The Frontend Breakthrough: From Backend Dev to UI Designer
Sachin Jain
Sep 17, 2025
Vibe Coding Blog Series
For countless backend developers, frontend development represents an intimidating frontier filled with design decisions, browser inconsistencies, and subjective aesthetics. This transformation from comfortable server-side logic to user-facing interfaces often creates a psychological barrier that prevents developers from embracing full-stack capabilities.
My own journey exemplifies this challenge. Years of architecting complex backend systems, optimizing database queries, and building robust APIs had given me confidence in server-side development. Yet the moment I needed to create a user interface, uncertainty crept in. CSS seemed unpredictable, JavaScript behavior felt inconsistent, and achieving visual appeal appeared entirely subjective.
The Frontend Paralysis: Understanding the Barrier
The transition from backend to frontend development involves more than learning new technologies—it requires a fundamental shift in thinking. Backend development focuses on logical structures, data relationships, and systematic problem-solving. Frontend development demands consideration of user psychology, visual hierarchy, and subjective design principles.
This paralysis stems from several cognitive factors:
Analytical vs. Creative Mindset Conflict
Backend developers excel at systematic problem-solving with clear right and wrong answers. Front-end development introduces ambiguity where multiple solutions can be considered correct, creating decision paralysis for analytically minded professionals.
Technology Overwhelm
The frontend ecosystem evolves rapidly with countless frameworks, libraries, and design systems. This abundance of choices contrasts sharply with the more stable, established patterns of backend development.
Design Confidence Gap
Many backend developers lack formal design training, leading to uncertainty about visual hierarchy, color theory, and user experience principles. This knowledge gap creates reluctance to make frontend decisions.
Perfectionism Barrier
Backend developers often pursue elegant, optimized solutions. Frontend development requires iterative refinement and subjective judgment calls that conflict with perfectionist tendencies.
My personal strategy had always been gravitating toward solutions requiring minimal design thinking. Oracle Apex provided a functional UI without demanding a deep understanding of underlying design principles. However, modern application development requires more sophisticated user interfaces that Apex couldn’t deliver.
The Framework Decision: A Strategic AI Collaboration
Approaching the frontend technology stack decision, I avoided asking for simple recommendations. Instead, I engaged in comprehensive architectural discussions that considered project constraints, timeline limitations, and skill development priorities.
The conversation began with contextual framing rather than technology queries:
I need to build a modern frontend for a multi-tenant document management system. My background is Python and Django development, but I have minimal frontend experience. The project timeline is four to six weeks for complete application rebuilding, and I’m working solo.
This approach prompted the AI to consider strategic factors beyond pure technical capabilities:
- Existing Skill Leverage: Recommendations aligned with my Python/Django expertise
- Learning Curve Optimization: Solutions that minimize new concept introduction
- Timeline Constraints: Pragmatic choices for rapid development cycles
- Future Scalability: Architecture decisions that wouldn’t create technical debt
The AI’s response provided strategic reasoning rather than superficial comparisons: Django with Bootstrap is strategically sound for your constraints. You’ll maintain familiarity with the Python ecosystem, leverage Django’s built-in authentication and form handling, while Bootstrap provides professional components that require no design expertise.
This wasn’t just technology selection—it was strategic architectural planning that acknowledged my specific context and limitations.
The Bootstrap vs. React Strategic Analysis
The decision between embracing React’s modern paradigms or staying within Django’s template system represented a critical architectural choice. Rather than defaulting to popular technologies, I explored the strategic implications through collaborative discussions on AI.
The conversation revealed necessary trade-offs:
React Advantages and Complexity
React offers powerful client-side interactivity, modern development patterns, and extensive community resources. However, it introduces significant complexity, including:
- Build System Configuration: Webpack, Babel, and Development Server Setup
- State Management: Component state, props, and potentially Redux complexity
- Learning Curve: JSX syntax, component lifecycle, and React-specific patterns
- Integration Challenges: Connecting React frontend with Django backend APIs
Django Templates with Strategic Enhancement
Django templates provide seamless integration with existing Django applications while offering enhancement opportunities:
- Immediate Productivity: Familiar template syntax and server-side rendering
- Authentication Integration: Built-in CSRF protection and user session management
- Incremental Enhancement: JavaScript can be added progressively without complete rewrites
- Deployment Simplicity: Single-server deployment without separate frontend build processes
The AI guided me toward a pragmatic conclusion: Django templates with targeted JavaScript enhancements offer the optimal balance for your timeline and experience level. React can be introduced later once the foundation is established and you’ve gained frontend confidence.
This decision exemplifies strategic thinking over the adoption of trendy technology. The choice prioritized rapid development and management of the learning curve while maintaining future enhancement possibilities.
The Bootstrap Transformation: From Functional to Professional
The transformation from basic HTML forms to professional user interfaces represents one of the most dramatic improvements in my development experience. Bootstrap’s component library and utility classes provided immediate visual enhancement without requiring deep CSS expertise.
Before: Functional but Unprofessional
<form> <input type="text" name="username"> <input type="password" name="password"> </form>
After: Professional and Responsive
<div class=container>
<div class=row justify-content-center>
<div class=col-md-6 col-lg-4>
<div class=card shadow-sm>
<div class=card-body>
<h3 class=card-title text-center mb-4>Welcome BackUsername/label>
<input type=text class=form-control required>
</div>
<div class=mb-3>
<label class=form-label>Password/label>
<input type=password class=form-control required>
</div>
<button type=submit class=btn btn-primary w-100>Sign In/button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
This transformation demonstrates Bootstrap’s powerful capabilities for rapid UI development.
The enhanced version provides:
- Responsive Grid System: Automatic adaptation to different screen sizes
- Visual Hierarchy: Clear content organization through cards and spacing
- Professional Styling: Modern button styles and form controls
- Accessibility Features: Proper label associations and semantic markup
The improvement occurred through the systematic application of Bootstrap components, rather than custom CSS development, enabling rapid professional results without requiring design expertise.
Multi-Step Registration Flow: UX Design Through AI Collaboration
Complex user interactions require careful UX design to prevent user abandonment and confusion. My multi-step registration flow presented significant design challenges that AI collaboration helped solve systematically.
The registration process involved four distinct phases:
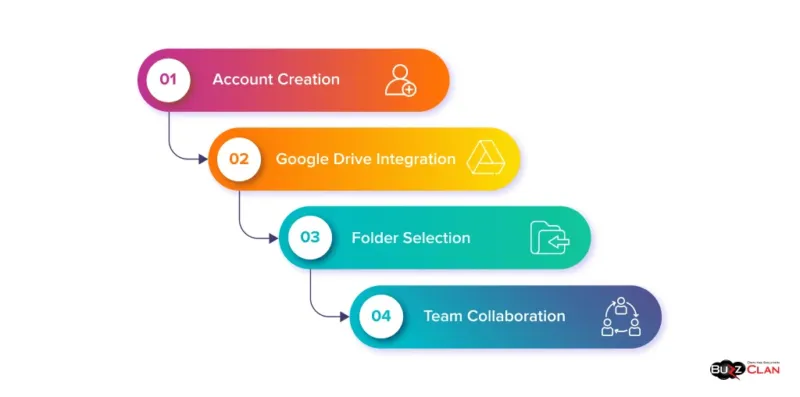
- Account Creation: Basic user information and password setup
- Google Drive Integration: OAuth connection and permissions
- Folder Selection: Choosing or creating document storage locations
- Team Collaboration: Inviting additional users and setting permissions
The improvement occurred through the systematic application of Bootstrap components, rather than custom CSS development, enabling rapid professional results without requiring design expertise.
Complex user interactions require careful UX design to prevent user abandonment and confusion. My multi-step registration flow presented significant design challenges that AI collaboration helped solve systematically.
The registration process involved four distinct phases:

- Account Creation: Basic user information and password setup
- Google Drive Integration: OAuth connection and permissions
- Folder Selection: Choosing or creating document storage locations
- Team Collaboration: Inviting additional users and setting permissions
Each step presented unique UX challenges that required strategic design decisions:
Information Architecture Planning
I need a registration flow that guides users through a complex setup without overwhelming them. How should I structure the multi-step process?
The AI provided comprehensive UX guidance: Break the process into discrete steps using Bootstrap’s progress components and card layouts. Each step should focus on a single objective with clear progress indication and navigation options.
Progress Communication Strategy
Users need constant awareness of their progress through complex flows. The AI suggested implementing a progress bar that shows the current step and remaining stages. Use descriptive step labels rather than numbers, and allow backward navigation to previous steps.
Error Handling and Recovery
Complex flows increase error probability, requiring sophisticated error management: Provide real-time validation feedback at each step. Store intermediate progress so users can return without losing information. Offer clear recovery paths for common errors.
This systematic approach to UX design, facilitated by AI collaboration, produced registration flows that felt intuitive and professional rather than overwhelming and confusing.
Form Enhancement: Real-Time Validation and User Feedback
Form interactions represent critical conversion points where poor UX design directly impacts business outcomes. My previous forms provided minimal feedback and unclear error states, creating user frustration and abandonment.
AI collaboration helped develop sophisticated form enhancement strategies:

Form interactions represent critical conversion points where poor UX design directly impacts business outcomes. My previous forms provided minimal feedback and unclear error states, creating user frustration and abandonment.
AI collaboration helped develop sophisticated form enhancement strategies:
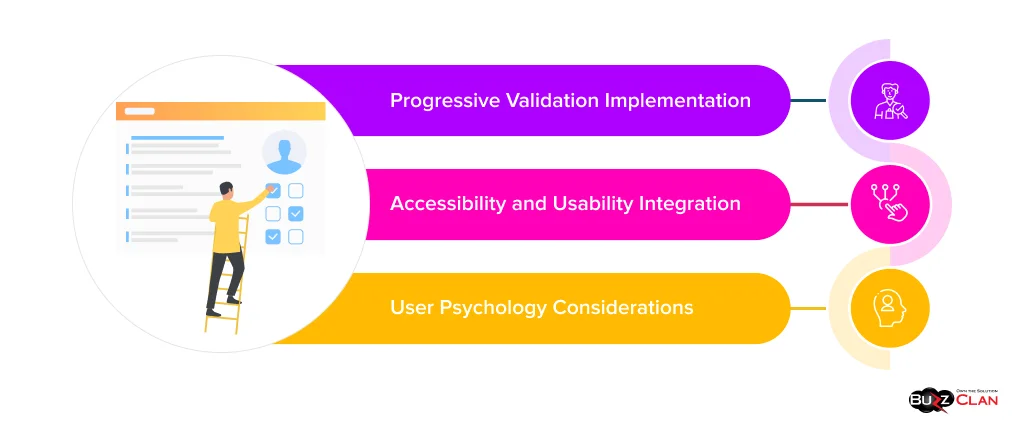
Progressive Validation Implementation
How can I provide immediate feedback on form errors without overwhelming users?
The AI recommended layered validation approaches: Implement Bootstrap’s validation classes for visual feedback. Use green indicators for valid fields and red for errors, accompanied by descriptive helper text. Add inline validation for format checking while preserving server-side validation for security.
Accessibility and Usability Integration
Form accessibility requires careful attention to screen readers, keyboard navigation, and color contrast. The AI provided comprehensive guidance: Ensure proper label associations using ‘for’ attributes. Provide aria-described by relationships for error messages. Use color plus text indicators to avoid relying solely on color for error communication.
User Psychology Considerations
Effective forms consider user mental models and behavior patterns: Position validation messages consistently below fields. Use positive language in error messages that guide users toward solutions rather than emphasizing mistakes. Group related fields visually to reduce cognitive load.
These enhancements transformed forms from functional barriers into smooth, confidence-building user experiences that guided users toward successful completion.
OAuth Integration: Building Trust Through Design
Technical integrations, such as OAuth, present unique UX challenges that extend beyond mere functionality. Users must feel confident about granting permissions to third-party services, requiring careful attention to trust-building design elements.
The Google Drive connection process needed to address user psychology and security concerns:
Trust Building Through Visual Design
How can I ensure the Google Drive connection feels safe and trustworthy?
AI guidance focused on psychological factors: Use a centered card layout with prominent Google branding and official connection language. Include a brief explanation of why the integration is necessary and what data will be accessed. Add visual status indicators showing connection progress.
Permission Transparency
Users require a clear understanding of the permission implications: provide a detailed explanation of the requested permissions before initiating the OAuth flow. Use plain language to explain data usage and storage policies clearly and concisely. Include links to privacy policies and help documentation.
Error Recovery and Support
OAuth flows can fail for various technical reasons requiring clear user guidance: Design clear error messages that explain common OAuth problems and provide specific recovery steps. Include contact information for additional support. Offer alternative connection methods.
This comprehensive approach to OAuth UX design transformed a potentially confusing technical process into a user experience that builds confidence, increasing conversion rates and reducing support requests.
Frontend Fundamentals: Learning Design Principles Through AI
The most valuable aspect of AI-assisted frontend development wasn’t code generation—it was design education. Through systematic questioning and explanation, I developed an understanding of fundamental frontend principles that transformed my approach to creating user interfaces.
Responsive Design Mastery
Rather than memorizing Bootstrap classes, I learned underlying responsive design principles:
- Grid System Understanding: Bootstrap’s grid system utilizes Flexbox to create flexible layouts that adapt to various screen sizes. The col-md-6 class means the element occupies half the container width on medium and larger screens, but full width on smaller screens.
- Breakpoint Strategy: Define content hierarchies that work across all screen sizes. Most important content should be visible on mobile devices, with progressive enhancement for larger screens.
Accessibility Fundamentals
AI collaboration introduced crucial accessibility concepts that improved both user experience and legal compliance:
- Semantic HTML Structure: Use heading tags (h1, h2, etc.) to create a logical content hierarchy. Screen readers rely on semantic structure to navigate content effectively.
- Color and Contrast Considerations: Ensure sufficient color contrast for text readability. Use color, along with additional indicators (icons, text), to convey critical information, as color-blind users may not be able to distinguish color differences.
- Keyboard Navigation Support: Design interfaces that work with keyboard-only navigation. All interactive elements should be reachable and operable without mouse input.
User Experience Psychology
The AI helped me understand user behavior patterns that inform better design decisions:
- Cognitive Load Management: Reduce the amount of information users must process simultaneously. Group related elements, use progressive disclosure, and provide a clear visual hierarchy.
- Mental Model Alignment: Design interfaces that match users’ expectations based on common patterns. Place navigation elements in expected locations and use familiar interaction patterns.
These educational conversations transformed my understanding from tactical code implementation to strategic UX design thinking.
Component Reusability: Systematic Frontend Architecture
As my frontend skills developed, I began thinking in terms of reusable components rather than individual pages. This architectural approach improved consistency, reduced development time, and created more maintainable codebases.
Template Inheritance Strategy
Django’s template inheritance system enables sophisticated component reuse:
< title>Default Title >
This systematic approach to template architecture ensures consistency throughout the entire application, while enabling rapid page development.
Component-Based Thinking
AI collaboration helped me develop component-based thinking patterns similar to modern JavaScript frameworks:
Think of your interface as composed of reusable building blocks. Create templates for common patterns, such as cards, forms, and navigation elements, to streamline workflow and enhance user experience. These components should accept data parameters and render consistently across different contexts.
This approach aligns with modern frontend development best practices while working within Django’s template system.
Integration with Modern Development Workflows
AI-assisted frontend development integrates seamlessly with contemporary development practices, enhancing rather than replacing established workflows.
Version Control Integration
Frontend assets require careful version control management:
- CSS and JavaScript Versioning: Track styling and interaction changes alongside backend modifications
- Asset Pipeline Management: Coordinate static file changes with application deployments
- Design System Evolution: Document component library changes and maintain backward compatibility
Testing Strategy Enhancement
Modern frontend development demands comprehensive testing approaches:
- Visual Regression Testing: Automated screenshot comparison to detect unintended visual changes
- Cross-Browser Compatibility: Systematic testing across different browser environments
- Accessibility Testing: Automated and manual accessibility validation using WCAG standards
- Performance Monitoring: Page load time optimization and rendering performance measurement
Deployment Optimization
Frontend assets require specific deployment considerations:
- Static File Optimization: Image compression, CSS minification, and JavaScript bundling
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): Geographic distribution of static assets for performance
- Cache Management: Strategic browser caching policies for optimal load times
- Progressive Enhancement: Graceful degradation for users with limited browser capabilities
Performance Optimization Through Strategic Design
Frontend performance directly impacts user experience, conversion rates, and search engine rankings. AI collaboration helped develop systematic approaches to performance optimization that balanced user experience with technical efficiency.
Image Optimization Strategy
Images often represent the most significant performance bottlenecks in frontend applications:
- Format Selection: Use modern image formats, such as WebP, for browsers that support them, with JPEG fallbacks for compatibility. SVG icons provide crisp graphics at any scale without bitmap file size penalties.
- Lazy Loading Implementation: Load images only when they appear in the user’s viewport. This reduces initial page load time while maintaining full functionality for users who scroll through content.
- Responsive Image Strategy: Serve appropriately sized images for different screen densities and viewport sizes. A mobile user doesn’t need desktop-sized images that consume unnecessary bandwidth.
CSS and JavaScript Optimization
Strategic code organization improves both development efficiency and runtime performance:
- Critical Path Optimization: Inline critical CSS required for above-the-fold rendering. Load non-critical styles asynchronously to avoid blocking initial page display.
- JavaScript Loading Strategy: Use async and defer attributes strategically. Libraries required for initial interactivity should load synchronously, while enhancement scripts can load asynchronously.
Progressive Enhancement Philosophy
Building applications that work for all users regardless of technical capabilities:
- Core Functionality First: Ensure essential features work without JavaScript. Progressive enhancement adds interactivity for capable browsers while maintaining accessibility for all users.
- Network Resilience: Design interfaces that provide meaningful feedback during slow network conditions. Show loading states and provide offline functionality where appropriate.
Accessibility as Fundamental Design Principle
Accessibility isn’t an afterthought—it’s a fundamental aspect of inclusive design that improves experiences for all users while ensuring legal compliance and broader market reach.
WCAG Compliance Implementation
Following Web Content Accessibility Guidelines creates systematic approaches to inclusive design:
- Perceivable Content: Provide text alternatives for images, captions for videos, and sufficient color contrast for text readability. Information shouldn’t rely solely on color or sound.
- Operable Interface: Ensure all interactive elements work with keyboard navigation. Provide sufficient time for users to complete tasks. Avoid content that flashes or causes seizures.
- Clear and understandable information: Use clear, simple language and consistent navigation patterns. Provide input assistance and error identification for forms.
- Robust Technology: Utilize semantic HTML that is compatible with assistive technologies. Test with screen readers and other accessibility tools to ensure optimal accessibility.
Inclusive Design Benefits
Accessibility improvements benefit all users, not just those with disabilities:
- Mobile Optimization: Keyboard navigation patterns improve mobile touch interfaces
- Performance Enhancement: Semantic HTML reduces page complexity and improves loading speeds
- SEO Improvements: Screen reader-friendly content structure enhances search engine understanding
- Cognitive Load Reduction: Clear visual hierarchy and simple language improve comprehension for everyone
The Confidence Transformation: From Avoidance to Enthusiasm
The most significant outcome of AI-assisted frontend development wasn’t the acquisition of technical skills—it was the psychological transformation from avoiding frontend work to embracing it enthusiastically.
Understanding the Why Behind Design Decisions
Rather than blindly following design patterns, I developed an understanding of underlying principles:
- Visual Hierarchy: How spacing, sizing, and contrast guide user attention
- Information Architecture: Organizing content to match user mental models
- Interaction Design: Creating intuitive interfaces that respond predictably to user actions
- Brand Consistency: Maintaining visual identity across different application sections
Building Design Intuition
Through systematic AI collaboration, I developed an intuitive understanding of effective design patterns:
- Layout Principles: Recognizing when grid systems enhance content organization
- Typography Hierarchy: Using font sizes and weights to create a readable content structure
- Color Psychology: Leveraging color associations to communicate meaning and emotion
- User Flow Optimization: Designing pathways that minimize friction and cognitive load
From Liability to Competitive Advantage
Frontend development transformed from my weakest skill to a significant strength. This change enabled:
- Full-Stack Autonomy: Complete application development without external design dependencies
- Client Communication: Speaking intelligently about user experience and design decisions
- Product Innovation: Proposing user experience improvements based on solid design understanding
- Team Collaboration: Effectively working with designers and product managers using shared vocabulary
Ready to Transform Your Frontend Development?
Accelerate Your UI/UX Journey with Expert Digital Transformation Services
Transform your frontend development capabilities through strategic design thinking and modern development practices. Our experienced team helps organizations implement user-centered design approaches that enhance engagement, increase conversion rates, and improve overall user satisfaction.
From responsive design implementation to accessibility compliance and performance optimization, we guide companies through comprehensive digital transformation strategies that prioritize user experience excellence.
Future-Proofing Frontend Skills
Modern frontend development continues evolving rapidly, requiring strategies for continuous learning and adaptation. AI collaboration provides frameworks for staying current with emerging technologies and best practices.
Technology Evaluation Framework
Rather than chasing every new frontend framework, develop systematic approaches to technology assessment:
- Business Value Analysis: Evaluate new technologies based on specific problem-solving capabilities rather than popularity or novelty. Does this technology solve existing pain points or enable new capabilities?
- Learning Investment Consideration: Assess the learning curve and long-term viability of new technologies. Will the time investment provide lasting value or become obsolete quickly?
- Integration Compatibility: Consider how new technologies integrate with existing systems and workflows to ensure seamless operation. Avoid creating additional complexity without proportional benefits.
Progressive Skill Development
Build frontend expertise incrementally rather than attempting comprehensive mastery immediately:
- Foundation Strengthening: Master fundamental HTML, CSS, and JavaScript concepts before embracing complex frameworks. Strong fundamentals enable faster adaptation to new technologies.
- Component-Based Thinking: Develop systematic approaches to UI architecture that translate across different frameworks and technologies. Focus on design patterns rather than specific implementations.
- User Experience Focus: Prioritize user experience principles over technical implementation details. Effective UX design remains valuable regardless of underlying technology changes.
Integration with Contemporary Development Practices
AI-assisted frontend development enhances rather than replaces established software engineering practices, creating synergistic improvements across the entire development lifecycle.
Agile Development Enhancement
Frontend AI collaboration accelerates agile development cycles:
- Rapid Prototyping: Quick creation of user interface mockups for stakeholder feedback
- Iterative Refinement: Fast implementation of design changes based on user testing
- Sprint Planning Accuracy: Better estimation of frontend development tasks through AI guidance
- Cross-Functional Communication: Improved collaboration between designers, developers, and product managers
Quality Assurance Integration
Modern quality assurance practices extend to frontend development through AI-assisted approaches:
- Automated Visual Testing: AI-powered screenshot comparison and visual regression detection
- Accessibility Auditing: Systematic evaluation of WCAG compliance and inclusive design principles
- Performance Monitoring: Continuous assessment of page load times and user experience metrics
- Cross-Device Testing: Comprehensive validation across different browsers, devices, and screen sizes
DevOps Pipeline Integration
Frontend assets require specialized deployment and monitoring strategies:
- Static Asset Optimization: Automated image compression, code minification, and bundle optimization
- Content Delivery Networks: Geographic distribution of frontend assets for improved performance
- Progressive Deployment: A/B testing of user interface changes with gradual rollout strategies
- User Analytics Integration: Systematic measurement of user interaction patterns and conversion metrics
FAQs

Get In Touch