Ransomware as a Service: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Mitigating the Threat
Deepak Dube
Jul 29, 2024
Introduction
In recent years, the cybersecurity landscape has witnessed a significant shift with the emergence of Ransomware as a Service (RaaS). This alarming trend has transformed ransomware from a threat primarily wielded by skilled hackers to a widely accessible tool for cybercriminals of varying expertise. As organizations grapple with the increasing frequency and sophistication of ransomware attacks, understanding the intricacies of RaaS has become crucial for developing effective defense strategies.
This comprehensive guide aims to illuminate the world of Ransomware as a Service, providing a deep dive into its definition, operational mechanics, notable examples, and its far-reaching impact on businesses and individuals alike. We will explore the evolution of this cybercrime model, examine real-world case studies, and discuss strategies to mitigate the risks associated with RaaS attacks.
By the end of this blog, readers will gain valuable insights into the inner workings of RaaS, its implications for cybersecurity, and practical measures to protect against this growing threat. Whether you’re an IT professional, business leader, or simply someone interested in understanding the latest developments in cybersecurity, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complex landscape of Ransomware as a Service.
What is Ransomware as a Service (RaaS)?
Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) is a business model in the cybercrime ecosystem that enables individuals or groups with limited technical skills to launch ransomware attacks. It’s a subscription-based model where ransomware developers lease out their malicious software to other cybercriminals, known as affiliates. These affiliates then use the ransomware to attack targets and extort money, sharing a percentage of the ransom payments with the RaaS providers.
The concept of RaaS mirrors legitimate Software as a Service (SaaS) models, offering a range of services including ransomware code, payment infrastructure, and even customer support for victims. This model has significantly lowered the barrier to entry for conducting ransomware attacks, leading to a proliferation of incidents across various industries and geographical regions.
How Does Ransomware as a Service Work?

The RaaS business model operates on a collaborative framework between ransomware developers and affiliates. Here’s a breakdown of how it typically works:
- Development: Skilled programmers create sophisticated ransomware packages, complete with encryption algorithms, payment systems, and decryption tools.
- Distribution: The ransomware is offered to potential affiliates on dark web marketplaces or through closed networks.
- Subscription: Affiliates subscribe to the service through a one-time fee or a profit-sharing agreement.
- Deployment: Affiliates use various methods (e.g., phishing emails and exploit kits) to infect target systems with the ransomware.
- Infection: Once a system is infected, the ransomware encrypts files and demands payment for decryption.
- Payment: If the victim pays the ransom, the payment is split between the affiliate and the RaaS provider according to their agreement.
- Support: Some RaaS providers offer customer support to victims, guiding them through the payment and decryption process to ensure payment.
Tools and platforms used in RaaS operations often include sophisticated ransomware builders, customizable dashboards for tracking infections and payments, and anonymous communication channels. While specific tools vary, many RaaS operations leverage cryptocurrencies for payments and use Tor networks for anonymity.
The Rise of RaaS
The evolution of ransomware into the RaaS model can be traced back to the mid-2010s. Here’s a brief timeline of its rise:
- 2016-2017: Early RaaS models emerge, with platforms like Satan and Philadelphia gaining attention.
- 2018-2019: RaaS becomes more sophisticated, with groups like GandCrab demonstrating the model’s profitability.
- 2020: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerates RaaS adoption as more businesses shift online, increasing potential targets.
- 2021: High-profile attacks by RaaS groups like DarkSide and REvil make headlines, bringing RaaS into mainstream awareness.
- 2022-2023: RaaS continues to evolve, with groups adopting more advanced tactics and targeting critical infrastructure.
- 2024 and beyond: Predictions suggest further sophistication in RaaS operations, potentially leveraging AI and machine learning technologies.
Notable Examples of Ransomware as a Service
Several RaaS groups have gained notoriety for their high-profile attacks and sophisticated operations. Here are some notable examples:
- Conti: Known for its aggressive tactics and high ransom demands, Conti has targeted numerous organizations, including government agencies and healthcare providers.
- DarkSide: Gained international attention for the Colonial Pipeline attack in 2021, which disrupted fuel supply in the southeastern United States.
- LockBit: Recognized for its rapid encryption process and self-spreading capabilities, LockBit has become one of the most active RaaS operations.
- Cerber: One of the early successful RaaS platforms, Cerber was known for its user-friendly interface and wide distribution.
Other significant groups include:
- REvil (Sodinokibi): Responsible for several high-profile attacks, including the JBS Foods incident.
- Avaddon: Known for its triple extortion tactics, combining file encryption, data theft, and DDoS attacks.
These examples illustrate the diverse landscape of RaaS operations, each with unique features and targeting strategies.
Impact of Ransomware as a Service
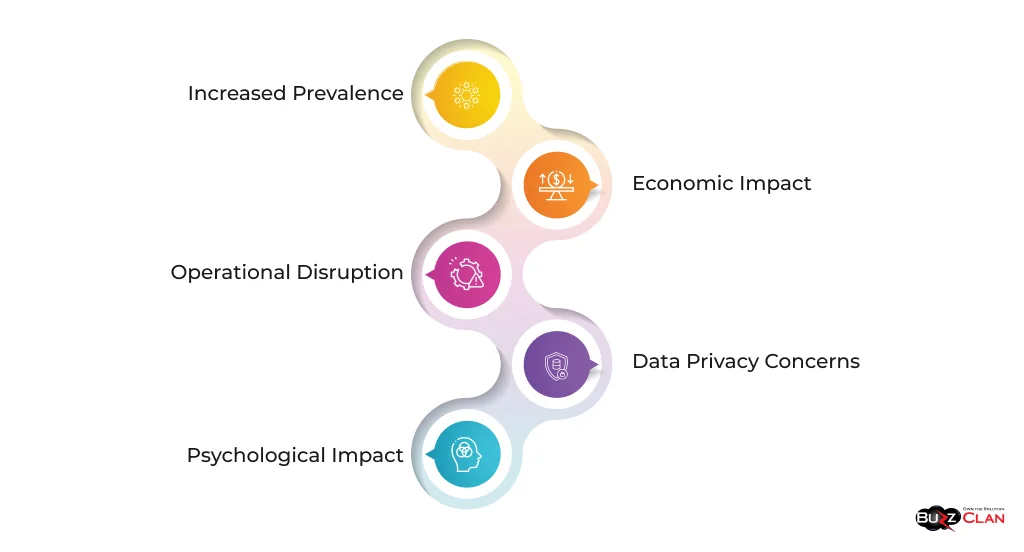
The rise of RaaS has significantly amplified the ransomware threat landscape:
- Increased Prevalence: RaaS has allowed for a dramatic increase in ransomware attacks. Lowering the technical barrier to entry, has enabled a wider range of individuals to conduct attacks, leading to a surge in incidents across various sectors.
- Economic Impact: The financial toll of RaaS attacks is staggering. In 2021 alone, global ransomware damage costs were estimated to exceed $20 billion. This includes ransom payments and costs associated with downtime, data recovery, and reputational damage.
- Operational Disruption: RaaS attacks have caused significant operational disruptions in critical sectors. The healthcare industry has been particularly hard hit, with attacks leading to postponed surgeries, diverted emergency services, and compromised patient care.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Many RaaS operations now employ double or triple extortion tactics, encrypting data and threatening to leak sensitive information. This has raised serious data privacy concerns and compliance issues for affected organizations.
- Psychological Impact: The pervasive ransomware threat has created fear and uncertainty among businesses and individuals, increasing stress and cybersecurity fatigue.
Mitigation Strategies Against Ransomware as a Service
Protecting against RaaS attacks requires a multi-faceted approach:
| Category | Measure |
|---|---|
| Preventive Measures |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Detection and Response |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Law Enforcement and Regulations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
To illustrate the impact of RaaS attacks and the key lessons learned, let’s examine two case studies:
Case Study 1: Colonial Pipeline Attack
In May 2021, the DarkSide RaaS group attacked Colonial Pipeline, the largest fuel pipeline in the United States. The attack led to a six-day shutdown, causing fuel shortages across the southeastern U.S. Colonial Pipeline paid a $4.4 million ransom, though some of it was later recovered by law enforcement.
Key lessons:
- The critical importance of segmenting IT and operational technology networks
- The need for robust incident response plans, including decision-making protocols for ransom payments
- The potential for ransomware attacks to have wide-reaching societal impacts
Case Study 2: Kaseya VSA Attack
In July 2021, the REvil RaaS group exploited a vulnerability in Kaseya’s VSA software, used by many managed service providers (MSPs). This single attack affected up to 1,500 businesses worldwide, demonstrating the potential for supply chain attacks in the RaaS model.
Key lessons:
- The importance of vetting and securing third-party software and services
- The need for rapid patch management, especially for critical vulnerabilities
- The potential for RaaS attacks to have cascading effects through service provider networks
Future Trends in Ransomware as a Service
As we look to the future, several trends are likely to shape the RaaS landscape:
- AI-Powered Attacks: Ransomware groups may leverage AI and machine learning to automate target selection, evade detection, and optimize ransom demands.
- IoT Targeting: As the Internet of Things (IoT) expands, RaaS operations may increasingly target these often less-secured devices.
- Cloud Service Attacks: With more businesses moving to the cloud, RaaS groups may focus on targeting cloud service providers for maximum impact.
- Ransomware Worms: Self-propagating ransomware could become more common, potentially leading to widespread, rapid infections.
- Increased Regulation: Governments and international bodies may implement stricter regulations on cryptocurrency and cybersecurity practices to combat RaaS.
- Advanced Evasion Techniques: RaaS developers will likely continue to innovate in evading detection, using techniques like file-less malware or living-off-the-land attacks.
Conclusion
Ransomware as a Service represents a significant evolution in the cybercrime landscape, democratizing access to sophisticated attack tools and dramatically increasing the prevalence of ransomware incidents. As this threat continues to evolve, organizations of all sizes must stay informed and implement robust defense strategies.
By understanding the mechanics of RaaS, learning from past attacks, and implementing comprehensive prevention and response measures, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to these attacks. However, the fight against RaaS is an ongoing battle that requires continuous vigilance, adaptation, and collaboration between businesses, cybersecurity professionals, and law enforcement agencies.
As we move forward, the key to combating RaaS lies in technological solutions that foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness, promote information sharing, and develop adaptive strategies that can keep pace with the ever-changing threat landscape. By taking a proactive and holistic approach to cybersecurity, we can work towards a future where the impact of RaaS is minimized and our digital ecosystems are more resilient against these evolving threats.
FAQs

Get In Touch
Follow Us
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Ransomware as a Service (RaaS)?
- How Does Ransomware as a Service Work?
- The Rise of RaaS
- Notable Examples of Ransomware as a Service
- Impact of Ransomware as a Service
- Mitigation Strategies Against Ransomware as a Service
- Case Studies and Real-World Examples
- Future Trends in Ransomware as a Service
- Conclusion
- FAQs