adoption are crucial to ensure that users can make the most of the BI system.
- Initial Training: Conduct training sessions to acquaint users with the BI tool's features.
- Ongoing Support: Offer continuous training and resources to help users as the system evolves.
- User Feedback: Encourage feedback to understand users' challenges, allowing for iterative improvements.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Last but not least, a home needs regular upkeep, as does your BI system.
- Performance Metrics: Regularly check if the system meets the defined business goals.
- Updates and Patches: Keep the software up-to-date to benefit from new features and security updates.
- Data Audits: Regularly audit the data for quality and compliance, making necessary adjustments.
Real-World Case Studies
Ah, case studies—the reality TV shows of the business world. They offer us the drama of a problem, the suspense of a solution, and the satisfaction of results, all wrapped up in a neat, little package. Let's explore real-world examples of businesses successfully implementing Business Intelligence (BI). Names have been withheld to protect the brilliant.
Case Study 1: The Retail Revolution
The Problem
A mid-sized retail company struggled with inventory management, often overstocking some items while running out of others. It was like a poorly organized closet—too many winter coats and not enough summer dresses.
The Solution
The company implemented a BI solution that integrated sales, supply chain, and customer feedback data. Through advanced analytics, they were able to predict inventory needs more accurately.
The Results
- A 25% reduction in storage costs due to optimized inventory.
- A 15% increase in sales owing to better product availability.
- A significant improvement in customer satisfaction ratings.
It's as if the company's closet got a makeover from a professional organizer—everything in its place and a place for everything.
Case Study 2: The Healthcare Hero
The Problem
A healthcare provider faces patient flow challenges, leading to longer wait times and decreased patient satisfaction. Imagine a waiting room resembling a train station during rush hour—unpleasant.
The Solution
The healthcare provider employed a real-time BI tool that analyzed patient check-in data, staff availability, and resource allocation.
The Results
- A 30% decrease in patient wait times.
- A 20% improvement in resource utilization, including staff and examination rooms.
- Enhanced patient satisfaction, leading to higher retention rates.
The waiting room went from a chaotic train station to a serene lounge, all thanks to BI.
Case Study 3: The Manufacturing Marvel
The Problem
A manufacturing company needed to improve its efficiency in its production line, leading to delays and increased costs. Think of it as a traffic jam in a factory setting.
The Solution
The company implemented a BI system that tracked machine performance, labor hours, and material usage, offering real-time insights into bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
The Results
- A 40% improvement in production speed.
- A 25% reduction in labor costs through optimized scheduling.
- Enhanced product quality, leading to a 10% increase in customer satisfaction.
- The factory went from a traffic jam to an autobahn, all thanks to the insightful data provided by BI.
And there you have it—real stories of companies who took the BI plunge and came out swimmingly. These case studies are a testament to the transformative power of Business Intelligence, showing that it's not just a corporate buzzword but a bona fide business lifesaver.
Next, we'll tackle some common challenges and how to overcome them. It's like the obstacle course of the BI world, and we're your trusty guide. Stay tuned!
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
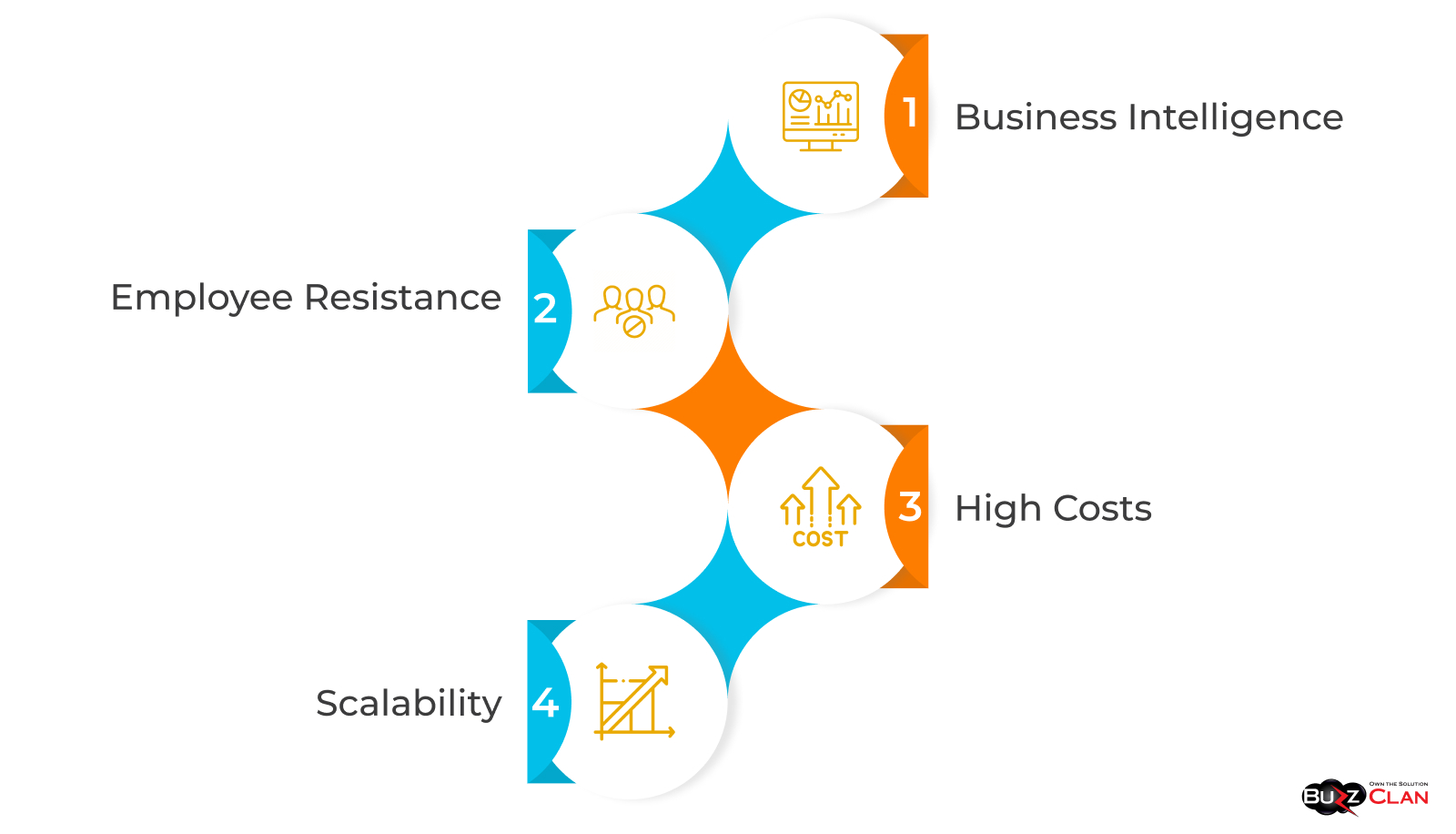
Like any hero’s journey, the path to Business Intelligence (BI) nirvana isn't without its dragons to slay. Challenges abound, whether grappling with data quality or battling the monster of high costs. But fear not, for every challenge has a solution—or in this case, a strategy. Let’s delve into some common pitfalls and how to leap over them.
Data Quality Issues
The Challenge
Poor data quality is like reading a map in the dark; you will get lost. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misleading insights, rendering your BI tools ineffective.
The Solution
- Data Auditing: Regularly audit your data sources to identify inaccuracies or inconsistencies.
- Data Governance: Implement policies to standardize data collection and reporting.
- Automated Cleaning: Use BI tools that offer automatic data cleaning features.
Remember, garbage in, garbage out. So make sure what you put into your BI system is as clean as a freshly laundered shirt.
Employee Resistance
The Challenge
Ah, the age-old issue of resistance to change. Employees may hesitate to adopt new tools, often due to a lack of understanding or fear of complexity.
The Solution
- Training: Conduct comprehensive training sessions to familiarize employees with the new BI tools.
- Pilot Programs: Roll out the BI system in phases, allowing employees to adapt gradually.
- Feedback Loops: Encourage employee feedback and make iterative improvements based on their suggestions.
Turning skeptics into believers requires a little education and a lot of open dialogue.
High Costs
The Challenge
BI tools can be expensive, not just the upfront costs. Ongoing maintenance and updates can also add up faster than a kid in a candy store.
The Solution
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Conduct a detailed cost-benefit analysis before implementing a BI solution to ensure it aligns with your budget and expected ROI.
- Scalable Solutions: Opt for BI tools that offer scalable pricing models, allowing you to start small and expand as needed.
- Hidden Costs: Be vigilant about additional costs like training, data overages, and add-on features.
Remember, the cheapest option is sometimes the most cost-effective in the long run. Look for value, not just price tags.
Scalability
The Challenge:
What works for a small business may not suit a large enterprise. As your business grows, your BI needs will evolve, and not all BI solutions are built to scale.
The Solution
- Future-Proofing: Choose a BI tool with scalability. This will save you the headache of migrating to a new system later.
- Modular Features: Opt for BI solutions that allow you to add features or users as your business grows.
- Performance Metrics: Regularly review performance metrics to ensure your BI system meets your business needs.
The Future of Business Intelligence
The future is where flying cars, robotic assistants, and Business Intelligence (BI) coalesce into a utopia of efficiency and innovation. Or at least, that’s the dream. While we may not have flying cars just yet, the future of BI looks quite exhilarating. Let's hop into our time machine and explore the next frontier for BI.
AI and Machine Learning in BI
The Future
Imagine a BI tool that gives you data and interprets it for you as if it were your personal business advisor. That’s the promise of AI and machine learning in BI. These technologies aim to automate complex data analysis, making predictions and even prescriptive suggestions.
The Impact
- Automated Insights: AI can automatically generate insights, highlighting trends or anomalies in your data.
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning algorithms can forecast future trends, allowing businesses to make proactive decisions.
- Natural Language Queries: Advanced AI could enable you to ask your BI tool questions in plain English and receive understandable answers.
AI and machine learning in BI are like the wise sages of the future, offering insights and guidance without being asked.
Real-time Analytics
The Future
The world moves fast, and businesses must keep up. Real-time analytics are becoming increasingly crucial, offering the ability to make decisions based on data as it comes in.
The Impact
- Immediate Decision-Making: Real-time data allows businesses to make decisions on the fly, from optimizing ad spending to rerouting supply chains.
- Customer Engagement: Real-time analytics can power personalized customer experiences, from tailored product recommendations to instant support.
Real-time analytics in BI are like having a super-responsive GPS that updates your route as conditions change, ensuring you're always on the most efficient path.
Integration with IoT Devices
The Future
The Internet of Things (IoT) is expanding. BI tools are starting to integrate with these smart devices, gathering data from various sources like sensors, wearables, and smart appliances.
The Impact
- Enhanced Data Collection: IoT devices can provide a wealth of new data points, from customer behavior to environmental conditions.
- Operational Efficiency: In industries like manufacturing or logistics, IoT integration can offer real-time insights into machine performance, inventory levels, and much more.
Think of IoT integration as adding many new sensors to your BI system, each providing its unique perspective and insights.
There you have it—answers to some of the most burning questions about BI. Next, we’ll provide additional resources to continue your BI journey. It's the treasure trove at the end of our BI quest, filled with eBooks, webinars, and more. Stay tuned!
Additional Resources
The grand finale—the "Where Do We Go from Here?" section. If this pillar page were a meal, consider this your dessert menu, offering delicious follow-up resources to satisfy your intellectual appetite. So, grab your metaphorical spoons and dig in!
- "The Beginner's Guide to Business Intelligence": Perfect for those just starting their BI journey, this eBook offers a comprehensive overview of BI basics.
- "Data-Driven Decision Making: A Handbook": This resource deepens into making informed choices based on data analytics.
- "BI for Small Businesses: A Practical Guide": Tailored for small business owners, this eBook explains how to leverage BI without breaking the bank.
eBooks
- "The Beginner's Guide to Business Intelligence": Perfect for those just starting their BI journey, this eBook offers a comprehensive overview of BI basics.
- "Data-Driven Decision Making: A Handbook": This resource deepens into making informed choices based on data analytics.
- "BI for Small Businesses: A Practical Guide": Tailored for small business owners, this eBook explains how to leverage BI without breaking the bank.
Webinars
- "Unlocking the Power of Real-time Analytics": A webinar that explores the benefits and challenges of real-time analytics in BI.
- "Navigating the BI Ecosystem": This webinar takes you through the various elements of a BI system, from data sources to user interfaces.
- "Building a Data-Driven Culture": Learn how to foster a culture that embraces data analytics, from top-level management to entry-level employees.
Podcasts
- "BI Unplugged: Conversations with Industry Experts": A podcast series featuring interviews with BI professionals, discussing trends, challenges, and best practices.
- "The Data Dive": This podcast focuses on real-world data analytics and BI applications, featuring case studies and success stories.
Online Courses
- "Introduction to Business Intelligence": An online course that covers the fundamentals, suitable for beginners.
- "Advanced BI Techniques": For those looking to deepen their understanding, this course covers complex topics like data modeling and predictive analytics.
Conclusion
And so, dear reader, we've reached the end of this comprehensive Business Intelligence (BI) guide. From its historical roots to its futuristic potentials, we've covered the A to Z of BI—think of it as your BI alphabet soup but with less slurping and more insightful sipping.
Summary of Key Points
- Evolution of BI: We journeyed through time to witness how BI evolved from traditional data analytics into today's modern, sophisticated process.
- What is BI: Demystified the core concepts, functionalities, and types of BI, turning it from an enigmatic acronym into a tangible asset for your business.
- BI Ecosystem: Explored the diverse landscape of BI, which includes various data sources, software, and users.
- Benefits: Unpacked the myriad advantages of implementing BI, from operational efficiency to strategic prowess.
- Industry Applications: Showcased how BI is a versatile player, significantly impacting sectors like healthcare, retail, and finance.
- Choosing BI Tools: Offered a matchmaking guide to find the BI tool that sings in harmony with your business needs.
- Implementation Steps: Provided a roadmap for implementing BI in your organization, making the journey less of a trek and more of a scenic drive.
- Case Studies: Brought in the real-world applications of BI, proving that it's not all talk and walks the walk.
- Challenges & Solutions: Addressed the hurdles you might face and how to overcome them with finesse.
- Future Trends: Gave a sneak peek into what's coming next in the world of BI, and let's just say the future looks bright—or at least, data-driven.
- FAQs & Resources: Wrapped up with quick answers to your burning questions and a treasure chest of resources to dive deeper into the world of BI.
FAQ

Get In Touch
