Navigating Cloud Cost: Strategies, Tools, and Trends for Optimal Cloud Spending
Gururaj Singh
Aug 6, 2024
Introduction to Cloud Cost Management
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, understanding and managing cloud costs has become a pivotal aspect of businesses’ operational efficiency and financial health. As organizations increasingly migrate to cloud platforms, comprehending and controlling cloud expenditures is more critical than ever.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Cloud Cost
- Complexity of Cloud Pricing Models: Cloud cost fundamentally revolves around the pricing models of cloud services, which can be intricate and variable. These models often include charges based on storage, compute power, data transfer, and additional services.
- Dynamic Usage Patterns: Unlike traditional fixed IT costs, cloud expenses are dynamic and closely tied to usage patterns. This fluidity offers flexibility but also requires vigilant management to avoid cost overruns.
Importance of Cloud Cost Management in Today’s Digital Landscape
- Budget Control and Optimization: Effective cloud cost management is essential for controlling IT budgets. It involves monitoring expenses and optimizing resource usage to ensure cost-effectiveness.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Understanding cloud costs enables informed decision-making. It helps businesses choose the right cloud services and allocate resources in a way that aligns with their strategic objectives.
- Avoiding Bill Shock: Cloud costs can quickly spiral without proper management, leading to ‘bill shock.’ Proactive cost management strategies are crucial to prevent unexpected high expenses.
- Enhancing Operational Efficiency: By aligning cloud usage with actual business needs, companies can enhance their operational efficiency, ensuring they get the most value from their cloud investments.
Cloud Cost Optimization
Effective management of cloud expenses involves more than just monitoring; it requires a strategic approach known as cloud cost optimization. This concept is crucial for businesses seeking to maximize the value of their cloud investments while minimizing unnecessary spending.
Defining Cloud Cost Optimization
- A Strategic Approach: Cloud cost optimization is a comprehensive approach encompassing identifying and implementing cost-saving measures within a cloud environment. It goes beyond mere cost tracking to proactive cost management.
- Focus on Efficiency and Value: The core of this strategy is to ensure that every dollar spent on cloud services contributes directly to business value. This includes evaluating the cost-to-benefit ratio of cloud resources and adjusting usage accordingly.
Strategies for Effective Cloud Cost Optimization
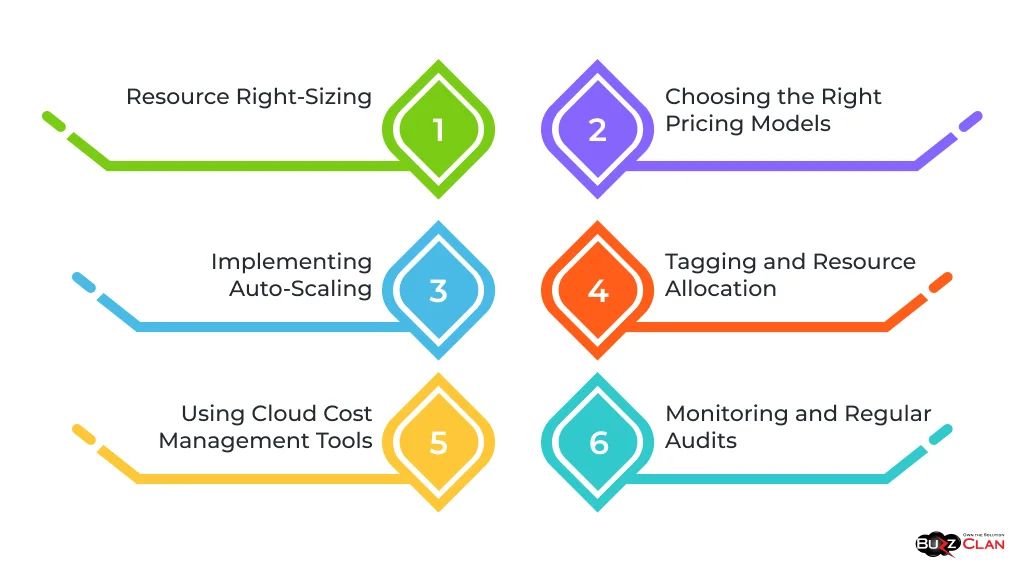
- Resource Right-Sizing: Regularly review and adjust cloud resources to match current needs. This involves scaling down or terminating unused or underutilized resources, avoiding paying for excess capacity.
- Choosing the Right Pricing Models: Cloud providers offer various pricing models, such as on-demand, reserved, or spot instances. Understanding and selecting the right model based on usage patterns can lead to significant cost savings.
- Implementing Auto-Scaling: Utilize auto-scaling capabilities of cloud services to adjust resources in response to changing demand automatically. This ensures that you only pay for what you use.
- Tagging and Resource Allocation: Implement a tagging strategy for cloud resources to track usage and costs by department, project, or application. This facilitates more accurate chargebacks and accountability within the organization.
- Using Cloud Cost Management Tools: Leverage specialized tools provided by cloud providers or third-party solutions for monitoring and optimization. These tools offer insights into cost trends, potential savings areas, and budget forecasting.
- Monitoring and Regular Audits: Continuously monitor cloud expenditure and conduct regular audits to identify wasteful spending or opportunities for further optimization.
Organizations can adopt these strategies to turn cloud cost management from a reactive exercise into a proactive strategic initiative. This approach reduces expenses and ensures that cloud investments are aligned with business objectives, driving efficiency and innovation.
Challenges in Cloud Cost Management
Navigating the complexities of cloud cost management is daunting for many businesses. The dynamic nature of cloud services and the intricacies of pricing models and usage patterns present several challenges that can significantly impact a company’s operations and budget.
Common Challenges in Managing Cloud Costs:
- Complex Pricing Structures: One of the primary hurdles is the complexity of cloud pricing models. Understanding and selecting the most cost-effective approach can be challenging with various options like pay-as-you-go, reserved instances, and spot pricing.
- Unpredictable Usage Patterns: While beneficial, the scalability and flexibility of cloud services can lead to unpredictable usage and costs. Sudden spikes in demand or inefficient resource allocation can significantly inflate expenses.
- Lack of Visibility and Control: Many organizations need help gaining complete visibility into their cloud spending. This lack of transparency makes controlling costs and allocating budgets easier.
- Decentralized Cloud Adoption: In larger organizations, different departments or teams may independently adopt cloud services, leading to decentralized and uncoordinated spending, known as ‘shadow IT.’
- Cost Allocation and Chargeback: Properly allocating cloud costs back to specific departments or projects can be complex, particularly in organizations with multiple cloud accounts or services.
Impact of These Challenges on Operations and Budget:
- Budget Overruns: Without effective cost management, companies can experience budget overruns, affecting financial planning and potentially leading to cuts in other critical areas.
- Reduced Operational Efficiency: Inefficient cloud spending can tie up resources that could be better used elsewhere, reducing overall operational efficiency.
- Inhibited Innovation: Excessive or unexpected cloud costs can limit a company’s ability to invest in innovation or new technologies, hindering long-term growth and competitiveness.
- Strained IT Resources: The need to monitor and adjust cloud usage continuously can strain IT resources, diverting attention from strategic initiatives to cost management.
Addressing these challenges requires a proactive approach to cloud cost management, incorporating robust monitoring tools, clear policies, and regular reviews of cloud spending. By doing so, businesses can turn these challenges into opportunities to optimize their cloud investment and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Cloud Hosting Costs
Cloud hosting costs vary widely based on the chosen models and providers. Understanding these variations is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions that align with their budgetary constraints and operational needs.
Analysis of Various Cloud Hosting Models and Their Cost Implications:
- Public Cloud: Often the most cost-effective option, public cloud services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer pay-as-you-go pricing. However, costs can escalate with increased usage, especially if not monitored closely.
- Private Cloud: While offering greater control and security, private clouds are typically more expensive. They involve upfront investments in infrastructure and ongoing maintenance costs.
- Hybrid Cloud: Combining public and private clouds, hybrid models offer a balance of cost-effectiveness and control. However, managing hybrid environments can be complex and require additional tools and expertise.
- Multi-Cloud: Using multiple public cloud services can optimize costs by leveraging each provider’s strengths. However, it introduces complexity in cost tracking and management across different platforms.
Comparing Costs of Different Cloud Hosting Providers:
- Price Variation: Major providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) have different pricing structures. AWS and Azure offer similar pricing models, while GCP often differentiates with lower prices for certain services.
- Discounted Pricing Options: Providers offer various discounts, such as AWS Reserved Instances or Azure Reserved VM Instances, which can significantly reduce costs for long-term commitments.
- Additional Costs: Beyond compute and storage, additional costs for data transfer, network usage, and specialized services like machine learning or IoT can vary by provider.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Comparing TCO, which includes direct and indirect costs, is vital. Some providers may offer lower initial pricing but higher ancillary costs.
Evaluating cloud hosting costs necessitates a thorough analysis of the hosting models and the pricing structures of various providers. Organizations must carefully assess their needs against these factors to identify the most cost-effective cloud hosting solution. Understanding these cost dynamics can lead to significant savings and more efficient use of cloud resources.
Cloud Service Cost Analysis
Understanding the cost structure of various cloud services is crucial for businesses to manage their cloud spending effectively. This analysis dives into the breakdown of costs associated with different cloud services and examines the factors that influence these costs.
Breakdown of Costs Associated with Different Cloud Services
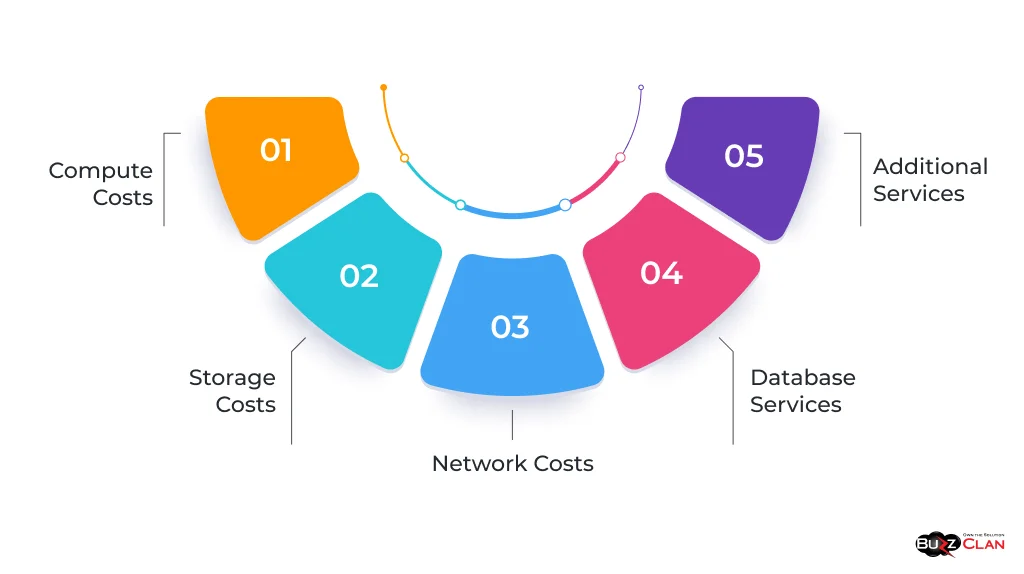
- Compute Costs: Often the most significant part of cloud service expenses, compute costs depend on the type of instances, their sizes, and the duration of use. Costs can vary significantly based on whether instances are reserved, on-demand, or spot instances.
- Storage Costs: Storage pricing is typically based on the amount of data stored, the storage class (e.g., standard, infrequent access, archive), and the duration of storage. Additional costs may be incurred for data retrieval and operations.
- Network Costs: These include data transfer fees, which can be substantial, especially when data is moved frequently between different cloud services or regions.
- Database Services: Managed database services are priced based on factors like the database engine type, storage capacity, and data transfer.
- Additional Services: Costs for services like machine learning, IoT, or big data analytics vary depending on the usage and complexity of the services.
Factors Influencing the Cost of Cloud Services:
- Service Model: The choice between Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS) influences costs. Each model bundles different levels of service, impacting the overall pricing.
- Resource Management: Efficient management of resources (like right-sizing instances and deleting unused resources) can significantly impact costs.
- Pricing Model Selection: Opting for reserved instances or committing to a certain usage level can lower prices than on-demand services.
- Geographic Region: Prices can vary based on the cloud provider’s region. This is due to differing operational costs and demand in various locations.
- Customization and Additional Features: Custom configurations and add-ons (like enhanced security or compliance features) can increase costs.
- Support and Maintenance Costs: Premium support services and maintenance fees can add to the overall cost, especially for complex cloud environments.
A thorough cloud service cost analysis enables businesses to identify key areas where they can optimize spending. By understanding and managing these costs effectively, organizations can maximize the value of their cloud investments.
Cost Management Tools and Platforms
Efficient cloud cost management is pivotal for businesses to optimize their cloud spending. Several tools and platforms are designed to assist in this area, offering a range of features to control, analyze, and optimize cloud costs.
Overview of Cloud Cost Management Tools:
- Datadog Cloud Cost Management: Known for its comprehensive monitoring capabilities, Datadog has extended its expertise to cloud cost management. It offers real-time cost tracking and analysis across multiple cloud platforms.
- AWS Cost Explorer: A native tool for AWS users, Cost Explorer allows for detailed analysis of AWS spending and usage patterns with customizable reports and forecasting capabilities.
- Azure Cost Management + Billing: Microsoft’s solution for Azure offers tools for analyzing and controlling Azure spending, along with recommendations for cost optimization.
- Google Cloud Cost Management: Built for the Google Cloud Platform, this tool provides insights into cloud costs with detailed reports, cost breakdowns, and budgeting tools.
- CloudHealth by VMware: A multi-cloud cost management solution, CloudHealth offers detailed reporting, cost allocation, and optimization recommendations across different cloud environments.
Features and Benefits of These Tools:
- Cost Visibility: These tools provide visibility into all cloud costs, breaking them down by services, departments, projects, etc., which is crucial for understanding spending patterns.
- Cost Optimization Recommendations: Many of these platforms offer recommendations for reducing costs, such as identifying underutilized resources or suggesting changes in pricing plans.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Features like budget setting, tracking, and forecasting help businesses plan their cloud expenses and avoid overspending.
- Customizable Alerts: Setting up alerts for budget overruns or unusual spending patterns enables proactive cost management.
- Reporting and Analytics: Advanced analytics and customizable reporting capabilities allow for a deep dive into cost data, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Multi-Cloud Management: For businesses using multiple cloud providers, tools like CloudHealth provide a unified platform for managing costs across different clouds.
Using these cloud cost management tools, businesses can gain crucial insights into their cloud spending, enabling them to make informed decisions, optimize costs, and align their cloud investments with their business objectives. The right tool helps track and control costs and plays a strategic role in the overall cloud management strategy.
Amazon Cloud Server Cost
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a dominant player in the cloud market, and understanding its pricing structure is key for businesses leveraging its services. This section provides a detailed analysis of Amazon cloud server costs and offers tips for cost-effective use of AWS services.
Detailed Analysis of Amazon Cloud Server Costs:
- On-Demand Instances: AWS charges for on-demand instances per hour or second, depending on the instance type and operating system. This option is flexible but often the most expensive.
- Reserved Instances: These instances require a commitment for 1 to 3 years, offering a significant discount (up to 75%) compared to on-demand pricing. Ideal for predictable usage.
- Spot Instances: Spot instances allow users to bid for unused AWS capacity at a potentially lower price. While cost-effective, they are subject to availability and can be terminated by AWS with short notice.
- Dedicated Hosts: Suitable for regulatory requirements that prevent hardware sharing, dedicated hosts are physical servers with EC2 instance capacity fully dedicated to a user.
- Additional Costs: Beyond instance costs, AWS charges for other services like data transfer, additional storage, and specific AWS services (like RDS or DynamoDB).
Tips for Cost-Effective Use of Amazon Cloud Services:
- Right-Size Your Instances: Regularly review and adjust the configurations of your AWS instances to match your actual usage, avoiding paying for unnecessary capacity.
- Utilize Reserved and Spot Instances: For predictable workloads, use reserved instances. For flexible, non-critical workloads, consider spot instances.
- Monitor and Optimize Continuously: Use AWS Cost Explorer and third-party tools to monitor your AWS spending and identify areas for cost reduction.
- Manage Data Transfer Costs: Be aware of data transfer charges, especially when moving data from AWS to the Internet or other regions.
- Leverage AWS Cost Management Tools: AWS offers several native tools like AWS Budgets and AWS Trusted Advisor, which can help manage and optimize your cloud costs.
- Automate to Save: Implement automation for starting and stopping instances to align with business hours or low-traffic periods.
Understanding Amazon cloud server costs and implementing these strategies can significantly reduce AWS expenses. Regular analysis and optimization of AWS usage are essential for maintaining a cost-effective cloud environment.
Top 5 SaaS Tools to Manage Cloud Costs

Google Cloud Platform: Cost and Management
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offers diverse services with a pricing structure catering to different business needs. Understanding this pricing model and implementing effective cost management strategies are key to optimizing your investments in GCP.
Overview of Google Cloud’s Pricing Structure:
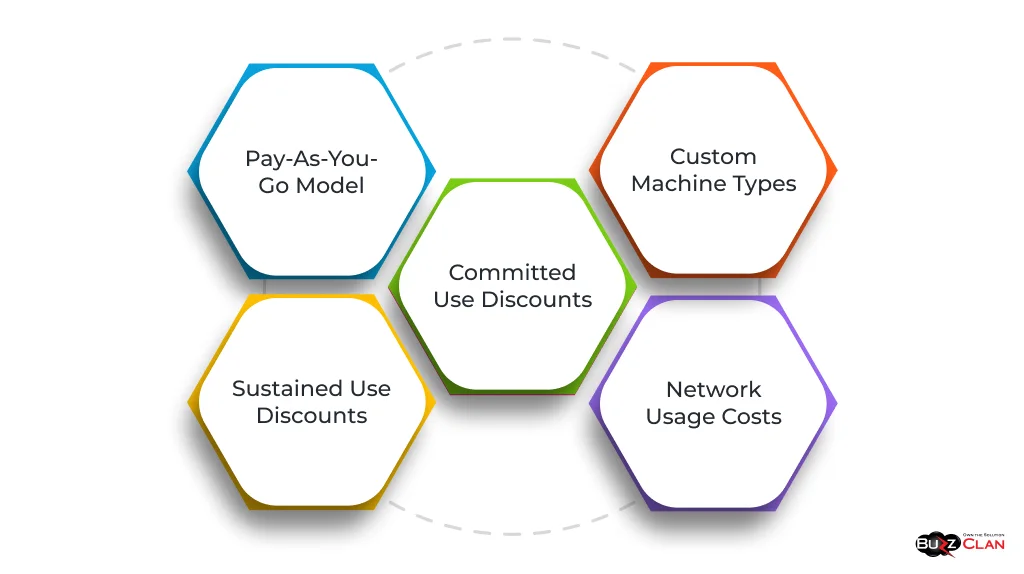
- Pay-As-You-Go Model: Like other cloud providers, GCP follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model, charging for services based on usage. This includes compute resources, storage, and data processing services.
- Sustained Use Discounts: GCP automatically applies discounts for instances used for a significant portion of the billing month, encouraging continuous usage.
- Committed Use Discounts: GCP offers committed use discounts for predictable usage, which involve a one- or three-year commitment in exchange for lower prices.
- Custom Machine Types: GCP allows the creation of custom machine types, providing flexibility and cost-effectiveness by letting users tailor resources to their specific needs.
- Network Usage Costs: GCP charges for network usage, including data transfer within and between regions, can significantly impact overall costs.
Strategies for Managing Costs on the Google Cloud Platform:
- Resource Monitoring and Optimization: Regularly monitor resource usage using Google Cloud’s monitoring tools. Identify underutilized resources and adjust them to match actual needs.
- Take Advantage of Discounts: Utilize sustained and committed use discounts for instances with predictable usage patterns.
- Budget Alerts: Set up budget alerts in Google Cloud Billing to get notified when spending exceeds your preset thresholds, helping to avoid unexpected charges.
- Use Preemptible VMs for Flexible Workloads: Preemptible VMs offer a cost-effective alternative significantly cheaper than regular instances for workloads that can tolerate interruptions.
- Data Transfer Management: Be aware of the costs associated with data transfer and design your architecture to minimize data movement between regions or out of GCP.
- Optimize Storage Costs: Regularly review and optimize your storage solutions, choosing the appropriate classes (like Nearline and Coldline) for different data storage needs.
By understanding Google Cloud’s pricing structure and implementing these cost management strategies, businesses can significantly reduce their cloud expenses while still leveraging the powerful capabilities of GCP. Regular analysis and adaptation to usage patterns and business needs are crucial for achieving cost-effective cloud operations on the Google Cloud Platform.
AWS Cloud Cost Management
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a comprehensive and widely used cloud platform, and effective cost management within AWS is crucial for businesses to optimize their cloud spending. Understanding AWS’s pricing models and employing best practices in cost management can lead to significant savings and more efficient cloud operations.
Insights into AWS Cloud Pricing Models and Cost Management:
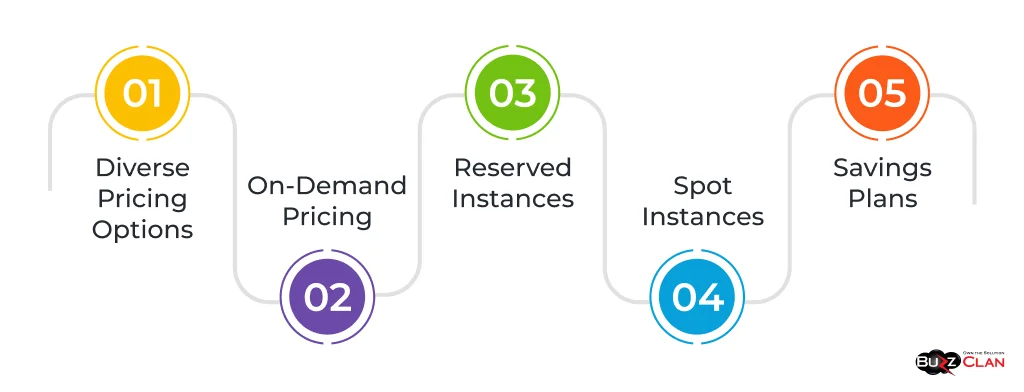
- Diverse Pricing Options: AWS offers several pricing options, including on-demand, reserved instances, spot instances, and savings plans. Each has its advantages and is suitable for different use cases.
- On-Demand Pricing: This is the most flexible option, where users pay for compute capacity by the hour or second with no long-term commitments. It is ideal for short-term, irregular workloads that cannot be interrupted.
- Reserved Instances: For applications with steady state or predictable usage, reserved instances provide a significant discount (up to 75%) compared to on-demand pricing in exchange for a commitment to use for one or three years.
- Spot Instances: Spot instances allow users to purchase unused AWS capacity at a lower price but can be interrupted by AWS with two minutes of notification when AWS needs the capacity back.
- Savings Plans: AWS offers Savings Plans, which provide lower rates across specific services in exchange for a commitment to a consistent amount of usage (measured in $/hour) for a one or three-year period.
Best Practices for Optimizing AWS Cloud Costs:
- Right-Sizing Resources: Regularly analyze and adjust AWS resources to ensure they are the right size for your needs, avoiding over-provisioning and unnecessary costs.
- Cost Allocation Tags: Implement cost allocation tags to organize and track AWS costs by project, department, or environment. This practice aids in understanding spending patterns and identifying areas for cost reduction.
- Utilize AWS Budgets: AWS Budgets allow you to set custom budgets to track your cost and usage from the simplest to the most complex scenarios.
- Monitor and Review Regularly: Use the AWS Cost Explorer to visualize AWS spending and usage. Regular reviews help identify wasteful spending and opportunities for cost-saving.
- Leverage AWS Trusted Advisor: This tool provides real-time guidance to help you provision your resources following AWS best practices, including cost-optimization recommendations.
- Automate to Save: Implement automation for starting and stopping instances to align with business hours or low-traffic periods, which can lead to significant cost savings.
By understanding the various pricing models of AWS and implementing these best practices, businesses can effectively manage and optimize their AWS cloud costs. Regular monitoring, analysis, and adjustments are key to achieving a cost-efficient cloud environment on AWS.
Cloud Server Cost Comparison
Choosing the right cloud server involves understanding the cost structures of various cloud providers. A comparative analysis of cloud server costs across major providers can guide businesses in making cost-effective decisions tailored to their needs.
Comparative Analysis of Cloud Server Costs Across Major Providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS offers a range of server options with varying pricing models. The on-demand instances are priced per hour or second, while reserved instances provide significant discounts for long-term commitments. AWS is known for its extensive service offerings but can become costly with add-ons and data transfer charges.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure’s pricing is competitive with AWS, offering a similar range of services and pricing models, including pay-as-you-go and reserved instances. Azure often provides more cost-effective solutions for Windows-based applications.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP’s pricing stands out with its sustained use discounts, which automatically apply for long-running workloads, and custom machine types that allow for more tailored configurations. GCP can be more cost-effective for certain types of workloads and data storage.
- IBM Cloud: IBM Cloud offers competitive pricing, especially for enterprises requiring hybrid cloud solutions. Its pricing can be advantageous for businesses leveraging AI and machine learning services.
Decision-Making Criteria for Selecting Cost-Effective Cloud Servers:
- Workload Requirements: Assess the specific needs of your workloads, including computing power, memory, and storage. Match these requirements with the server types offered by different providers.
- Pricing Structure: Understand each provider’s pricing structure. Consider not just the computer costs but also storage, data transfer, and any additional services needed.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Evaluate the ease of scaling resources up or down with each provider. Flexibility in scaling is crucial for managing costs effectively, especially for businesses with fluctuating workloads.
- Long-Term Commitments vs. Pay-As-You-Go: Decide whether a long-term commitment (like reserved instances) or a pay-as-you-go model aligns better with your budget and usage patterns.
- Additional Features and Support: Consider the value of additional features, support services, and the ecosystem the cloud provider offers. Sometimes, these can justify a higher price.
- Geographic Availability: Ensure the cloud provider has data center locations that meet your latency and data sovereignty requirements, as these can also impact costs.
This table compares major providers’ cloud server costs and offerings to help you evaluate their options based on pricing models, workload suitability, scalability, additional features, and geographic availability:
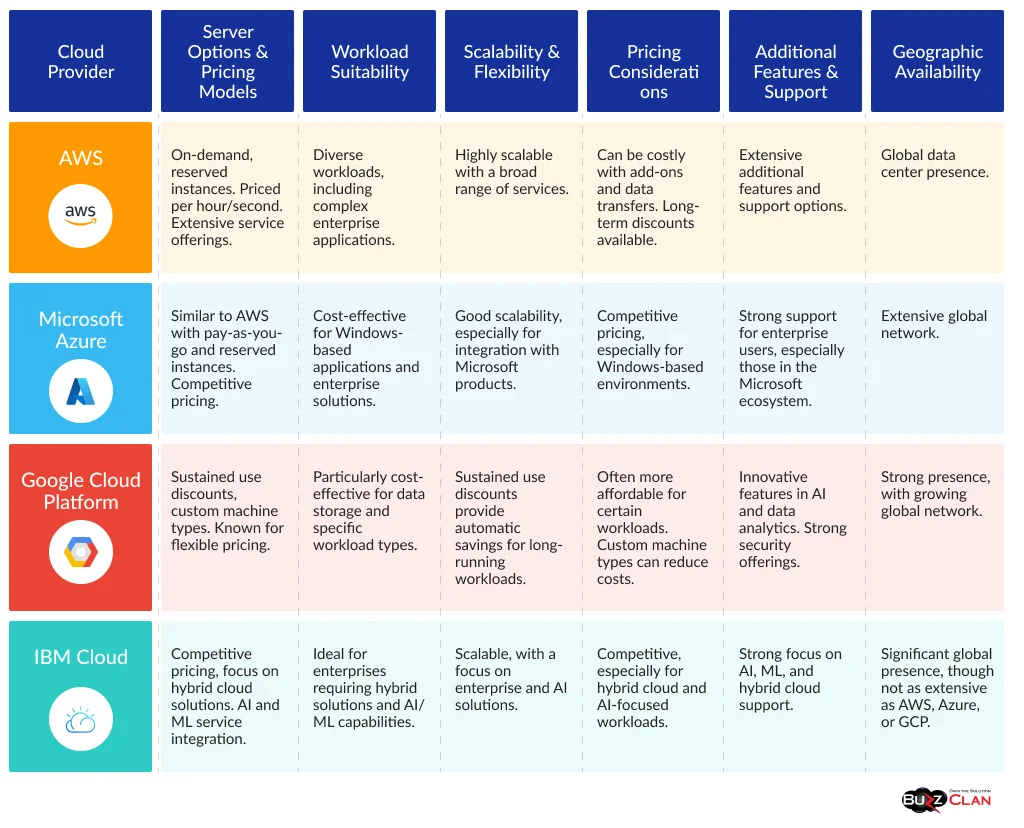
A thorough comparison and understanding of cloud server costs and offerings from different providers enable businesses to make informed decisions. By considering these criteria, businesses can select cloud servers that meet their technical requirements and offer the best value for their investment.
Cloud Cost Predictions and Trends
As cloud computing continues to evolve, so do the strategies for managing and optimizing cloud costs. Keeping an eye on emerging trends and predictions is essential for businesses to stay ahead in their cloud cost management strategies. This section explores the anticipated trends in cloud cost management and forecasts the potential changes in cloud costs in the near future.
Future Trends in Cloud Cost Management:
- Advancements in AI and Machine Learning: One of the most significant trends is the increasing use of AI and machine learning for cloud cost optimization. These technologies can predict usage patterns, automatically adjust resources, and provide insights for cost-saving opportunities.
- Increased Focus on FinOps (Financial Operations): FinOps, which brings financial accountability to cloud spending, is gaining traction. This practice involves cross-functional teams working collaboratively to optimize cloud costs while maximizing business value.
- Greater Emphasis on Multi-Cloud Strategies: As businesses diversify their cloud portfolios to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize costs, multi-cloud management tools will become more sophisticated to provide consolidated cost reporting and management across different platforms.
- More Granular Cost Optimization Tools: Cloud providers and third-party vendors will likely offer more advanced and granular cost optimization tools, providing deeper insights and more precise control over cloud expenditures.
- Automation in Cost Management: Automation in cloud cost management will become more prevalent, with systems capable of making real-time adjustments based on predefined rules or AI-driven predictions to optimize costs.
Predictions for Cloud Cost Changes:
- Dynamic Pricing Models: Cloud providers may introduce more dynamic and flexible pricing models to cater to the varying needs of businesses, potentially leading to more cost-effective solutions.
- Cost Reduction Through Sustainable Practices: As sustainability becomes a bigger concern, there could be a push towards more energy-efficient cloud services, which might also result in cost reductions.
- Increased Transparency in Billing: Expect to see more transparency in cloud billing, with providers offering clearer breakdowns and insights into costs, helping businesses to understand better and manage their spending.
- Growing Importance of Cost Governance: Cost governance will become a crucial aspect of cloud management, with businesses implementing stricter policies and practices to keep cloud costs in check.
These trends and predictions indicate that cloud cost management is set to become more intelligent, collaborative, and automated. Businesses that adapt to these changes and leverage the latest tools and practices will be better positioned to manage their cloud costs effectively and derive the maximum value from their cloud investments.
Implementing Cost-effective Cloud Solutions
Implementing cost-effective strategies is crucial for businesses navigating the complexities of cloud costs. This section offers a step-by-step guide to deploying such strategies and case studies demonstrating successful cloud cost management implementations.
Step-by-Step Guide on Implementing Cost-Effective Cloud Strategies:
- Assessment of Current Cloud Usage and Costs: Begin by thoroughly assessing your current cloud infrastructure, including resource use, idle resources, and cost allocation.
- Identifying Areas for Cost Reduction: Pinpoint areas where costs can be reduced, such as underutilized resources, expensive services that can be downgraded, or resources that can be terminated.
- Setting Up Cost Monitoring and Management Tools: Implement cloud cost management and monitoring tools for real-time visibility into cloud spending.
- Optimizing Resource Utilization: Right-size cloud resources to match the actual demand, leveraging auto-scaling where applicable.
- Adopting Cost-effective Pricing Models: Evaluate and select the most cost-effective pricing models cloud providers offer, such as reserved or spot instances.
- Implementing Cost Governance Policies: Develop and enforce cloud usage policies to avoid unnecessary spending and ensure cost-effective usage across the organization.
- Regular Review and Adjustment: Conduct regular cloud usage and cost reviews, adjusting strategies to align with changing business needs and cloud pricing models.
Case Studies on Successful Cloud Cost Management Implementations:
- E-commerce Platform Leveraging Reserved Instances: An e-commerce company significantly reduced its cloud expenses by adopting reserved instances for its predictable workloads, resulting in a 30% reduction in cloud costs.
- Tech Startup Optimizing with Auto-Scaling: A tech startup implemented auto-scaling to adjust its resource usage in real-time, optimizing costs and improving application performance during varying traffic periods.
- Financial Services Firm Implementing Cost Governance: A financial services firm established a robust cost governance framework, leading to more disciplined cloud usage and a 25% reduction in overall cloud expenditures.
Businesses can develop and execute cost-effective cloud strategies by following these steps and learning from successful implementations. This proactive approach to cloud cost management is essential for optimizing cloud investments and achieving long-term financial sustainability.
Reducing Cloud Costs: Strategies and Tips
Reducing cloud costs is a critical concern for businesses utilizing cloud computing. Implementing practical strategies and learning from real-world examples can lead to significant savings and more efficient cloud usage. Here are strategies, tips, and examples to help reduce cloud expenses effectively.
Practical Strategies and Tips for Reducing Cloud Expenses:
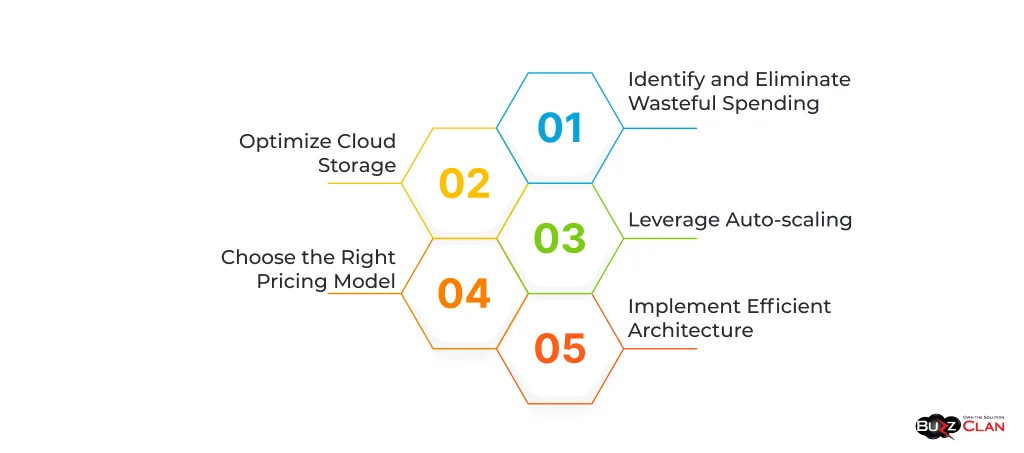
- Identify and Eliminate Wasteful Spending: Regularly audit cloud resources to identify unused or underutilized instances and services. Terminating these can lead to immediate cost savings.
- Optimize Cloud Storage: Evaluate your storage needs and choose the right type of storage (e.g., cold storage for infrequently accessed data) to reduce costs.
- Leverage Auto-scaling: Implement auto-scaling to adjust the capacity to maintain steady, predictable performance at the lowest possible cost.
- Choose the Right Pricing Model: Evaluate different pricing models (like on-demand, reserved instances, or spot pricing) and choose the one that best fits your usage patterns.
- Implement Efficient Architecture: Design a cloud architecture that maximizes efficiency, such as using serverless architectures where appropriate to pay only for the resources you use.
Real-world Examples of Cost-Saving Measures in Cloud Environments:
- Global Retailer Leveraging Reserved Instances: A global retail company saved up to 40% on their cloud costs by switching a significant portion of their workloads to reserved instances, locking lower rates for long-term use.
- Media Company Using Auto-scaling and Spot Instances: A media streaming company implemented auto-scaling and used spot instances for non-critical workloads, achieving a 30% reduction in their cloud computing costs.
- Healthcare Provider Optimizing Storage: A healthcare provider moved their archival data to cold storage and implemented lifecycle policies to automatically transition data, reducing storage costs by over 50%.
By adopting these strategies and learning from the experiences of others, businesses can effectively reduce their cloud costs. Regular evaluation and adjustment of cloud strategies are essential to ensure ongoing cost optimization in the dynamic cloud environment.
Conclusion: Mastering Cloud Cost Management
As we conclude our exploration of cloud cost management, it’s clear that mastering this aspect is not just beneficial but essential for businesses leveraging cloud technologies. Effective cloud cost management strategies can lead to significant savings, improved operational efficiency, and a more decisive competitive edge.
Recap of Key Points Discussed in the Blog:
- Understanding Cloud Costs: We began by emphasizing the importance of understanding various cloud pricing models and the need for effective cloud cost management in the digital landscape.
- Strategies for Cost Optimization: We delved into various strategies for cloud cost optimization, including right-sizing resources, selecting appropriate pricing models, and leveraging cost management tools.
- Navigating Challenges: We discussed the common challenges in cloud cost management, such as complex pricing structures, unpredictable usage patterns, and their impact on operations and budget.
- Provider-Specific Insights: The blog provided insights into the cost structures and management strategies for major cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure, helping readers make informed decisions.
- Practical Tips and Real-World Examples: We shared practical tips for reducing cloud expenses and drew lessons from real-world examples, demonstrating successful cost-saving measures in cloud environments.
Final Thoughts on the Importance of Proactive Cloud Cost Management:
- A Necessity, Not a Choice: In today’s cloud-first world, proactive cloud cost management is not optional but necessary for business sustainability and growth.
- Aligning Costs with Business Goals: Effective cost management ensures that cloud investments align closely with business goals, maximizing the value derived from cloud technologies.
- Continuous Process: Cloud cost management is an ongoing process. It requires regular review, adaptation, and alignment with the evolving cloud services and business needs.
- Empowering Innovation: By saving on unnecessary costs, businesses can redirect their investments towards innovation and strategic initiatives, driving future growth and success.
In summary, mastering cloud cost management is critical to modern business strategy. By staying informed, utilizing the right tools, and regularly reviewing and adjusting cloud spending, businesses can minimize expenses and maximize the benefits they reap from their cloud investments.
FAQs

Get In Touch
