Cloud Deployment Models: Enterprise Implementation Guide 2025
Harash Jindal
May 12, 2025
Did you know global cloud spending will hit a whopping $723 billion in 2025? Organizations worldwide use the cloud to simplify their operations and stay ahead of competitors. Gone are the days when only enterprises leveraged the benefits of cloud computing. Today, even SMBs aim for operational agility and provide tailored solutions with cloud functionalities. Once a luxury, the cloud has become necessary, and it will only increase manifold with AI and ML in the picture.
But have you ever wondered how organizations achieve so much with the cloud? Well, it’s the courtesy of cloud deployment models. While some offer excellent scalability and cost efficiency, some let you exercise extensive control over your cloud operations. This piece will explore them and help you make the best of the cloud. Let’s go!
What Are Cloud Deployment Models?
Cloud deployment models describe the multiple ways cloud services are available to users. But what makes them different? Cost, control levels, security, and ownership make these models suitable for diverse business needs. You must understand these models in depth to better fulfill your requirements. If you are on a budget and still wish to jump on the cloud train, then the public cloud would be an ideal choice; however, if you have strict privacy needs, a public cloud becomes a no-brainer. There are other models to explore; let’s have a look at them so that you can decide better.
Types of Cloud Deployment Models
Let’s understand the various types of cloud deployment models.
Public Cloud

Did you know that Netflix uses the public cloud to stream content to its users globally? Such is the public cloud’s prowess, which is why it is a favorite of business owners. Your cloud providers handle infrastructure management for you, saving you the hassle. Wait, there is more to it! These models are the most cost-effective and offer superlative scaling functionalities.
You only need to enjoy the pay-as-you-go models and have a good internet connection! However, there are a few cons, too. You have limited control over resources, and security concerns must be addressed.
Private Cloud

Tech giants like JP Morgan Chase depend on private cloud to safeguard their sensitive financial data from cybercriminals while maintaining operational efficiency. These cloud environments are dedicated to a single organization. The good part is that you can easily rope in a third-party provider if you don’t have ample resources to host it on-premise. The best thing about this cloud model is access to excellent customization capabilities and top-notch security.
Compliance issues no longer bother you as you stay ahead of them. However, managing it is complex and may burn a hole in your finances. The list doesn’t end here. You will have a tough time managing your scalability needs in this environment. Thus, it is best suited for industries like healthcare, government, or financial services, as they have strict regulatory requirements. Now that you know what a private cloud is, let’s understand its types.
- On-Premises Private Cloud: In this model, the cloud infrastructure is hosted and maintained within the organization’s data centers. You have complete control over the hardware and software, which makes it ideal for strict compliance. However, this model requires upfront investment and ongoing maintenance efforts.
- Managed Private Cloud: These environments are managed by third-party service providers. However, you still have complete control over the data.
- Hosted Private Cloud: This model is similar to the managed private cloud model but is hosted in an off-site data center.
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): These clouds operate within a public cloud but offer an isolated environment for a single organization. Thus, you can leverage the benefits of both with ease.
Hybrid Cloud

Let’s reveal a fact. The hybrid cloud market is expected to reach $145 billion by 2026. Yes, you read that right! The enhanced need for agility and cost savings drives these numbers. But what makes this cloud environment an excellent choice for businesses? A hybrid cloud is the perfect blend of private and public clouds. You can quickly scale using a public cloud while keeping your data secure with the public cloud!
Well-known names like BMW use this strategy to manage their operation and store sensitive information seamlessly. And the influence doesn’t cease here! Coca-Cola’s adoption of hybrid cloud strategies helped them reduce their IT costs by huge margins. However, if you have a variety of complex integration and management, this cloud model is unsuitable. Data transfer delays and higher operational costs can further add to the misery.
Community Cloud

This cloud model is unique. It is shared by organizations that have similar goals, compliance needs, and security requirements. But who manages them? Well, it is handled by one of the organizations or a third party. You can collaborate with other companies and create personalized solutions with ease. The benefits don’t end here! You can share costs and boost compliance with industry standards quickly. However, there is another side to the story. The scope for scalability is limited, and conflicts between organizations can exist.
Public Cloud Vs. Private Cloud Vs. Hybrid Cloud Vs. Community Cloud
Understanding the differences between cloud deployment models will help you do justice to your operational requirements.
| Aspect | Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud | Community Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ownership | They are owned and managed by the cloud service provider. | Mainly owned by the organization or by a third party. | Combination of both public and private ownership. | Shared ownership among community members or organizations. |
| Cost | It is the best model when it comes to cost efficiency. | High initial costs coupled with ongoing maintenance expenses. | The costs are affordable, and keeping non-critical operations in the public cloud is suggested. | The cost is shared among community members, which makes it affordable for participants. |
| Scalability | It is highly scalable as resources can be added/removed on demand. | The scope is limited by on-premise infrastructure. | Excellent scalability is possible with the public cloud. | The scalability is moderate and depends on the community’s contribution. |
| Control | There is limited control over infrastructure and resources. | You get complete control over infrastructure and resources. | Partial control abilities due to the public cloud. | Shared control among the community |
Further Reading
Deployment Configurations For Cloud Deployment Models
Let’s look at some sample deployment configurations for the different cloud models.
Public Cloud
Here is a deployment configuration example of a mobile app hosted on Amazon Web Services (AWS)
| Public Cloud Configuration | |
|---|---|
| Providers | AWS |
| Resources | Virtual Machines (EC2), Storage (S3), Databases (RDS) |
| Network | Internet-based access |
| Security | Provider-managed firewalls, encryption, and access control |
| Use- Case | Provider-managed firewalls, encryption, and access control |
Private Cloud
Let’s see a deployment configuration example of the bank that decides to run its private cloud.
| Private Cloud Configuration | |
|---|---|
| Providers | VMware, OpenStack, Microsoft Private Cloud |
| Resources | On-premise or dedicated cloud servers |
| Network | Private network (LAN/VPN) |
| Security | High-level access control, firewalls, encryption |
| Use- Case | Banking, Government Agencies, Large Enterprises |
Hybrid Cloud
Here is how a retail company uses a private cloud to run daily operations, but AWS handles high-traffic during a peak season sale.
| Hybrid Cloud Configuration | |
|---|---|
| Providers | AWS (Public) + On-premises VMware (Private) |
| Resources | Mix of on-premise servers and cloud services |
| Network | VPN or dedicated connection like AWS Direct Connect |
| Security | Controlled data transfer, identity management |
| Use- Case | Disaster recovery, cloud bursting (scaling workloads dynamically) |
Community Cloud
Here is how industry-specific providers share servers among organizations with similar requirements.
| Community Cloud Configuration | |
|---|---|
| Providers | Government or industry-specific cloud providers |
| Resources | Shared servers among organizations with similar requirements |
| Network | Secure, industry-specific network |
| Security | Compliance-focused, strict data-sharing policies |
| Use- Case | Research collaborations, healthcare data sharing |
Types of Cloud Services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)
Let’s understand the different types of cloud services.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)

Do you wish to access virtual computing resources over the net with ample flexibility and cost-effective options? Well, IaaS helps you do that and much more. You can control the infrastructure and configure it per your needs. Moreover, you can leverage high scalability and manage fluctuating workloads. However, there are a few disadvantages associated with this cloud service model.
You need strong technical expertise to configure and manage the environments. You are also responsible for maintaining and securing the virtual environment. Such environments best suit web hosting, backups, and disaster recovery.
Examples
- Amazon EC2
- Linode
- Alibaba Cloud Google Compute Engine
- IBM Cloud
- RackSpace
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
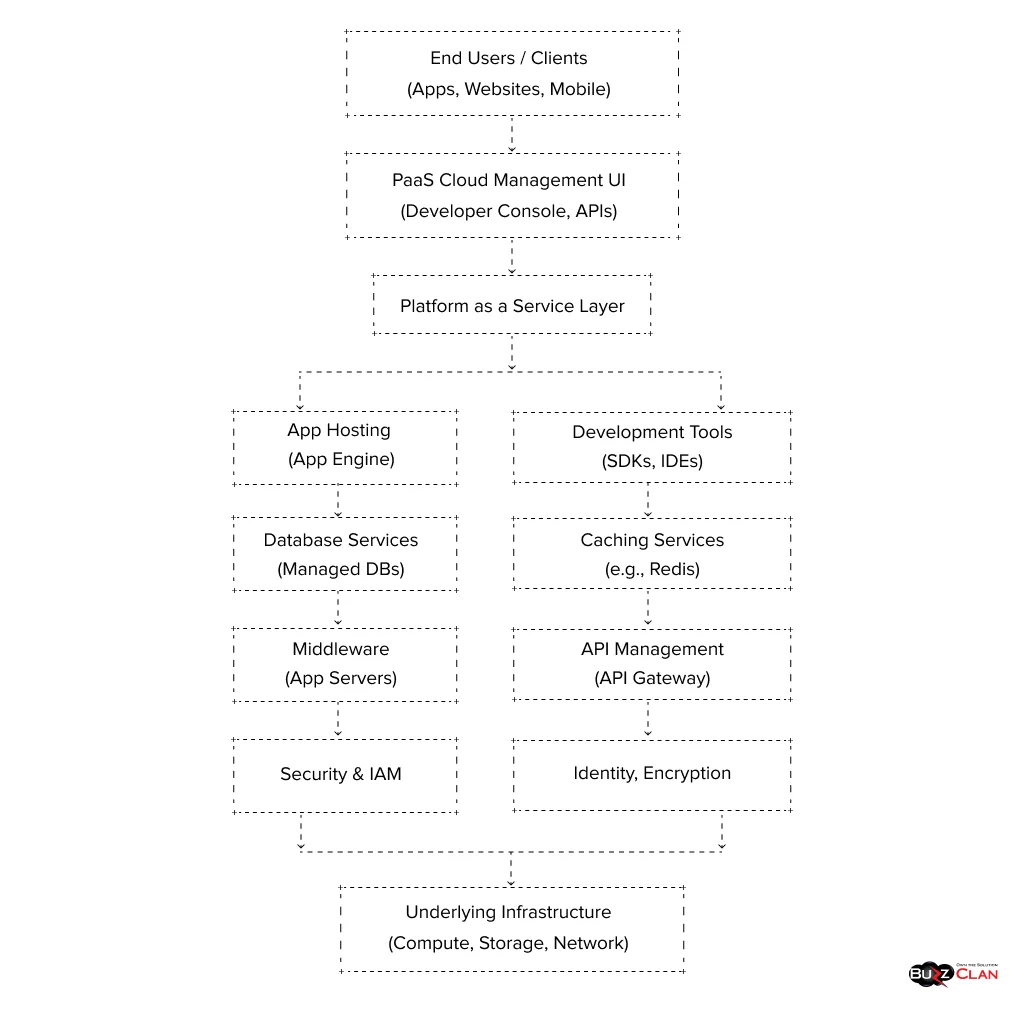
Are your developers tired of managing infrastructure and seldom get time to code innovative applications? Then PaaS is a cure for all your issues! You will get access to tools, development frameworks, and operating systems. This means developers can solely focus on application development. You can even market your applications better as you save time and get access to built-in tools for performance monitoring and scalability.
However, all that glitters is not gold. You get limited control over the infrastructure and are dependent on your PaaS provider, which can lead to vendor lock-in. These environments are best used for building mobile apps, microservices, and API development.
Examples
- Google App Engine
- AWS
- IBM Cloud
- Red Hat OpenShift
- Microsoft Azure App Service
- Heroku
Software as a Service (SaaS)
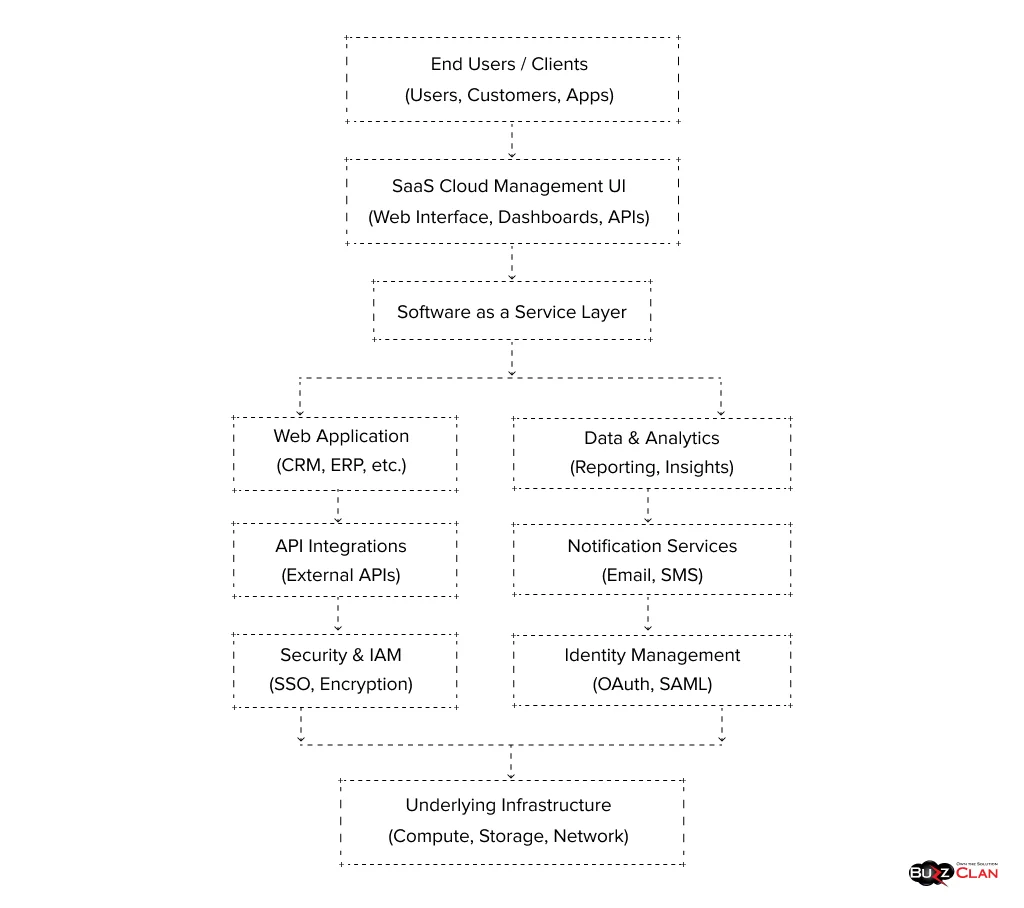
If you demand ready-to-use solutions, consider them fulfilled with SaaS. All you need to do is invest in a good internet connection and a subscription fee to access them through a web browser. The best part is that you don’t need to update these apps manually, as you will always have the latest version.
With no need for software installation or paying upfront hardware and software costs, you can stay well within your organizational budget. However, you must forego extensive customization and address data privacy concerns on the go. Thus, before investing in a solution, do a solid background check on your cloud provider. You can use project management solutions and email services to test SaaS applications.
Examples
- Google Workspace
- Salesforce
- DocuSign
- Dropbox
- Shopify
- Slack
- Microsoft 365
Further Reading
Security Concerns With Cloud Deployment Models
Security issues must be addressed in the different cloud deployment models. Here is a list of concerns and their solutions.
Public Cloud
Since public clouds are operated and owned by third parties, you must deal with multi-tenancy risks, shared infrastructure vulnerabilities, and data sovereignty. Here is how you can protect your cloud environment.
- Encrypt your data at rest and in transit. Since hackers now use advanced evasion techniques, implement strong key management policies.
- Connect with your cloud service providers to understand how they handle infrastructure security. At the same time, you will be responsible for securing workloads, configurations, and applications.
- Are cyber threats creating havoc? Don’t fret! Make sure you have firewalls, Intrusion Detection and prevention Systems (IDPS), and virtual private clouds (VPC) in place. Implementing Zero-Trust Architecture is a must for that extra layer of security.
- Unauthorized access creates more issues than external threats can ever do! Thus, it is a must to leverage multi-factor authentication and role-based access control (RBAC)
- Ensure your business is aligned with GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, or ISO 27001, and thoroughly verify your cloud provider’s compliance certifications.
- Deploying Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions is a no-brainer for real-time anomaly detection and response.
- The last step is to secure your public-facing APIs with OAuth, API gateways, and JWT to prevent attacks and unauthorized access.
Private Cloud
Since a private cloud is dedicated to a single organization, you can customize your cloud operations according to business needs and exercise enhanced control. However, you must have stringent internal security and compliance management policies.
- You must implement privilege policies and biometrics to limit access to sensitive data.
- Make sure your hypervisors have solid configurations to prevent attacks on virtual machines. Segmentation using software-defined networking can help you avoid such attacks.
- Don’t take the security of your data centers lightly. Video surveillance and environmental monitoring are a must to prevent suspicious activities and unauthorized physical access.
- Remember that outdated systems are a common attack point for hackers. Thus, it is essential to update your operating systems and firmware and mitigate vulnerabilities regularly.
- The top encryption algorithms must secure data at rest and in transit. This will help you enforce a strong security posture across the organizational spectrum.
- The first step in mitigating insider threats is conducting thorough background checks and providing cybersecurity training. Behavioral analytics can help you detect threats proactively and prevent system breaches.
- A rock-solid backup and disaster recovery system prevents downtime and maintains customer trust in a cyber attack.
Hybrid Cloud
While hybrid environments help you reap the benefits of private and public clouds, you must deal with specific challenges. Here is how you can deal with them.
- To ensure your data flows securely between environments, make use of virtual private networks (VPNs) and SDNs
- Using cloud security posture management (CSPM) solutions, ensure that uniform security controls have been applied across all cloud environments.
- To ensure robust security, centralized IAM and Single Sign-On (SSO) policies must be implemented across cloud and on-premise environments.
- Ensure all regulatory requirements are fulfilled across all cloud platforms with real-time audit logging and security compliance automation.
Community Cloud Security
Let’s look at how you can deal with security issues that come with community cloud.
- Implementing identity federation mechanisms to ensure secure authentication measures across multiple organizations.
- Ensure you work with other organizations with clear policies for data ownership, incident response, and security responsibilities.
- Make sure all organizations use threat intelligence platforms to enhance collective defense.
- Align with industry-specific regulations to avoid compliance-related fines and penalties.
- Have a community-wide disaster recovery plan with clearly defined roles and responsibilities.
Further Reading
Regulatory Compliance Framework For Cloud Deployment Models
Here is how you can ensure compliance in different cloud environments.
Public Cloud
Since infrastructure is shared among multiple tenants, you must ensure only the authorized personnel have access. While the top cloud providers are compliant, the ultimate onus of guaranteeing compliance in a public cloud environment lies on you. If you are new to the cloud, roping in consultants to train your team will significantly help. You will also need to be thorough with the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM) and NIST 800-53 as they will guide you in managing risks and security controls in public cloud environments.
Private Cloud
While private clouds offer more control over infrastructure, guaranteeing compliance in these environments can become challenging. You must implement robust encryption mechanisms and ensure continuous monitoring is done. And your role doesn’t end here. You will also need to ensure that your business fulfills the guidelines of the top cybersecurity frameworks. With careful analysis and expert support, you will be able to manage compliance needs with ease.
Hybrid Cloud
Since data moves frequently between on-premise and public cloud environments, you must ensure the data is classified appropriately, encrypted, and can be accessed selectively. If you are not using Zero Trust Architectures (ZTA), it is time to start doing it, as it will help you enforce consistent compliance policies across hybrid deployments. Also, ensure you are well-versed with GDPR’s Article 32 on processing security and ISO 27701 to maintain a unified compliance posture across cloud and on-premise systems.
Multi Cloud
Managing compliance across multiple cloud service providers can be tricky, as you must manage various security controls and take care of regulatory considerations. Automated compliance tools can help you to an extent. However, you must be adept with cloud security frameworks to ensure nothing slips through the cracks.
Migration Strategy and Best Practices
Migrating to the cloud requires a structured approach. Thus, you need a robust strategy based on your workload requirements. Let’s have a look at the techniques used in different cloud environments.
- Public Cloud Migration: Before moving your workloads to a public cloud, you must assess your existing applications to ensure compatibility. Automated migration tools can streamline data and application transfers. Identity access management (IAM) can help mitigate security risks and ensure compliance with data residency laws, making the process seamless.
- Private Cloud Migration: Security hardening and virtualization are necessary for private cloud migration. Implement it in phases, starting with non-critical workloads before moving to core applications. Security measures such as endpoint protection and SIEM (Information and Event Management) must be enforced to meet compliance requirements.
- Hybrid Cloud Migration: To migrate to a hybrid cloud setup, the first step is to classify your data and determine which data stays on-premise and moves to the cloud. VPNs and cloud gateways are your trusted tools to help you integrate on-prem and cloud workloads. To gain that extra edge, make sure you are using a microservices architecture. Not only will they help you optimize your performance, but when combined with continuous monitoring, they will also help you maintain a consistent security stance.
- Multi-Cloud Migration: A multi-cloud migration approach involves deploying applications across multiple cloud providers to prevent vendor lock-in and optimize performance. You must use infrastructure-as-code (IaC) tools like Terraform to standardize deployments. Multi-cloud networking solutions can improve workload interoperability and ensure top-notch scalability and security across cloud environments.
Best Practices for Cloud Migration
Here are some techniques that will help you ease out the whole process:
- Ensure you assess your cloud infrastructure and workloads beforehand to eliminate bottlenecks.
- Strategic implementation of ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes is necessary for seamless real-time integration. To prevent theft, you must also ensure your data is encrypted well during migration.
- Adopting a shared responsibility model will help you easily adhere to compliance requirements.
- Use Kubernetes, Docker, and serverless computing to boost performance and reduce costs. FinOps practices will further help you keep costs in check.
- You cannot initiate the migration process and consider your job done. Make sure you monitor performance and stay updated in real-time.
Edge Computing Integration With Cloud Deployment Models
Edge computing helps you boost the prowess of cloud deployment models by processing the data closer to the source. This way, latency is reduced, and you can also look forward to optimizing bandwidth usage and improving real-time processing. Let us have a look at how edge computing integration aids cloud deployment.
| Metric | Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud | Multi Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latency (ms) | 20–50 ms (Can vary per region) | 5–15 ms (Low due to local control) | 10–30 ms (Optimized for locality) | 15–40 ms (Depends on inter-cloud communication) |
| Data Transfer Cost ($/GB) | The data transfer cost is high as egress fees apply. | The cost is low as the transfers are made on-premises. | The costs are dependent on data routing. | The costs will vary as multiple providers offer different pricing models. |
| Compute Efficiency | The efficiency is high, and operations are managed centrally. | A dedicated hardware makes computing efficiency higher than that of public cloud environments. | The efficiency is high as the workload is optimized across environments. | The compute efficiency is moderate as it requires orchestration. |
| Scalability | Scalability is high, and you can quickly achieve global cloud outreach. | Due to hardware limitations, only moderate scalability is achieved. | Scalability is high, with ample flexibility across environments. | Multiple providers offer high scalability. |
| Security | The security is moderate as it is a shared responsibility. | Top-notch security as there is complete control over data. | Security is not a challenge as it is controlled with hybrid policies. | Cross-cloud complexity adds security risks, and the security level is not comparable to that of other cloud environments. |
| Deployment Complexity | The complexity is lower due to cloud-native edge services. | The deployment complexity is high as custom infrastructure is needed. | Complexity is moderate as some integration effort is required. | Multi-cloud synchronization leads to high complexity. |
| Best Use Cases | Best used in IoT and AI environments and content delivery networks. | Ideal for industrial automation, healthcare, and finance domains. | A must-have for smart cities, retail, and enterprise IT environments. | Suited for disaster recovery and multi-region data replication. |
Multi-Cloud Strategy- Implementation and Management Challenges
You must overcome a few implementation and management challenges when dealing with multi-cloud environments.
Implementation Challenges
Here is a list of implementation challenges you need to address.
- Integration Complexity: You may work with different cloud providers, and they have their unique architectures. However, your existing systems don’t need to be compatible with them. You must use the best quality middleware and interoperability strategies to overcome this. This will help you smoothly transfer data across cloud environments and make the best of multi-clouds.
- Security & Compliance Needs: Each cloud provider has security standards and compliance requirements. However, keeping up with them and maintaining security across multiple environments can be challenging. Luckily, you need not worry if you work with certified cloud providers.
- Optimizing Costs: Not all cloud providers will fit your budget, making tracking and optimizing costs difficult. Moreover, unused or underutilized resources can add to unexpected expenses. If you have been working with a cloud provider for a long time, you must also be careful about vendor lock-in. A possible solution is to use cost management tools and closely monitor your cloud usage.
- Ensuring The Right Skillset: Dealing with multi-cloud environments requires the expertise of skilled professionals who understand multiple cloud platforms. However, handling them and training multi-cloud experts can be expensive and time-consuming. For the same, you will need to implement the drive in phases. You must also talk with multiple cloud providers and learn about their discounts and packages.
Management Challenges
Here is a list of management challenges you need to address.
- Managing Workloads: You need to understand monitoring tools to keep an eye on what is happening across multiple cloud platforms.
- Automated Deployments: You need robust DevOps and Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) tools to automate deployments across multiple cloud platforms. The first thing is to have the best tools, but a different story to maintain a strong synchronization between these tools. If you fail to do so, you will incur complications.
- Risks with Vendor Lock-In: Some cloud services are proprietary and may not easily migrate to another provider. You must design workloads that use containers, open standards, and microservices. As a standard practice, work only with providers who offer ample flexibility.
- Managing Backups and Recoveries: Managing backup policies, failover strategies, and disaster recovery means added complexity. If you are inconsistent with these processes, you will have issues ensuring business continuity.
Best Practices for Overcoming Multi-Cloud Challenges
You need to follow some practices to overcome multi-cloud management and implementation challenges.
- Take advantage of cloud management platforms to streamline your operations. VMware Aria and Morpheus are some good examples.
- Make Kubernetes part of your multi-cloud strategy to ensure robust workload portability. Not all employees need to access sensitive data, so strengthening your security policies by implementing identity access management (IAM) is essential.
- To avoid overshooting your budget, use cloud cost management tools and FinOps principles to optimize costs proactively.
- Lastly, use Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) tools like Terraform to standardize your deployments.
Cost Optimization Strategies
While all cloud deployment models offer flexibility and scalability at varying levels, you must check costs. Here are some techniques for optimizing your cloud spending.
Rightsize Your Resources
Half your job is done if you are rightsizing your resources! You must select the right storage type and network configurations and choose the right instance type. Often, organizations overprovision resources, which leads to wastage. Luckily, with auto-scaling techniques and load-balancing features, you can ensure only the necessary resources are used during peak times and released during regular business hours. You must also check the multiple pricing models with your cloud providers and use them strategically to reduce costs. While some models will help you leverage attractive discounts, some will let you utilize excess cloud capacity at a fractional cost.
Optimize Storage
Cloud storage is another factor when it comes to cost reduction. You don’t need to use high-performance storage for all workloads. You need to classify your data based on access frequency and retention policies. Check about tiered storage options with your cloud providers and move the infrequently accessed data to cheaper storage classes. The second most important thing to do is deduplicate and compress your data. Also, having cost governance and monitoring tools is essential if operating in a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud environment. They will help you analyze areas where costs can be reduced. Since a business has multiple teams, allocate dedicated budgets to avoid overshooting your expenses. Lastly, cloud-native and FinOps practices can be used, which combine various teams to optimize spending across cloud environments.
Leverage Serverless Computing and Containerization
Another effective way to control costs is through serverless computing and containerization. And why do we say that? Well, serverless architectures will help you eliminate the need for underlying infrastructure, ensuring you only pay for the exact computing time. When it comes to containers, they will help you maximize resource utilization, and this is possible by running multiple lightweight applications on shared infrastructure. To gain that extra edge, you can incorporate Kubernetes by automating workload distribution across available resources.
Negotiate Agreements With Cloud Providers
You must put on your negotiating hat to get the best cloud costs. For enterprises, the scope is much higher as you can customize cloud plans based on your usage patterns. Review your licensing costs to prevent overpaying for unused features if you wish to go further.
Case Studies & Real-World Applications
With different cloud deployment models, let’s look at how tech giants achieve maximum benefits and operational efficiency.
Public Cloud
Netflix, the popular media entertainment company, shifted its entire infrastructure to Amazon Web Services (AWS) in 2008. The change was initiated due to the massive global demand for video streaming. Amazon used elastic computing and load-balancing functionalities to help Netflix handle 200M+ subscribers. Further, AWS Lambda and spot instances were used to reduce compute costs for non-critical workloads. Instead, lower-cost instances were used. Cloud solutions like S3 storage, managed content, and delivered low-latency streaming across borders.
Outcomes
- 40% reduction in infrastructure costs
- 99.99% uptime
- 15% faster content delivery using content delivery networks
Private Cloud
Bank of America was previously dependent on third-party cloud service providers. However, the effort to change this started in 2013. The reason was to maintain data sovereignty and regulatory compliance while maximizing cloud capabilities. For the same, the bank hired cloud experts to host secure banking applications with complete control over the infrastructure. The experts analyzed the systems and conducted risk analysis to enable fraud detection with 99.99% accuracy. They even implemented SDN to reduce network latency by 30% and allow seamless real-time trading techniques.
Outcomes
- Bank of America saved $2 billion in 5 years by reducing its dependency on third-party cloud service providers.
- Due to cloud-optimized workflows, BOA could process loans 25% faster.
- 100% compliance with regulations like GDPR and SOX.
Hybrid Cloud
The aviation giant Boeing shifted its analytics to Microsoft Azure in 2016 and adopted a hybrid cloud approach while keeping sensitive information on-premises. After implementation, they could easily collect 5TB of flight data per aircraft daily for predictive maintenance. The Azure stack helped the hybrid cloud seamlessly bridge on-premise and cloud workloads. All this was possible while keeping their aircraft designs and manufacturing data confidential.
Outcomes
- 30% reduction in maintenance costs
- 40% faster aircraft design simulations, accelerating time-to-market for new models.
- $1.5 billion was saved annually
Multi Cloud
Deciding to work with two rivals, Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services, was a phenomenal decision for Coca-Cola. Since 2016, Coca-Cola has used AWS SAP HANA to manage global inventory & logistics. Wait, there is more to it! They run AI-driven demand forecasting with 99% accuracy and use IoT-enabled vending machines and digital marketing platforms.
Outcomes
- There was a 20% reduction in supply chain inefficiencies, which improved delivery times.
- A 30% reduction in customer engagement was witnessed.
- Leveraging multiple cloud vendors made 10% cost savings in IT operations possible.
Achieve Cloud Supremacy With BuzzClan’s Tailored Solutions
The growing digital landscape demands top-notch security and advanced efficiency at every level of customer interaction. While the cloud helps you achieve that, we take the whole idea on a new spectrum. Maximized operational efficiency and advanced security measures are just the beginning with BuzzClan. Our team of experts understands your needs and develops a detailed roadmap to ease the process and help you get the best benefits. Whether you are a startup or an enterprise, our cloud solutions help you achieve your goals. We specialize in:
- Predictive scaling capabilities
- ROI-focused implementation
- Automated compliance and monitoring
- Reduced cloud spending by up to 40%
- Real-time cost monitoring
- Providing 99% uptime
- Reduced deployment time by up to 60%
- Seamless application modernization
- Cloud-native development expertise
- Industry-specific compliance expertise
Conclusion
As you navigate the web of digital transformation, choosing the right cloud deployment model becomes necessary. Predictions suggest that 85% of enterprises will adopt a cloud-first approach by 2026. Whether you decide to test the waters with public cloud services, achieve excellent data privacy with private clouds, or create a win-win situation with hybrid and multi-cloud models, the sky is the limit regarding cloud adoption. All you need to do is partner with the right cloud provider and train your employees on cloud best practices to create a culture that can help you reap collective benefits.
FAQs

Get In Touch

