What is Staffing?
Nidhi Rani
Jan 3, 2024
Introduction
Welcome to the fascinating staffing world—where talent meets opportunity, and businesses find the human fuel to power their operations. At its core, staffing is the process of recruiting, selecting, and placing individuals into suitable roles within an organization. Whether it’s filling a short-term vacancy or hiring for a permanent executive role, staffing is the linchpin that holds the structure of a business together.
Importance of Staffing in Modern Businesses
In today’s fast-paced business environment, staffing takes center stage for several reasons:
- Talent as a Competitive Advantage: In an era where technology can be replicated and processes can be outsourced, individuals’ unique skills and culture fit to become a competitive edge.
- Operational Efficiency: The right staffing decisions ensure the workforce is utilized to its full potential, increasing productivity and operational efficiency.
- Adaptability and Scalability: Modern businesses face constant changes—market fluctuations, technological advancements, or global challenges. Adequate staffing provides the flexibility to adapt and scale according to these changes.
- Legal and Ethical Compliance: Proper staffing ensures businesses meet legal requirements and ethical norms, reducing the risk of lawsuits and reputational damage.
What is Staffing?
Staffing is the organized process of finding, evaluating, and establishing a working relationship with individuals, known as employees, either temporarily or permanently. While it might sound like a straightforward HR activity, staffing encompasses a range of functions—from job posting and candidate sourcing to interviews, evaluations, and employment contracts. It’s akin to putting together a jigsaw puzzle where each piece, or employee, must fit perfectly to create a complete picture of a successful organization.
The Importance of Effective Staffing
If staffing is the jigsaw puzzle, adequate staffing is the art of solving it in record time and with minimal errors. Effective staffing is indispensable:
Quality Talent Pool: It ensures you have access to a pool of qualified candidates, elevating your workforce’s quality.
- Resource Optimization: Effective staffing aligns the workforce with the organization’s objectives, ensuring optimal utilization of human resources.
- Employee Satisfaction: When employees are well-matched to their roles and the company culture, it increases job satisfaction and, subsequently, productivity.
- Business Growth: With the right team, businesses are better positioned to meet their objectives, be it expansion, diversification, or innovation.
Key Components of Staffing
Staffing is not a one-size-fits-all process; it has multiple components that contribute to its complexity:
Recruitment:
The initial phase of sourcing candidates through various channels such as job portals, social media, and recruitment agencies.
Selection:
Involves screening applications, conducting interviews, and evaluating candidates based on their skills, experience, and fit for the organization.
Placement:
The final step is matching selected candidates to appropriate organizational roles.
Onboarding:
We introduce new hires to the organization’s culture, processes, and policies.
Development and Training:
Ongoing process of enhancing employees’ skills and preparing them for future roles.
Retention:
Strategies employed to keep talented employees engaged and reduce turnover.
History and Evolution
Origins of Staffing Practices
The staffing concept is as old as human civilization, though the term and its modern implications are relatively new. In ancient times, staffing was a matter of survival—assigning roles based on physical abilities or skills, such as hunting, gathering, and building. Fast forward to the Industrial Revolution, and more formalized staffing processes emerge. The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the rise of personnel departments, a precursor to modern HR, focused primarily on hiring, payroll, and basic employee relations.
Evolution Over the Years
As businesses evolved, so did staffing practices. In the 20th century, they introduced concepts like talent management, employee engagement, and organizational culture into the staffing lexicon. Staffing agencies and headhunters came into play, adding another layer of specialization to the process. Technologies such as applicant tracking systems (ATS) and digital job boards revolutionized how candidates were sourced and managed, making the process more efficient but also more complex.
Current Trends in Staffing
Fast forward to the 21st century, and staffing has become an intricate tapestry woven with threads of technology, globalization, and evolving work models. Here are some current trends shaping staffing:
- Remote Work: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work, transforming how companies think about location and staffing. As a result, digital presence has become more important than ever—everything from video call etiquette to having a clear profile picture on internal platforms now plays a role in how employees are perceived and collaborate in virtual environments.
- AI and Automation: Artificial Intelligence is increasingly used in candidate sourcing, screening, and even initial rounds of interviews.
- Gig Economy: The rise of freelance and contract work is changing the landscape of permanent staffing, offering opportunities and challenges.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Modern staffing practices are placing a greater emphasis on creating diverse and inclusive workplaces.
The history of staffing is a fascinating journey from rudimentary role assignments to complex, technology-driven processes. Understanding this evolution is not just an academic exercise; it provides context for why certain practices exist today and offers insights into where staffing is headed.
Types of Staffing Solutions
Staffing is a more cohesive structure. Much like a well-tailored suit, it must be customized to fit an organization’s unique needs. So, let’s break down the types of staffing, each serving a specific purpose in the corporate wardrobe.
Temporary Staffing
Definition : Temporary staffing involves hiring employees for a specified period to fill in for absent employees or meet seasonal demands.
Advantages:
- Flexibility to meet short-term goals
- Reduced administrative and payroll burden
- Quick onboarding and separation processes
Disadvantages:
- Limited engagement and loyalty from temporary staff
- Risk of lower-quality work due to less time spent in training and orientation
- Best for Companies with fluctuating workloads, retail businesses with seasonal demands, or organizations that need specialized skills for short-term projects.
Permanent Staffing
Definition :This involves hiring employees with the intent of long-term employment.
Advantages:
- Builds a stable workforce
- Allows for more profound training and career development
- Increases employee loyalty and engagement
Disadvantages:
- Longer and more complex hiring process
- Increased costs in benefits and severance package.
- Best for Organizations looking for long-term growth and stability, requiring specialized skill sets critical to their operations.
Contractual Staffing
Definition : In contractual staffing, individuals are hired for a specific project or for a fixed duration.
Advantages:
- Expert skills for specific projects
- No long-term commitment or benefits
- Easier compliance with employment laws
Disadvantages:
- This may involve higher hourly rates
- Less control over contractual staff
- Best for Businesses that require specialized skills but not on a long-term basis, such as IT companies, research institutions, and consultancies.
Outsourced Staffing
Definition: Outsourced staffing involves contracting an external organization to manage specific business functions or departments.
Advantages:
- Focus on core business activities
- Reduced labor costs
- Easier scalability
Disadvantages:
- Lower control over company culture and performance
- Risk of confidential information leakage
- Best for Organizations looking to cut costs or manage non-core functions more efficiently, such as customer service, data entry, or human resources.
Importance of Staffing in Business
You don’t build a house without a sturdy foundation and can’t grow a successful business without effective staffing. It’s not just about filling desks; it’s about finding the right minds to fill those office chairs (or virtual workspaces). Here’s why:
Talent Acquisition
Definition: The process of sourcing, attracting, interviewing, hiring, and onboarding the most suitable candidates for open roles within an organization.
Why It’s Crucial:
- Businesses are as good as those running them. Skilled employees contribute directly to product quality, customer satisfaction, and the bottom line.
- The right talent can drive innovation, improve performance, and create a competitive edge.
Best Practices:
- Utilize multi-channel recruiting strategies that include social media, job boards, and referrals.
- Focus on employer branding to attract high-quality candidates.
Strategies for Successful - Talent Acquisition: Utilize multi-channel recruiting strategies that include social media, job boards, and referrals. Focus on employer branding to attract high-quality candidates.
Cost Management
Definition: The strategic alignment of resource expenditure, including staffing, to achieve efficiency and effectiveness.
Why It’s Crucial:
- Staffing is often the largest operational cost for businesses.
- Mismanagement here can be financially disastrous.
- Efficient staffing can result in cost savings by reducing turnover, improving productivity, and negating the need for constant rehiring and retraining.
Best Practices:
- Utilize workforce analytics to understand hiring needs.
- Engage in succession planning to prepare for future vacancies.
Flexibility and Scalability
Definition: The ability to adapt staffing levels to meet the operational demands of the business, either by scaling up or down.
Why It’s Crucial:
- Businesses face market volatility, seasonal demands, and unexpected challenges. The staffing model needs to be flexible enough to adapt.
- Scalability ensures that the staffing model can grow with it as a business grows without compromising operational efficiency.
Best Practices:
- Consider a hybrid staffing model that includes permanent, temporary, and contractual employees.
- Engage in workforce planning to anticipate future staffing needs.
Staffing Challenges
While staffing is fundamental to a business’s success, it’s not without its hiccups. Here’s a look at some common staffing challenges and how to navigate the stormy seas:
Skills Gap
Definition: The difference between the skills businesses need and potential employees possess.
Impact:
- Slows productivity as existing staff might need to be equipped to perform specific tasks.
- It can delay product launches, decrease service quality, and ultimately impact profitability.
Solutions:
- Invest in training programs to upskill current employees.
- Partner with educational institutions to create a pipeline of skilled talent.
Budget Constraints
Definition: Financial limitations that affect an organization’s ability to recruit, hire, and retain employees.
Impact:
- Limits the ability to attract top talent due to non-competitive salaries or benefits.
- This may result in understaffing, affecting morale and increasing staff workload.
Solutions:
- Consider alternative staffing models like freelancers or part-time staff to fill gaps without inflating costs.
- Use internal promotions or lateral moves to fill positions, which can be cost-effective and improve morale.
Rapid Changes in Staffing Needs
Definition: The quick fluctuation in workforce requirements due to market conditions, technological shifts, or other external factors.
Impact:
- Creates a reactive hiring environment where the focus shifts from quality to immediacy.
- It strains HR departments that must be equipped to handle rapid changes.
Solutions:
- Use advanced analytics to predict staffing needs based on various business metrics.
- Establish a talent pool that can be tapped into when urgent hiring needs arise.
Staffing Models
Selecting the suitable staffing model is like choosing the right coffee blend—it has to fit your taste, kick, and budget. Here’s the lowdown on the most common models:
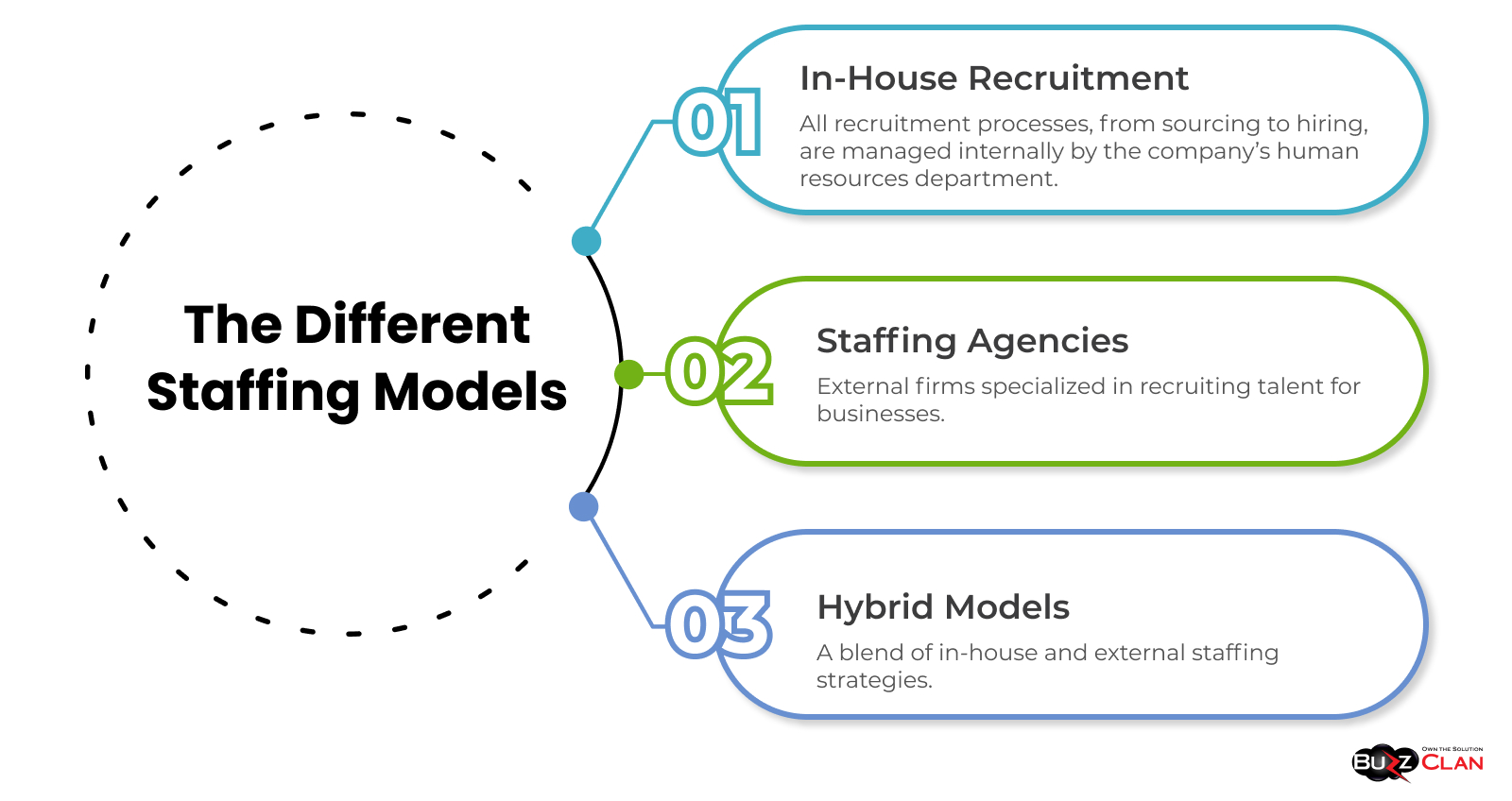
In-House Recruitment
Definition: All recruitment processes, from sourcing to hiring, are managed internally by the company’s human resources department.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Better control over candidate quality, culture fit, and costs.
- Cons: Time-consuming, resource-intensive, and may need more specialized skills for niche roles.
Best for:
- Companies with a stable workforce and the internal resources to manage the recruitment process.
Staffing Agencies
Definition: External firms specialized in recruiting talent for businesses.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Speedy hiring, access to a broader talent pool, and specialized expertise in niche fields.
- Cons: High fees, less control over the process, and potential culture fit issues.
Best for:
- Organizations with fluctuating staffing needs, specialized roles, or limited internal recruiting resources.
Hybrid Models
Definition: A blend of in-house and external staffing strategies.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Combines the control of in-house recruitment with the speed and specialization of staffing agencies.
- Cons: Complex management and potential conflicts between internal and external processes.
Best for:
- Companies that have varied staffing needs that require both volume and specialized roles.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Every coin has two sides, and staffing is no exception. On one side, you’ve got your recruitment strategies; on the other, you have legal and ethical considerations. Ignoring these is like leaving the lid off the blender—it’s bound to create a mess.
Employment Laws
Definition: Laws that regulate the relationship between employers and employees, covering areas such as minimum wage, benefits, and workplace safety.
Importance:
- Failure to comply can result in lawsuits, fines, and reputational damage.
Guidance:
- Stay updated on national and local employment laws.
- Conduct regular compliance audits to ensure you’re on the straight and narrow.
Discrimination and Equality
Definition: Ensuring fair treatment and equal opportunity for all candidates and employees, regardless of gender, race, religion, age, or other protected categories.
Importance:
- Promotes a diverse and inclusive workplace, which has been shown to improve productivity and creativity.
Guidance:
- Implement and enforce a strong anti-discrimination policy.
- Conduct diversity and inclusion training for staff involved in the recruitment process.
Contractual Obligations
Definition: Legal commitments between the employer and the employee, usually outlined in an employment contract.
Importance:
- Protects both parties by clearly defining roles, expectations, and compensation.
Guidance:
- Always have employment contracts reviewed by legal experts.
- Maintain transparency with employees regarding contractual obligations.
Case Studies
Case studies serve as the mirror and microscope of the staffing world. They reflect what’s working and allow you to zoom in to understand why. Let’s explore a trio of scenarios across different organization sizes and types.
Case Study 1: Small Business
Scenario: A small tech startup struggled with high employee turnover.
Action: Implemented an in-house recruitment model focused on culture fit and soft skills.
Outcome:
- 30% reduction in turnover rates within the first year.
- Increase in employee engagement and productivity.
Key Takeaway: Focusing on culture fit can be as crucial as technical skills in reducing turnover and enhancing performance for small businesses.
Case Study 2: Enterprise
Scenario: A multinational corporation faced delays in filling specialized roles.
Action: Outsourced staffing for specialized positions to multiple niche staffing agencies.
Outcome:
- Cut down the time-to-hire by 40% for specialized roles.
- Achieved a higher quality talent pool, leading to successful project completions.
Key Takeaway: For large enterprises with diverse needs, utilizing specialized staffing agencies can streamline the hiring process and enhance the quality of hires.
Case Study 3: Non-Profit Organization
Scenario: A non-profit had many unqualified applicants for mission-critical roles.
Action: Implemented an in-house recruitment process focusing on values alignment alongside skills evaluation.
Outcome:
- 25% increase in applicant quality.
- Better alignment of staff with the organization’s mission and values.
Key Takeaway: In mission-driven organizations, aligning values in the staffing process can significantly improve the quality of applicants and overall mission fulfillment.
Conclusion
Ah, the grand finale! This conclusion would be the standing ovation if staffing were a theatrical masterpiece. You’ve journeyed with us from the prehistoric origins of staffing (no, there were no applicant tracking systems back then) to the contemporary landscape as dynamic as a caffeinated squirrel.
- What is Staffing: Staffing is not just an HR term but a comprehensive process that involves finding, evaluating, and matching people to organizational roles. Think of it as a complex jigsaw puzzle—except each piece has unique skills, quirks, and LinkedIn profile.
- Importance in Business: Staffing is critical to operational efficiency and long-term strategic goals. Talent isn’t just a resource; it’s a competitive edge sharper than a double-edged sword.
- Types of Staffing: Whether it’s temporary, permanent, contractual, or outsourced staffing, each has its place and importance. It’s like choosing between a Swiss Army knife and a sledgehammer—both valid, but for different reasons.
- Challenges: Yes, there are roadblocks like skills gaps, budget constraints, and rapid changes in staffing needs. But as they say, challenges are just opportunities in work clothes.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: This isn’t the Wild West; modern staffing practices come with legal and ethical guidelines. Ignore them; you’re riding into a reputational (potentially legal) sunset.
- Case Studies & FAQs: We’ve given real-world examples and answered your most burning questions. It’s like the extra cheese on a gourmet pizza. You didn’t think you needed it, but you’re glad it’s there.
Additional Resources
We’re glad you’ve made it this far on your journey to mastering the staffing domain. If you’re hungry for more knowledge (and, honestly, who isn’t?), here’s a curated list of credible resources to keep you informed and ahead of the curve.
eBooks
“Who: The A Method for Hiring” by Geoff Smart and Randy Street
- A staple in the staffing industry, this book offers a methodology for hiring the right people for the right roles.
- Reference: Amazon Link
“First Break All the Rules” by Marcus Buckingham and Curt Coffman
- This book provides valuable insights into what the world’s most excellent managers do differently when staffing and managing talent.
- Reference: Amazon Link
Whitepapers
“The Future of Staffing: Trends to Watch” by LinkedIn Talent Solutions
- A comprehensive look at the changing landscape of staffing, from technology trends to the influence of remote work.
- Reference: Usually accessible through LinkedIn Talent Solutions’ website.
Ah, the FAQs—where curiosity meets answers and where we quench your thirst for staffing knowledge one question at a time. Think of this section as the “Bonus Features” on a DVD; you find all the juicy details that didn’t make it into the main show. So, without further ado, let’s unravel the mysteries of staffing!
Harvard Business Review: Articles on Staffing
- A treasure trove of articles dealing with the ins and outs of staffing, written by industry experts.
- Reference: HBR’s Topic Page on Staffing
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
- For the data junkies, this is the go-to source for employment statistics and other labor-related data.
- Reference: BLS Website
Monster Hiring Resource Center
- From how-to guides to legal advice, Monster’s resource center offers many staffing resources.
- Reference: Monster Hiring Resource
FAQs

Get In Touch
Follow Us
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Importance of Staffing in Modern Businesses
- What is Staffing?
- The Importance of Effective Staffing
- Key Components of Staffing
- History and Evolution
- Types of Staffing Solutions
- Importance of Staffing in Business
- Staffing Challenges
- Staffing Models
- Legal and Ethical Considerations
- Case Studies
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources
- FAQs





