What is Generative AI? A Complete Guide to Its Definition, Uses, and Impact
Abhi Garg
Dec 4, 2025
The artificial intelligence revolution has entered a transformative phase. While traditional AI systems have been analyzing data and making predictions for decades, a new breed of AI has emerged that doesn’t just understand information – it creates it. This is generative AI, and it’s fundamentally changing how enterprises operate, innovate, and compete.
Consider this: in just one year, between 2023 and 2024, generative AI adoption doubled to 65% among companies, with early adopters seeing returns of $3.70 for every dollar invested. Yet despite this explosive growth, many organizations still struggle to understand what generative AI truly is, how it differs from traditional AI approaches, and, most critically, how to harness it effectively for business transformation.
At BuzzClan, we see generative AI as a productivity and innovation accelerator for enterprises. It’s not merely a technological upgrade – it’s a fundamental shift in how businesses can approach problem-solving, creativity, and operational efficiency. Our experience implementing generative AI solutions across diverse industries has shown us that success requires more than just adopting the latest model. It demands strategic integration, robust governance, and a clear understanding of the technology’s capabilities and limitations.
This comprehensive guide cuts through the hype to deliver practical insights on generative AI – from its core technologies and real-world applications to implementation strategies and future trends. Whether you’re a C-suite executive evaluating AI investments, a technical leader planning deployment, or a business strategist exploring competitive advantages, this resource provides the knowledge foundation you need.
Introduction to Generative AI
Generative artificial intelligence represents a paradigm shift from AI systems that analyze and classify to those that create and generate. At its core, generative AI is artificial intelligence that responds to a user’s prompt or request with generated original content, such as audio, images, software code, text, or video.
Unlike traditional AI approaches that excel at recognition, prediction, and decision-making based on existing patterns, generative AI synthesizes entirely new content. Think of it as the difference between an AI that can identify whether an image contains a cat versus an AI that can create an original, photorealistic image of a cat that never existed.
The technology emerged from advances in deep learning and neural networks, but the real breakthrough came with the development of sophisticated model architectures capable of learning from massive datasets. The cost of generating a response from a generative AI model has dropped by a factor of 1,000 over the past two years, making what once required supercomputer-scale resources now viable for routine business applications.
What makes this particularly significant for enterprises is the versatility. Twenty-three percent of organizations are now scaling agentic AI systems somewhere in their enterprises, with an additional 39 percent experimenting with AI agents that can plan and execute multi-step workflows autonomously. These systems don’t just generate content – they’re beginning to take action, transforming how work gets done.
The business impact is measurable and compelling. Organizations report that 44% are piloting generative AI programs in 2025, up from 15% in early 2023, with 10% in production. This acceleration signals that generative AI has moved beyond the experimental phase into strategic deployment territory.
How Generative AI Works
To understand generative AI, you need to grasp three fundamental stages that transform raw data into novel outputs: training, customization, and generation. Each stage plays a critical role in determining what the system can create and how well it performs.
The Foundation: Training Large-Scale Models
Most generative AI models start with a foundation model, a type of deep learning model that learns to generate outputs that are statistically probable when prompted. During training, these models ingest vast quantities of data – millions of images, billions of words, or countless hours of audio – learning the underlying patterns, relationships, and structures.
The training process doesn’t involve memorization. Instead, the model builds a mathematical representation of how the elements in the data relate to one another. For language models, this means understanding grammar, context, semantic relationships, and even nuances like tone and style. For image models, it means learning compositions, textures, spatial relationships, and visual concepts.
These models use neural networks, a way of processing information that mimics the way biological neural systems work, just like the connections in our brains. Over millions of training iterations, neural networks adjust their internal parameters until they can reliably predict what comes next or what logically fits within a given context.
Strengthening Your Security Posture
After pre-training on general data, generative AI models are typically customized for specific tasks or domains. This fine-tuning process involves training on more targeted datasets relevant to particular use cases – customer service conversations for chatbots, legal documents for contract generation, or medical images for diagnostic applications.
Fine-tuning allows organizations to adapt powerful foundation models to their specific needs without the astronomical costs of training from scratch. A customer service chatbot, for instance, can be fine-tuned on a company’s historical support tickets, learning industry-specific terminology, common issues, and appropriate response patterns.
Modern approaches include techniques like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which combines search with generation to ground outputs in real data, helping reduce hallucinations – those instances when AI confidently generates plausible-sounding but incorrect information.
Generation: From Prompt to Output
The generation phase is where users interact with the model, providing prompts or inputs that trigger the creation of new content. The model processes the prompt through its learned representations, using sophisticated probability calculations to determine the most appropriate output given the input and its training.
For text generation, this happens token by token – the model predicts the most likely next word, then uses that word as part of the context to predict the following word, building sentences and paragraphs iteratively. For images, modern diffusion models work by gradually transforming noise into structured images from text descriptions, refining details at multiple steps.
The quality of outputs depends on several factors: the richness of the training data, the size and architecture of the model, the specificity and clarity of prompts, and the fine-tuning applied for particular domains. This is why prompt engineering – the art and science of crafting effective inputs – has become a critical skill in AI deployment.
Key Features and Capabilities
Generative AI systems possess several defining characteristics that distinguish them from traditional AI approaches and determine their utility for enterprise applications.
Content Creation Across Multiple Modalities
Modern generative AI isn’t limited to a single type of output. Leading systems can now create:
- Text Generation: From simple completions to complex long-form content, including articles, reports, emails, code, and conversational responses. 51% of marketers are using or experimenting with generative AI for content creation, with 76% using it for copywriting.
- Image Synthesis: Creating original images from text descriptions, modifying existing images, generating variations, and even producing photorealistic renders of objects or scenes that don’t exist.
- Code Development: Translating natural language descriptions into functional code, completing code snippets, debugging, and even generating entire applications from specifications.
- Audio and Video: Synthesizing realistic speech, creating music, generating video content, and producing multimedia presentations.
Contextual Understanding
What separates modern generative AI from earlier attempts is sophisticated contextual awareness. These systems don’t just predict the next word based on the previous word – they understand the broader context of the entire conversation, document, or task. This enables:
- Maintaining consistency across long documents
- Understanding nuanced instructions with multiple steps
- Adapting tone and style to match requirements
- Drawing connections between disparate pieces of information
Adaptive Learning and Personalization
While the base models are pre-trained, generative AI systems can adapt to specific contexts through fine-tuning, prompt engineering, and in-context learning. This allows organizations to:
- Customize outputs to match brand voice and guidelines
- Incorporate domain-specific knowledge and terminology
- Learn from user feedback to improve over time
- Personalize interactions based on user preferences and history
Creative Problem Solving
Most remarkably, generative AI can approach problems creatively, generating novel solutions rather than selecting from pre-defined options. This manifests in:
- Brainstorming multiple approaches to challenges
- Combining concepts in unexpected ways
- Generating variations and alternatives for comparison
- Exploring solution spaces that humans might not consider
These capabilities make generative AI particularly valuable for knowledge work, creative industries, software development, and strategic planning – areas where generating new ideas and content is central to value creation.
Core Technologies Behind Generative AI
The remarkable capabilities of generative AI emerge from several sophisticated technical architectures, each with distinct approaches to learning and generation. Understanding these technologies helps organizations select the right tools for specific applications.
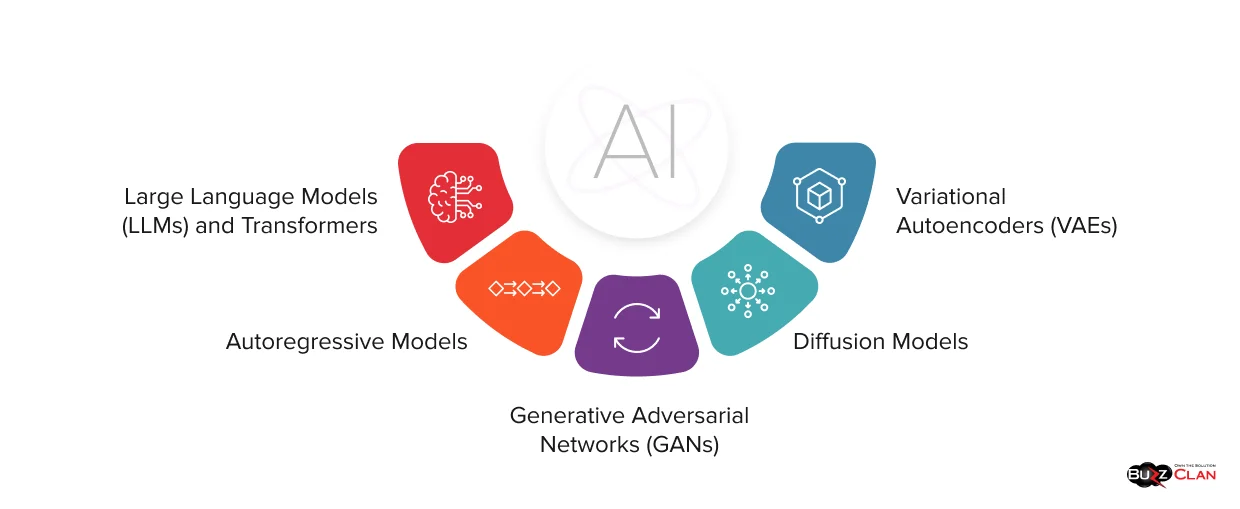
Large Language Models (LLMs) and Transformers
Large language models are a common foundation model for text generation, built on transformer architecture. Introduced in 2017, transformers revolutionized natural language processing through their attention mechanism, which allows models to weigh the importance of different parts of input when generating output.
Transformers employ self-attention, enabling them to focus on various chunks of input data, regardless of their length, and assign importance to each. This parallel processing capability makes them far more efficient than earlier sequential models, such as RNNs.
Leading examples include GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) models from OpenAI, Claude from Anthropic, Gemini from Google, and open-source alternatives like LLaMA and Mistral. The leading models like Claude Sonnet 4, Gemini Flash 2.5, Grok 4, and DeepSeek V3 are built to respond faster, reason more clearly, and run more efficiently.
For enterprises, LLMs enable applications like intelligent document processing, automated customer support, content generation, code development, and complex data analysis – all through natural language interfaces that dramatically lower technical barriers.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
GANs combine two neural networks: a generator, typically a convolutional neural network that generates content from text or image prompts, and a discriminator, typically a deconvolutional neural network that distinguishes authentic from counterfeit images.
This adversarial training creates a competitive dynamic in which the generator continuously improves at generating realistic outputs to fool the discriminator, while the discriminator gets better at spotting fakes. The result is high-quality synthetic content, particularly effective for:
- Photo-realistic image generation
- Style transfer and image-to-image translation
- Data augmentation for training other AI models
- Creating synthetic datasets for privacy-preserving applications
- Video game character and environment generation
While transformers have overtaken GANs in some applications, GANs hold considerable promise for generating media such as realistic images and voices, video, 3D shapes, and drug molecules.
Diffusion Models
Diffusion models have emerged as a powerful alternative for image generation, powering systems like Stable Diffusion, DALL-E, and Midjourney. Diffusion models add and then remove noise to generate high-quality, high-detail images that are nearly realistic of natural scenes.
The process works through iterative refinement – starting with pure noise and gradually removing it according to learned patterns, guided by text prompts or other conditioning inputs. This approach offers several advantages:
- Superior image quality with fine details
- Better controllability over the generation process
- More stable training compared to GANs
- Ability to generate variations and make targeted edits
For business applications, diffusion models enable custom image creation for marketing, product visualization, design prototyping, and synthetic data generation for computer vision systems.
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
VAEs use an encoder-decoder architecture to generate new data, typically for image and video generation, such as generating synthetic faces for privacy protection. VAEs learn to compress data into a latent space representation, then reconstruct and generate new samples from this compressed form.
The key advantage of VAEs lies in their ability to learn smooth, continuous latent spaces, making them particularly useful for:
- Controlled generation with specific attributes
- Interpolation between different examples
- Anomaly detection by identifying outliers
- Data compression and reconstruction
While VAEs typically produce less sharp images than GANs or diffusion models, their mathematical properties make them valuable for applications requiring explicit control over generation parameters.
Autoregressive Models
Autoregressive models generate content sequentially, predicting each element based on previously generated elements. This category includes many LLMs but extends to audio and video generation. The sequential nature makes them excellent for:
- Maintaining consistency in long-form content
- Generating structured outputs like code or formatted documents
- Time-series data generation
- Music composition where temporal relationships matter
Each of these technologies has strengths suited to different applications. Many modern systems combine multiple approaches – for instance, using transformers for text understanding and diffusion models for image generation in text-to-image systems.
Benefits and Applications of Generative AI
The business case for generative AI extends far beyond technological novelty. Organizations implementing these systems report measurable improvements across multiple dimensions, from operational efficiency to innovation velocity.
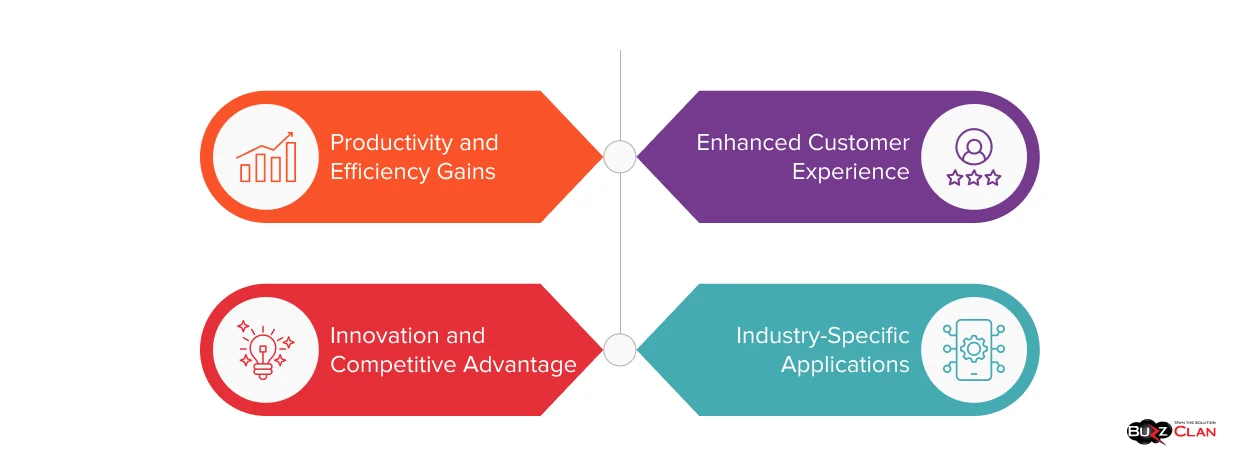
Productivity and Efficiency Gains
Companies achieving returns of $3.70 per $1 invested in generative AI largely do so through productivity enhancements. The technology accelerates tasks that traditionally consumed significant human time:
- Content Creation at Scale: Marketing teams can generate dozens of variations of ad copy, email campaigns, and social media posts in minutes rather than days. Technical writers produce documentation faster. Designers create mockups and variations rapidly for testing.
- Software Development Acceleration: Developers using AI-powered coding assistants report 30-50% faster completion times for routine coding tasks. The technology handles boilerplate code, suggests implementations, catches bugs, and generates test cases.
- Knowledge Work Augmentation: Professionals spend less time on information gathering, initial draft creation, and routine analysis. Generative AI handles the first-pass work, allowing humans to focus on refinement, strategy, and high-judgment tasks.
Enhanced Customer Experience
59% of companies see generative AI transforming customer interactions, with implementations driving measurable improvements:
- 24/7 Intelligent Support: AI-powered chatbots handle routine inquiries instantly, escalating complex issues to humans with full context. This reduces wait times while maintaining service quality.
- Personalization at Scale: Generative AI creates personalized recommendations, content, and experiences for millions of customers individually – something impossible with manual approaches.
- Multilingual Accessibility: Real-time translation and localization make products and services accessible to global audiences without maintaining separate teams for each language.
Innovation and Competitive Advantage
Beyond efficiency, generative AI enables entirely new capabilities:
- Rapid Prototyping: Companies test dozens of product concepts, designs, and strategies quickly and cheaply before committing resources to full development.
- Synthetic Data Generation: Organizations create training data for other AI systems, test edge cases, and simulate scenarios without privacy concerns or data collection costs.
- Research Acceleration: Scientists use generative AI to explore chemical compounds, analyze research papers, generate hypotheses, and identify patterns across vast literature.
Organizations treating AI as a catalyst to transform their organizations and redesign workflows see the most significant impact, rather than just automating existing processes.
Industry-Specific Applications
Different sectors leverage generative AI’s capabilities in unique ways:
- Healthcare: Generating synthetic medical images for training, analyzing patient records for insights, creating personalized treatment plans, and accelerating drug discovery through molecular generation.
- Financial Services: Financial services companies see 4.2x returns on generative AI investments, using it for fraud detection, risk assessment, automated report generation, and personalized financial advice.
- Manufacturing: Optimizing production schedules, generating maintenance predictions, creating design variations, and simulating production scenarios.
- Retail: Personalizing shopping experiences, generating product descriptions, creating virtual try-on experiences, and optimizing inventory through demand forecasting.
- Legal and Professional Services: Drafting contracts, analyzing case law, summarizing documents, and conducting due diligence faster and more thoroughly.
- Education: Creating personalized learning materials, generating practice problems, providing intelligent tutoring, and adapting content to different learning styles.
The breadth of applications explains why 89% of enterprises are actively advancing their generative AI initiatives in 2025, with 92% planning to increase investment by 2027.
Challenges and Limitations of Generative AI
Despite its transformative potential, generative AI presents significant challenges that organizations must navigate thoughtfully. Understanding these limitations is crucial for responsible and effective deployment.
Accuracy and Hallucination Issues
One of the most significant challenges is the tendency for generative AI to produce confident-sounding but incorrect information – a phenomenon known as hallucination. Models can still contradict retrieved content even when using retrieval-augmented generation approaches.
This creates risks in applications where accuracy is critical:
- Medical advice systems generating plausible but dangerous recommendations
- Legal research tools citing non-existent case law
- Financial analysis containing made-up statistics
- Technical documentation with subtle but critical errors
Organizations address this through fact-checking workflows, human review processes, grounding outputs in verified data sources, and confidence-scoring systems. However, 54% of workers worry that generative AI outputs may be inaccurate, highlighting ongoing concerns.
Data Quality and Bias
Generative AI models reflect the biases present in their training data. Since most models train on internet-scale datasets, they can perpetuate:
- Gender, racial, and cultural stereotypes
- Historical biases in hiring, lending, or criminal justice
- Underrepresentation of minority viewpoints
- Western-centric perspectives
59% of employees worry about bias in AI systems. Addressing this requires careful dataset curation, bias testing, diverse evaluation teams, and ongoing monitoring of outputs for problematic patterns.
The challenge intensifies as high-quality, diverse, and ethically usable training data becomes harder to find and more expensive to process in 2025.
Security and Privacy Concerns
73% of employees worry about new security risks from AI systems, and their concerns are well-founded:
- Data Leakage: Models trained on proprietary data might inadvertently expose sensitive information in their outputs.
- Prompt Injection Attacks: Malicious users can craft inputs that manipulate AI systems into revealing data, bypassing safety measures, or performing unintended actions.
- Deepfakes and Misinformation: The same technology that creates applicable content can generate convincing fake images, videos, and audio for deceptive purposes.
- Intellectual Property Questions: Unclear legal frameworks for AI-generated content pose risks to both source data and outputs.
Implementation and Integration Challenges
56% of organizations struggle to integrate AI into existing systems, while 66% find it difficult to establish clear ROI metrics. Common obstacles include:
- Technical Complexity: Deploying generative AI requires specialized infrastructure, expertise, and ongoing maintenance.
- Cost Management: While per-query costs have dropped dramatically, enterprise-scale deployment can still require significant investment in compute resources.
- Change Management: 42% of C-suite executives report that AI adoption is tearing their companies apart, leading to conflicts over resources, workflows, and power dynamics.
- Talent Shortage: 45% of businesses cite talent shortage as a primary obstacle to AI implementation.
Governance and Compliance
The regulatory landscape for AI is evolving rapidly, with different jurisdictions taking varying approaches. Organizations must navigate:
- Data protection regulations like GDPR
- Industry-specific compliance requirements
- Emerging AI-specific regulations
- Ethical guidelines and responsible AI frameworks
Establishing robust governance requires clear policies on acceptable use, output review processes, data handling protocols, and accountability structures.
Generative AI vs. Traditional AI
Understanding the distinction between generative AI and traditional AI approaches is crucial for determining which tools suit specific business needs. While both fall under the AI umbrella, they solve fundamentally different problems.
Core Differences in Purpose and Approach
Generative AI creates novel content, whereas traditional AI forecasts future events and outcomes. This fundamental difference shapes their entire design and application:
Traditional AI (including Predictive AI) excels at:
- Analyzing historical patterns
- Making predictions about future events
- Classifying data into categories
- Identifying anomalies and outliers
- Optimizing decisions based on defined parameters
Generative AI focuses on:
- Creating new content and data
- Synthesizing information from diverse sources
- Generating variations and alternatives
- Producing human-like text, images, or audio
- Solving open-ended creative problems
The technical approaches differ significantly. Traditional AI uses machine learning to perform statistical analysis to anticipate and identify future occurrences, relying on simpler models to gather large amounts of data. Generative AI, in contrast, is trained on massive volumes of raw data and draws from encoded patterns and relationships to understand user requests and create relevant new content.
Data Requirements and Training
The data needs differ substantially:
- Traditional AI: Requires high-quality, labeled data with clear relationships between inputs and outputs. The focus is on the accuracy of historical data, as predictions are only as good as the patterns the data reveals.
- Generative AI: Generative AI models are trained on large datasets containing millions of sample content. Data diversity matters more than perfection – the model learns from exposure to varied examples.
Output Characteristics
The nature of what these systems produce differs fundamentally:
Traditional AI outputs:
- Quantifiable predictions (sales forecasts, risk scores)
- Classifications (spam vs. legitimate email)
- Recommendations from existing options
- Deterministic results from given inputs
Generative AI outputs:
- Original, unique content
- Multiple valid solutions to open-ended problems
- Creative variations and alternatives
- Non-deterministic results (different outputs from the same prompt)
Complementary Roles in Enterprise Applications
Rather than viewing these as competing approaches, forward-thinking organizations strategically combine them. Generative AI can help design product features, while predictive AI can forecast consumer demand or market response for these features.
Consider a retail company:
- Predictive AI forecasts which products will sell well based on historical trends
- Generative AI creates personalized marketing content for those products
- Traditional AI optimizes pricing and inventory levels
- Generative AI generates product descriptions and visual content
This complementary relationship extends across industries. Manufacturing companies use predictive AI for maintenance scheduling and generative AI for design optimization. Financial firms use predictive models for risk assessment and generative AI for report creation and client communication.
The distinction becomes particularly important in cloud infrastructure decisions, where different AI workloads have varying compute, storage, and latency requirements. Organizations need strategies that effectively accommodate both analytical and generative AI workloads.
Generative AI vs. Machine Learning
The relationship between generative AI and machine learning is often misunderstood. Generative AI isn’t separate from machine learning – it’s a specific application of it. Understanding this relationship clarifies capabilities and limitations.
Machine Learning as Foundation
Machine learning underlies all AI types by enabling models to learn from data. It’s the fundamental technique that allows systems to improve performance without explicit programming for every scenario.
Machine learning encompasses three main approaches:
- Supervised Learning: Models learn from labeled examples, mapping inputs to outputs. Used for classification and prediction tasks.
- Unsupervised Learning: Models find patterns in unlabeled data. Used for clustering, dimensionality reduction, and discovering hidden structures.
- Reinforcement Learning: Models learn through trial and error, receiving rewards for desired behaviors. Used for optimization and decision-making in dynamic environments.
Generative AI as a Specialized Application
Generative AI uses machine learning techniques to generate new outputs, while traditional machine learning models focus on tasks such as classification and prediction.
Generative AI typically combines multiple machine learning techniques:
- Deep Learning: Uses neural networks with many layers to learn hierarchical representations of data. Almost all modern generative AI systems use deep learning.
- Transfer Learning: Leverages knowledge from pre-trained models and applies it to new tasks. This is how foundation models work – trained once on massive datasets, then adapted to specific applications.
- Self-Supervised Learning: The model learns by predicting parts of its input data, creating its own training labels. This enables learning from vast amounts of unlabeled data.
- Few-Shot and Zero-Shot Learning: The ability to perform tasks with minimal or no task-specific training examples, using knowledge from pre-training.
Evolution of Techniques
The evolution reflects growing sophistication:
- First Generation Machine Learning (pre-2012): Relatively simple models like decision trees, support vector machines, and basic neural networks. Required extensive feature engineering and struggled with complex patterns.
- Deep Learning Era (2012-2020): Convolutional neural networks revolutionized computer vision. Recurrent networks improved sequence processing. But models were task-specific and required large labeled datasets.
- Foundation Model Era (2020-present): Large-scale pre-training on diverse data creates general-purpose models that can be adapted to many tasks. Generative AI becomes practical for production use.
Practical Implications
For organizations, this hierarchy matters:
- Starting Simple: Not every problem requires generative AI. Many business challenges are better solved with traditional machine learning approaches that are simpler to implement, explain, and maintain.
- Building Progressively: Organizations often begin with predictive analytics using classical machine learning, then expand to deep learning for complex pattern recognition, and finally incorporate generative AI for content creation needs.
- Choosing Appropriately: The decision should be driven by the problem type:
– Need predictions from historical data? Predictive machine learning
– Need to generate new content or ideas? Generative AI
– Need to optimize sequential decisions? Reinforcement learning
The digital transformation journey typically involves strategically implementing various AI and machine learning approaches, tailored to specific business processes and objectives.
Types of Generative AI Models
The generative AI landscape encompasses several distinct model architectures, each optimized for different types of content generation and use cases. Understanding these variations helps organizations select appropriate technologies for specific applications.
Text Generation Models
Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs): These models, including GPT, Claude, Gemini, and LLaMA variants, dominate text generation. ChatGPT remains the dominant tool, with 62.5% of the consumer AI tool market as of late 2024, though enterprise preferences vary by specific requirements such as data privacy, customization options, and integration capabilities.
LLMs excel at:
- Long-form content creation
- Code generation and completion
- Question answering and information synthesis
- Summarization and analysis
- Multilingual translation
Encoder-Decoder Models: Originally designed for tasks like translation, these models are optimized for transforming one sequence into another. They’re particularly effective for structured transformations, such as converting requirements into code, reformatting data, or translating between technical and business language.
Image Generation Models
- Diffusion Models: Currently leading in image quality, diffusion models like Stable Diffusion, DALL-E 3, and Midjourney work by iteratively refining noise into coherent images based on text prompts. They offer exceptional detail, creative flexibility, and controllability.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): While somewhat supplanted by diffusion models in some applications, GANs remain valuable for specific use cases such as face generation, style transfer, and super-resolution. Their real-time generation capabilities make them useful for applications requiring immediate outputs.
- Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs): Introduced in 2020, NeRFs are a technique for generating 3D content from 2D images. They’re increasingly crucial for virtual reality, product visualization, and digital twin applications.
Multimodal Models
The cutting edge involves models that work across multiple types of content:
- Vision-Language Models: Systems like GPT-4V, Gemini, and Claude can process both images and text, enabling applications like image captioning, visual question answering, and document understanding that combine text and graphics.
- Text-to-Video Models: Emerging systems can generate video content from text descriptions, though these remain computationally expensive and less mature than image generation.
- Audio Models: Specialized models for music generation (like MusicLM), speech synthesis (like ElevenLabs), and sound effect creation are enabling new creative possibilities.
Specialized Domain Models
Beyond general-purpose models, specialized variants optimize for specific domains:
- Code Generation Models: Systems like GitHub Copilot, Tabnine, and Replit Ghostwriter are explicitly fine-tuned for software development, understanding programming languages, patterns, and best practices.
- Scientific Models: AlphaFold for protein structure prediction, molecular generation models for drug discovery, and tools for scientific literature analysis represent domain-specific applications.
- Design Models: Tools optimized for architectural design, product visualization, graphic design, and CAD operations leverage generative AI while adhering to domain-specific constraints and requirements.
Generative AI for Infrastructure & Operations
The impact of generative AI extends beyond content creation into the infrastructure and operational backbone of modern enterprises. This convergence is reshaping how organizations approach cloud computing, DevOps practices, and IT operations.
Infrastructure as Code Generation
Generative AI can translate natural language descriptions into functional code, and this capability extends to infrastructure specifications. DevOps teams can now:
- Generate Terraform and CloudFormation Templates: Describe infrastructure requirements in plain language and get deployment-ready infrastructure-as-code configurations.
- Create Kubernetes Manifests: Convert application requirements into properly configured container orchestration specifications.
- Automate Documentation: Generate comprehensive documentation for existing infrastructure by analyzing configurations.
Organizations implementing cloud migration strategies leverage generative AI to accelerate the translation of on-premises architectures into cloud-native designs, significantly reducing the time and expertise required for migration planning.
AIOps and Intelligent Operations
Generative AI is revolutionizing IT operations management:
- Intelligent Incident Response: When alerts trigger, generative AI can:
-Analyze logs and telemetry data to identify root causes
– Generate incident summaries and impact assessments
– Suggest remediation steps based on similar historical incidents
– Draft communication updates for stakeholders
- Predictive Maintenance: Combined with predictive models, generative AI creates actionable maintenance plans, generates work orders, and produces technician guidance for optimal repair procedures.
- Capacity Planning: Rather than just predicting resource needs, generative AI can propose specific infrastructure changes, cost optimizations, and scaling strategies with detailed implementation plans.
Security Operations Enhancement
73% of employees worry about new security risks from AI systems, but generative AI also strengthens security postures:
- Threat Intelligence Synthesis: Analyzing vast amounts of security data, threat reports, and vulnerability databases to generate actionable intelligence summaries.
- Security Policy Generation: Creating comprehensive security policies, compliance documentation, and incident response playbooks tailored to organizational needs.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Generating test cases for security testing, creating exploitation scenarios for red team exercises, and drafting remediation guidance.
Organizations focusing on cybersecurity increasingly use generative AI to augment security teams, though always with human oversight for critical decisions.
Database and Data Pipeline Optimization
In data engineering contexts, generative AI assists with:
- Query Optimization: Analyzing slow queries and generating optimized alternatives with explanations of performance improvements.
- Schema Design: Suggesting database schemas based on application requirements and expected usage patterns.
- ETL Pipeline Generation: Creating data transformation logic from requirements, including handling edge cases and data quality checks.
- Data Quality Rules: Generating comprehensive data validation rules based on sample datasets and business requirements.
Cost Optimization
Infrastructure costs represent a significant concern. Generative AI aids in cloud cost optimization by:
- Analyzing usage patterns and generating rightsizing recommendations
- Creating cost allocation models and chargeback reports
- Drafting FinOps policies and budget alerts
- Generating forecasts with scenario planning for different growth trajectories
The combination of generative AI with traditional analytics tools creates a powerful capability for infrastructure teams. However, the technology works best as an augmentation tool rather than a replacement for human expertise and judgment.
Future Trends in Generative AI
The generative AI landscape is evolving at unprecedented speed, with several clear trends shaping where the technology heads next. Understanding these directions helps organizations plan strategic investments and prepare for the coming changes.
Agentic AI and Autonomous Systems
The shift is now toward autonomy, with 78% of executives agreeing that digital ecosystems will need to be built for AI agents as much as for humans over the next three to five years.
AI Agents Beyond Generation: Rather than just creating content in response to prompts, next-generation systems will:
- Plan and execute multi-step workflows autonomously
- Interact with multiple software systems and APIs
- Make decisions with minimal human intervention
- Coordinate with other AI agents to accomplish complex objectives
Enterprise Automation Evolution: We’re moving from AI that assists with tasks to AI that owns entire processes – from customer onboarding to procurement workflows to financial reporting cycles.
Multimodal Integration
The boundaries between text, image, audio, and video generation are dissolving:
- Unified Foundation Models: Single models that can seamlessly work across all modalities, understanding and generating any type of content as needed for the task.
- Real-World Interaction: AI systems that can perceive the physical world through sensors, understand context, and take appropriate actions – critical for robotics, autonomous vehicles, and smart infrastructure.
- Embodied AI: Systems that don’t just process information but can interact with and manipulate the physical environment.
Enhanced Reasoning and Reliability
New benchmarks like RGB and RAGTruth are being used to track and quantify hallucination failures, marking a shift toward treating hallucination as a measurable engineering problem rather than an acceptable flaw.
- Chain-of-Thought Improvements: Systems that explicitly show their reasoning process, making outputs more explainable and trustworthy.
- Factuality Guarantees: Techniques for grounding outputs in verified sources with citation capabilities, reducing hallucination risks.
- Self-Correction Mechanisms: Models that can evaluate their own outputs, identify errors, and refine responses without human intervention.
Specialized and Efficient Models
The trend isn’t just toward larger models:
- Domain-Specific Optimization: Highly specialized models trained on targeted datasets that outperform general-purpose models for specific industries or tasks.
- Efficiency Improvements: Smaller, more efficient models democratize access, with inference costs dropping 280 times since 2022, enabling deployment on edge devices and reducing environmental impact.
- Mixture of Experts: Architectures that activate only relevant portions of large models for specific queries, dramatically improving efficiency.
Regulatory and Ethical Frameworks
As adoption accelerates, governance structures mature:
- AI Regulations: Governments worldwide are implementing AI-specific regulations addressing transparency, accountability, bias, and safety requirements.
- Industry Standards: Sector-specific guidelines for responsible AI use in healthcare, finance, education, and other regulated industries.
- Transparency Requirements: Expectations for organizations to disclose AI use, explain decisions, and provide human appeal mechanisms.
- Copyright and Attribution: Evolving legal frameworks around AI training data, generated content ownership, and attribution requirements.
Integration with Traditional Enterprise Systems
The future involves seamless blending of generative AI into existing technology stacks:
- ERP and CRM Integration: Generative AI is becoming a native capability within enterprise software, not a separate tool.
- No-Code Interfaces: Business users building custom AI applications without programming through natural language specifications.
- Automated Workflow Enhancement: AI automatically identifies process improvement opportunities and implements changes with approval.
Organizations should monitor these trends while maintaining pragmatic focus on current capabilities and proven use cases. The most successful implementations balance innovation with stability, ensuring new capabilities integrate smoothly with existing operations.
Generative AI for Enterprise Digital Transformation
Digital transformation isn’t just about adopting new technology – it’s about fundamentally rethinking how organizations create value, serve customers, and operate efficiently. Generative AI accelerates this transformation across multiple dimensions.
Reimagining Business Processes
Traditional automation excels at structured, repetitive tasks. Generative AI extends automation into knowledge work:
- Document-Centric Workflows: Organizations handling high volumes of documents – contracts, proposals, reports, analysis – can now automate creation, review, and extraction at unprecedented scale.
- Communication Acceleration: Customer service, internal support, and cross-functional collaboration benefit from AI-assisted communication that maintains quality while dramatically increasing speed.
- Strategic Analysis: Instead of humans spending days gathering and analyzing information for decisions, generative AI can synthesize inputs from dozens of sources, identify patterns, and draft initial recommendations in minutes.
Workforce Augmentation, Not Replacement
Boston Consulting Group found that successful AI transformations allocate 70% of their efforts to upskilling people, updating processes, and evolving culture.
- Amplifying Expertise: Subject matter experts can accomplish more by delegating routine aspects of their work while focusing on high-value judgment and strategy.
- Democratizing Capabilities: Junior employees access knowledge and assistance that historically required years of experience, flattening learning curves.
- New Role Creation: AI may replace 85 million jobs but create 97 million new ones by 2025, with opportunities in prompt engineering, AI training, AI ethics, and system integration.
Accelerating Innovation Cycles
Generative AI compresses innovation timelines:
- Rapid Prototyping: Testing dozens of product concepts, designs, or strategies quickly and inexpensively before committing significant resources.
- Research Acceleration: Synthesizing insights from vast research literature, generating hypotheses, and identifying patterns humans might miss.
- Competitive Intelligence: Analyzing market trends, competitor activities, and customer feedback at a scale that provides early warning of opportunities and threats.
Customer Experience Transformation
70% of CX leaders plan to integrate generative AI across touchpoints by 2026, fundamentally changing how organizations interact with customers:
- Hyper-Personalization: Every customer interaction is tailored to individual preferences, context, and history across all channels.
- Proactive Support: Anticipating customer needs and addressing them before issues arise.
- Continuous Availability: Intelligent assistance 24/7 across time zones and languages.
Data-Driven Culture Evolution
Generative AI democratizes data access and insight generation:
- Natural Language Analytics: Business users query data and receive insights without SQL knowledge or data science expertise.
- Automated Reporting: Regular business reports generated automatically with narrative explanations of key trends and anomalies.
- Decision Support: Context-aware recommendations that synthesize multiple data sources and business objectives.
Organizations pursuing comprehensive digital transformation must view generative AI not as a standalone initiative but as a capability that enhances and accelerates broader transformation efforts.
Case Studies: Companies Using Generative AI Successfully
Real-world implementations demonstrate how organizations across industries capture value from generative AI. These examples illustrate both the potential and the practical considerations of deployment.
Financial Services: Transforming Customer Advisory
A major wealth management firm implemented generative AI to enhance financial advisor productivity and client experience. The system analyzes client portfolios, market conditions, and individual goals to generate personalized investment recommendations and communication materials.
Results:
- 40% reduction in time advisors spend on routine research and documentation
- 3x increase in clients reviewed per advisor per week
- Improved client satisfaction through more frequent, personalized communication
- Maintained compliance through automated review of AI-generated content
Key Success Factors:
- Extensive fine-tuning on regulatory-compliant financial content
- Human-in-the-loop review for all client-facing materials
- Integration with existing CRM and portfolio management systems
- Comprehensive advisor training on effective AI collaboration
Healthcare: Accelerating Clinical Documentation
A healthcare network deployed generative AI to assist physicians with clinical documentation, converting physician-patient conversations into structured notes and orders.
Results:
- 2 hours saved per physician per day on documentation
- 30% increase in patient visit capacity without additional hiring
- Reduced physician burnout scores
- Improved billing accuracy through comprehensive documentation
Key Success Factors:
- Domain-specific training on medical terminology and workflows
- Seamless integration with electronic health record (EHR) systems
- Gradual rollout with physician champions
- Robust privacy and security measures exceeding HIPAA requirements
Manufacturing: Optimizing Product Development
An industrial equipment manufacturer uses generative AI throughout its product development lifecycle—from initial design concepts to technical documentation.
Results:
- 50% reduction in time from concept to prototype
- 25% decrease in design iterations through AI-generated alternatives
- Automated generation of technical manuals reduces documentation time by 70%
- Improved cross-functional collaboration through natural language requirements translation
Key Success Factors:
- Integration with existing CAD and PLM systems
- Training on the company’s historical designs and specifications
- Validation processes ensuring generated designs meet safety and performance requirements
- Change management addressing engineer’s concerns about AI impact
Retail: Personalizing Customer Experience
A major e-commerce company implemented generative AI for product descriptions, marketing content, and personalized recommendations.
Results:
- Generated unique product descriptions for 2 million SKUs in multiple languages
- 18% increase in conversion rates through personalized product recommendations
- 60% reduction in time to launch marketing campaigns
- Improved SEO performance through AI-optimized content
Key Success Factors:
- A/B testing to validate AI-generated content performance
- Brand guidelines enforcement through prompt engineering
- Human review for high-visibility campaigns
- Continuous learning from customer interaction data
Professional Services: Enhancing Consulting Delivery
A global consulting firm uses generative AI to accelerate the creation of client deliverables, from initial proposals to final reports.
Results:
- 35% increase in consultant productivity
- Faster proposal turnaround, enabling pursuit of more opportunities
- Improved consistency and quality across global teams
- Enhanced knowledge management through AI-assisted documentation
Key Success Factors:
- Extensive training on the firm’s methodologies and past deliverables
- Quality control processes ensuring partner-level review
- Gradual adoption with early wins building confidence
- Clear guidelines on appropriate vs. inappropriate AI use
These case studies share common success patterns: clear business objectives, thoughtful integration with existing workflows, appropriate human oversight, and substantial investment in change management.
BuzzClan’s Approach to Generative AI
At BuzzClan, our approach to generative AI is grounded in pragmatic enterprise transformation, not technology for its own sake. We’ve developed a comprehensive methodology for helping organizations navigate from initial exploration through scaled deployment, based on real-world implementations across diverse industries and use cases.
Strategy & Roadmap Development
Every successful generative AI initiative starts with strategic clarity. We work with organizations to:
- Identify High-Impact Use Cases: Not every application of generative AI delivers equal value. We assess your processes, pain points, and opportunities to identify where AI can deliver measurable business impact, whether by improving customer experience, accelerating product development, reducing operational costs, or enabling new capabilities.
- Develop Phased Roadmaps: Rather than attempting enterprise-wide transformation simultaneously, we create pragmatic roadmaps that start with manageable pilots, capture quick wins that build organizational confidence, and progressively expand to more complex applications.
- Establish Success Metrics: Roughly 97% of enterprises struggle to demonstrate business value from early generative AI efforts. We define clear, measurable success criteria from the outset, whether productivity gains, cost reductions, revenue increases, or improvements in customer satisfaction.
- Address Organizational Readiness: Technology deployment is the easier part. We assess your data readiness, technical infrastructure, talent capabilities, and change management needs to ensure successful adoption.
Implementation & Integration
Turning strategy into reality requires both technical expertise and operational excellence:
- Architecture Design: We design solutions that integrate seamlessly with your existing technology stack – whether cloud infrastructure, enterprise applications, data platforms, or development tools. Our experience spans AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, enabling us to work with your preferred platforms.
- Model Selection and Customization: We help you navigate the complex landscape of available models to select optimal solutions for your specific requirements. This includes evaluation of commercial vs. open-source options, fine-tuning approaches, and deployment architectures.
- Data Pipeline Development: Generative AI is only as good as the data it accesses. We build robust data pipelines that connect AI systems to your enterprise data while maintaining security, privacy, and governance requirements.
- Production Deployment: Moving from prototype to production requires attention to scalability, reliability, monitoring, and cost optimization. We implement production-grade solutions with appropriate redundancy, failover, and observability.
AI Governance & Compliance
Responsible AI deployment requires comprehensive governance:
- Policy Framework Development: We help establish clear policies covering acceptable use, output review processes, data handling, privacy protection, and ethical guidelines.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks related to bias, accuracy, security, privacy, and regulatory compliance.
- Audit and Monitoring: Implementing systems to track AI usage, detect problems early, and provide transparency into how systems make decisions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring implementations meet industry-specific requirements – whether HIPAA for healthcare, SOC 2 for SaaS, PCI DSS for payments, or emerging AI-specific regulations.
How BuzzClan Enables Enterprise Adoption
Our end-to-end approach addresses the full spectrum of needs:
- Technical Excellence: Deep expertise in AI/ML technologies, cloud platforms, data engineering, and software development – the full technical stack required for successful implementations.
- Industry Knowledge: Understanding of industry-specific requirements, workflows, and constraints that shape how generative AI should be applied.
- Change Management: Recognizing that technology alone doesn’t drive transformation, we support the organizational change required for successful adoption.
- Ongoing Optimization: Generative AI systems improve through use. We provide ongoing support to monitor performance, gather feedback, and continuously optimize systems.
Client Outcomes
Organizations partnering with BuzzClan typically achieve:
- Faster Time to Value: Leveraging proven patterns and frameworks to accelerate from concept to production
- Reduced Implementation Risk: Avoiding common pitfalls through experienced guidance
- Higher ROI: Focusing investments on the highest-impact applications
- Sustainable Solutions: Building systems designed for ongoing operation, not just pilots
Internal Capability Building: Transferring knowledge to develop your team’s AI expertise
Whether you’re taking initial steps with generative AI or scaling existing implementations, BuzzClan provides the expertise, methodology, and support to maximize your success.
Contact our AI specialists to discuss how generative AI can accelerate your digital transformation initiatives.
Conclusion
Generative AI represents more than an incremental advance in technology – it’s a fundamental expansion of what computers can do. For decades, software excelled at processing and analyzing information according to defined rules and patterns. Now, systems can create, imagine, and generate novel solutions to open-ended problems.
The business implications are profound. Industry analysts predict that companies delaying AI adoption risk significant competitive disadvantages, as early adopters establish data advantages and operational efficiencies that compound over time.
Yet the path forward isn’t without challenges. Organizations must navigate technical complexity, data quality concerns, security risks, regulatory uncertainty, and significant organizational change. Success requires more than technology deployment – it demands strategic vision, comprehensive governance, substantial talent development, and cultural evolution.
The winners won’t necessarily be those with the most sophisticated AI systems. They’ll be organizations that thoughtfully integrate generative AI into their workflows, maintaining the right balance between automation and human judgment, efficiency and quality, innovation and risk management.
Several principles guide successful adoption:
- Start with Business Problems, Not Technology: The question isn’t “how can we use generative AI?” but rather “what business challenges can this technology help us solve?”
- Build Incrementally: Begin with contained pilots that deliver measurable value. Learn, refine, and expand progressively rather than attempting transformation overnight.
- Invest in People: Boston Consulting Group found that successful AI transformations allocate 70% of their efforts to upskilling people, updating processes, and evolving culture. Technology is the easier part.
- Establish Strong Governance: Responsible AI use requires clear policies, robust oversight, and mechanisms for addressing problems quickly when they arise.
- Stay Pragmatic: Don’t let perfect be the enemy of good. Early implementations won’t be flawless, but you’ll learn more from real deployment than endless pilots.
The trajectory is clear – the market is projected to reach $356 billion by 2030, with generative AI becoming as foundational to business operations as email and spreadsheets are today. The question isn’t whether your organization will use generative AI, but how quickly and effectively you’ll integrate it into your competitive strategy.
Organizations that move thoughtfully now, learning through careful implementation while building internal expertise and establishing governance frameworks, will be positioned to accelerate as the technology matures. Those waiting for perfect solutions or complete certainty will find themselves increasingly unable to compete with AI-augmented competitors.
FAQs

Get In Touch