The Complete Guide to Compliance-Driven Cloud Networking and Security Architecture
Gururaj Singh
Aug 13, 2025
Organizations must move beyond treating compliance as an afterthought in cloud networking. The BuzzClan Framework integrates regulatory controls directly into network architecture, creating self-governing infrastructure that maintains compliance automatically while enhancing performance and reducing operational overhead.
The modern enterprise faces an unprecedented challenge: building robust, scalable cloud networks while simultaneously meeting increasingly complex regulatory requirements. Traditional approaches treat compliance and networking as separate domains that occasionally intersect during audits or security reviews. This fragmented methodology creates vulnerabilities, increases operational complexity, and often leads to costly remediation efforts after non-compliance issues surface.
Forward-thinking organizations recognize that compliance-driven cloud networking isn’t just about meeting regulatory requirements—it’s about creating competitive advantages through superior architecture, automated governance, and proactive risk management.
The convergence of digital transformation and regulatory evolution demands a new paradigm. Cloud networks must be designed with compliance as a foundational element, not a bolt-on feature. This approach transforms regulatory requirements from operational burdens into architectural strengths that drive innovation and operational excellence.
Understanding Integrated Compliance-Driven Cloud Networking
Integrated compliance-driven cloud networking represents a fundamental shift in how organizations architect their cloud infrastructure. Rather than designing networks first and adding compliance controls later, this methodology embeds regulatory requirements directly into the network’s DNA.
At its core, this approach recognizes that modern cloud networks operate in highly dynamic environments where manual compliance monitoring becomes impossible at scale. Traditional compliance models, built for static on-premises infrastructure, break down when applied to elastic, multi-tenant, and geographically distributed cloud environments.
The integrated approach transforms compliance from a reactive, audit-driven process into a proactive, architecture-driven capability. Every network decision—from subnet segmentation to traffic routing—incorporates compliance considerations from the outset. This methodology creates networks that are inherently compliant, self-monitoring, and capable of adapting to regulatory changes without requiring extensive reconfiguration.
Key characteristics of integrated compliance-driven cloud networking include:
- Embedded Controls: Compliance requirements are translated into network policies, access controls, and traffic management rules that operate at the infrastructure level. These controls become part of the network fabric rather than external oversight mechanisms.
- Automated Governance: Network behavior automatically aligns with regulatory requirements through policy-driven automation. Changes to the network environment trigger compliance validation processes that either approve modifications or flag potential violations before they impact operations.
- Continuous Validation: Real-time monitoring and assessment ensure ongoing compliance without relying on periodic manual audits. The network continuously validates its configuration and behavior against applicable regulatory frameworks.
- Adaptive Architecture: Networks can evolve in response to changing regulatory requirements without requiring complete redesigns. New compliance rules are incorporated into existing network policies through configuration updates rather than infrastructure overhauls.
Pro-Tips for Navigating Cloud Compliance
- Start with Regulatory Mapping: Before designing any network component, create comprehensive mappings between your applicable regulatory frameworks and specific network requirements. This ensures that technical decisions align with compliance obligations from the beginning.
- Implement Policy-as-Code: Transform compliance requirements into executable policies that can be version-controlled, tested, and deployed automatically. This approach eliminates the gap between compliance documentation and actual network behavior.
- Design for Auditability: Build comprehensive logging, monitoring, and reporting capabilities into every network component. Audit trails should be immutable, searchable, and capable of demonstrating compliance to regulatory bodies without manual intervention.
- Embrace Zero-Trust Principles: Compliance-driven networks benefit significantly from zero-trust architectures that verify every connection, encrypt all communications, and maintain detailed access logs. These principles align naturally with most regulatory frameworks.
- Plan for Multi-Region Compliance: Different geographical regions may have varying regulatory requirements. Design networks that can apply region-specific controls automatically based on data location, user origin, or transaction jurisdiction.
Types of Cloud Networking
Modern cloud networking encompasses several architectural models, each with distinct compliance implications and regulatory considerations.
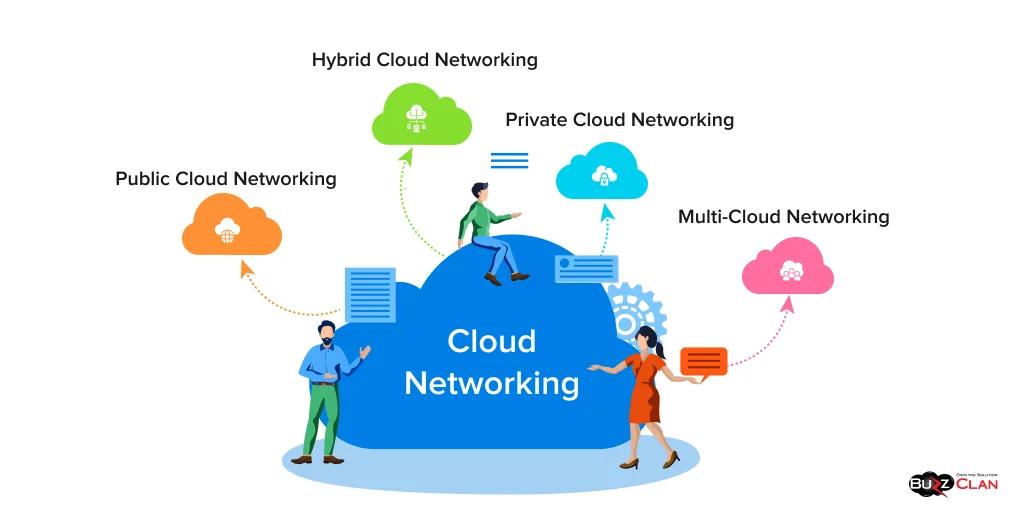
- Public Cloud Networking leverages shared infrastructure provided by major cloud service providers. While cost-effective and scalable, public clouds introduce shared responsibility models where organizations must understand precisely which compliance controls they manage versus those handled by the cloud provider. Public cloud strategies require careful attention to data sovereignty, encryption key management, and regulatory jurisdiction issues.
- Private Cloud Networking offers dedicated infrastructure that provides greater control over compliance implementation, but requires organizations to manage all aspects of regulatory adherence. Private clouds excel in scenarios where regulatory requirements mandate specific infrastructure controls or when organizations need complete visibility into all network operations.
- Hybrid Cloud Networking combines public and private cloud elements, creating complex compliance scenarios where different regulatory controls may apply to other network segments. Successful hybrid implementations require sophisticated policy engines that can apply appropriate controls based on workload location, data classification, and regulatory requirements.
- Multi-Cloud Networking spans multiple cloud providers, introducing additional complexity in maintaining consistent compliance postures across different platforms. Organizations must ensure that compliance controls operate uniformly regardless of the underlying cloud provider while managing varying security models and operational procedures.
Each networking model presents unique opportunities and challenges for implementing compliance-driven architectures. The key lies in understanding how regulatory requirements map to specific network designs and ensuring that chosen architectures can support both current compliance needs and future regulatory evolution.
Further Reading
Building Regulatory Controls Into Cloud Infrastructure
- Security-First Architecture forms the foundation of compliance-driven cloud networking. This approach prioritizes security considerations in every architectural decision, recognizing that most regulatory frameworks fundamentally concern themselves with data protection, system integrity, and operational transparency.
- Defense-in-depth is central to effective security-first designs, implementing multiple layers of controls protect against various threat vectors. Network segmentation isolates sensitive workloads, micro-segmentation provides granular access control, and encrypted communications ensure data protection both in transit and at rest.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Integration ensures that network access aligns with regulatory requirements for user accountability, authentication, and authorization. Robust IAM systems provide the foundation for demonstrating compliance with regulations that require detailed access logging and user activity monitoring.
- Data Classification and Protection mechanisms automatically identify sensitive data and apply appropriate network-level protections. These systems ensure that regulatory requirements for data handling are enforced at the network infrastructure level, regardless of application-specific implementations.
- Network Segmentation and Isolation create logical boundaries that align with regulatory requirements for data separation, system isolation, and operational segregation. Effective segmentation strategies support compliance requirements while maintaining operational efficiency and system performance.
- Encryption and Key Management systems ensure that all network communications and stored data meet regulatory requirements for cryptographic protection. These systems must operate seamlessly within the network infrastructure while providing the auditability and key lifecycle management required by various compliance frameworks.
- Monitoring and Logging Infrastructure captures all network activities in formats suitable for regulatory reporting and audit requirements. These systems must balance comprehensive monitoring with performance considerations while ensuring that log data remains tamper-proof and accessible for compliance reporting.
The BuzzClan Framework: A Unified Approach to Cloud Networking and Compliance
The BuzzClan Framework represents a paradigm shift from traditional approaches that treat compliance and networking as separate disciplines. Our methodology integrates these domains into a unified architecture that treats compliance as a fundamental network design requirement rather than an external constraint.
Core Principles of the BuzzClan Framework
- Compliance by Design ensures that regulatory requirements inform every network architecture decision from initial planning through ongoing operations. Rather than retrofitting compliance controls onto existing networks, this approach builds compliance capabilities into the network foundation.
This principle transforms how organizations approach network design. Instead of asking “How do we make this network compliant?” the question becomes “How do we design a network that cannot be non-compliant?” This shift in perspective leads to fundamentally different architectural choices that prioritize long-term compliance and sustainability over short-term implementation convenience.
- Automated Governance eliminates manual compliance processes that introduce human error and scale limitations. The framework implements policy-driven automation that continuously monitors network behavior, validates configuration changes, and maintains compliance postures without requiring constant human intervention.
Automated governance systems within the BuzzClan Framework utilize machine learning algorithms to identify potential compliance drift before it impacts operations. These systems learn from historical compliance patterns, regulatory updates, and operational changes to provide predictive compliance management that prevents violations rather than merely detecting them after they occur.
- Continuous Validation replaces periodic audit cycles with real-time compliance monitoring that provides immediate feedback on network compliance status. This approach enables organizations to address compliance issues proactively rather than discovering problems during formal audit processes.
The continuous validation component includes automated testing of compliance controls, regular validation of security configurations, and ongoing assessment of network behavior against regulatory requirements. This creates a compliance posture that improves over time rather than degrading between audit cycles.
- Adaptive Architecture enables networks to evolve in response to changing regulatory landscapes without requiring complete redesigns. The framework anticipates regulatory evolution and builds flexibility into network architectures that can accommodate new requirements through configuration updates rather than infrastructure replacements.
Implementation Architecture
The BuzzClan Framework operates through several integrated components that work together to create compliance-driven cloud networking environments.
- Policy Engine serves as the central nervous system that translates regulatory requirements into executable network policies. This engine maintains current versions of applicable regulations, maps regulatory requirements to specific network controls, and generates configuration templates that ensure compliance across all network components.
- Compliance Orchestrator coordinates compliance activities across multi-cloud and hybrid environments. This component ensures that compliance policies are consistently applied regardless of the underlying infrastructure provider while managing the complexity of different cloud platforms and their varying security models.
- Monitoring and Analytics Platform provides real-time visibility into network compliance status through comprehensive dashboards, automated reporting, and predictive analytics. This platform enables compliance teams to understand current compliance postures while identifying trends that may indicate future compliance risks.
- Automated Response System takes immediate action when compliance violations are detected or predicted. This system can automatically remediate certain types of breaches, escalate complex issues to human operators, and maintain detailed logs of all compliance-related activities for audit purposes.
Automation and Compliance Tools
Automated compliance monitoring represents a fundamental shift from reactive to proactive compliance management. Traditional approaches rely on periodic assessments that create windows of unknown compliance status between evaluations. Automated systems provide continuous monitoring that eliminates these blind spots while reducing the operational overhead associated with manual compliance activities.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Integration ensures that compliance requirements are embedded directly into infrastructure provisioning processes. Tools like Terraform, CloudFormation, and Azure Resource Manager templates can include compliance policies that are automatically applied when new network resources are created. This integration creates immutable compliance baselines where infrastructure cannot be deployed without meeting predetermined compliance requirements. Infrastructure changes must pass through compliance validation processes before being applied to production environments.
- Policy Management Platforms provide centralized control over compliance policies across multi-cloud environments. These platforms translate high-level compliance requirements into specific technical controls while maintaining consistency across different cloud providers and network environments. Leading policy management solutions include Open Policy Agent (OPA), HashiCorp Sentinel, and AWS Config Rules. These tools enable organizations to define compliance policies once and apply them consistently across different environments and cloud platforms.
- Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) Integration connects compliance monitoring with incident response processes. When compliance violations are detected, SOAR platforms can automatically initiate remediation procedures, notify relevant stakeholders, and maintain detailed records of compliance incidents.
- Compliance Dashboard and Reporting Tools provide real-time visibility into compliance status across all network components. These tools generate automated reports suitable for regulatory submissions while providing operational teams with actionable insights into compliance trends and potential issues.
- Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning capabilities identify patterns in compliance data that may indicate emerging risks or opportunities for optimization. These systems learn from historical compliance patterns to predict potential violations and recommend preventive measures.
Widely Used Cloud Compliance Standards
- SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2) frameworks focus on five trust service criteria: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. Cloud networks supporting SOC 2 compliance must implement comprehensive logging, access controls, and security monitoring capabilities that demonstrate adherence to these principles.
Network architectures supporting SOC 2 compliance typically implement automated log collection and analysis, role-based access controls with detailed activity monitoring, and incident response procedures that include compliance notification requirements. The dynamic nature of cloud environments requires automated compliance controls that can demonstrate continuous adherence to SOC 2 requirements.
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) imposes specific requirements for networks that process, store, or transmit payment card data. These requirements include network segmentation, encryption, access controls, and monitoring capabilities that must be consistently applied across cloud environments.
Cloud networks supporting PCI DSS compliance often implement network micro-segmentation to isolate payment processing systems, automated vulnerability scanning and patch management, and comprehensive audit logging with tamper-proof storage. The standard’s requirements for quarterly vulnerability scans and annual penetration testing must be integrated into ongoing cloud network operations.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) establishes requirements for protecting healthcare information that directly impact cloud network design. HIPAA compliance requires administrative, physical, and technical safeguards that must be implemented at the network infrastructure level.
Cloud networks supporting HIPAA compliance implement encryption for all data in transit and at rest, comprehensive audit logging with detailed access tracking, and network segmentation that isolates healthcare information from other data types. Business Associate Agreements with cloud providers must clearly define responsibilities for maintaining HIPAA-compliant network environments.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and other privacy regulations impose requirements for data protection, user consent management, and data subject rights that significantly impact cloud network architectures. These regulations require networks to support data portability, deletion requests, and geographic restrictions on data processing.
Networks supporting GDPR compliance implement data discovery and classification systems, automated data retention and deletion capabilities, and geographic routing controls that ensure data remains within appropriate jurisdictions. Privacy by design principles must be embedded into network architectures to support ongoing GDPR compliance.
- ISO 27001/27002 provides comprehensive frameworks for information security management that require systematic approaches to network security, risk management, and compliance monitoring. These standards emphasize continuous improvement and regular assessment of security controls.
- FedRAMP (Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program) establishes specific security requirements for cloud systems used by U.S. federal agencies. FedRAMP compliance requires detailed security control implementation, continuous monitoring, and regular assessment by authorized third parties.
- Regional and Industry-Specific Standards such as PIPEDA in Canada, CCPA in California, and industry-specific regulations in financial services, healthcare, and government sectors create additional compliance requirements that must be integrated into cloud network designs.
Overcoming Challenges with the BuzzClan Framework
- Multi-Cloud Complexity represents one of the most significant challenges in implementing compliance-driven cloud networking. Different cloud providers offer varying security models, compliance certifications, and operational procedures that can create inconsistencies in compliance postures across multi-cloud environments.
The BuzzClan Framework addresses multi-cloud complexity through provider-agnostic policy engines that translate compliance requirements into platform-specific configurations. This approach ensures that compliance controls operate consistently across different cloud platforms while leveraging each provider’s native security capabilities.
- Standardization and Abstraction capabilities within the framework create unified interfaces for managing compliance across different cloud providers. This reduces the operational complexity associated with multi-cloud environments while ensuring that compliance requirements are met regardless of the underlying infrastructure provider.
- Evolving Regulatory Landscapes create ongoing challenges as new regulations are introduced and existing requirements are updated. Organizations must maintain compliance with current rules while preparing for future regulatory changes that may require significant architectural modifications.
The framework’s adaptive architecture anticipates regulatory evolution through modular compliance control implementations that can be updated without requiring complete network redesigns. Regular regulatory monitoring and predictive analysis help organizations prepare for upcoming regulatory changes before they become mandatory.
- Regulatory Intelligence Integration provides automated monitoring of regulatory updates and changes that may impact network compliance requirements. This capability enables organizations to proactively adapt their compliance strategies rather than reactively respond to new regulatory requirements.
- Maintaining Security in Dynamic Cloud Environments requires compliance controls that can operate effectively in environments characterized by elastic scaling, frequent configuration changes, and ephemeral infrastructure components.
The BuzzClan Framework implements immutable compliance baselines that ensure new infrastructure components automatically inherit appropriate compliance controls. This approach eliminates compliance gaps that can occur when infrastructure scales rapidly or when new resources are provisioned without proper security configurations.
Transform Your Cloud Network with BuzzClan’s Integrated Compliance Framework
- Embedding compliance into your network architecture
- Automating regulatory adherence
- Reducing risk while boosting performance
Real-World Implementation Examples
A global financial services organization implemented the BuzzClan Framework to achieve PCI DSS compliance across a multi-cloud environment spanning AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. The implementation included automated network segmentation, encrypted communications channels, and comprehensive audit logging that provided consistent compliance postures across all three cloud providers.
The solution reduced compliance management overhead by 75% while improving audit performance and eliminating previous instances of compliance violations. Automated compliance monitoring provided real-time visibility into compliance status across all cloud environments, enabling the organization to demonstrate continuous compliance to regulatory auditors.
A healthcare technology company utilized the framework to maintain HIPAA compliance while supporting rapid scaling of telehealth services during peak demand periods. The implementation included automated data classification, geographic routing controls, and comprehensive access logging that maintained compliance during periods of significant infrastructure scaling.
Selecting the Right Cloud Providers for Compliance Success
- Shared Responsibility Model Understanding forms the foundation of successful cloud provider selection for compliance-driven networking. Organizations must clearly understand which compliance responsibilities they retain versus those handled by the cloud provider to avoid dangerous compliance gaps.
Different cloud providers offer varying levels of compliance support, ranging from basic infrastructure security to comprehensive compliance management services. Organizations must evaluate provider capabilities against their specific regulatory requirements while considering the operational implications of different shared responsibility models.
- Provider Compliance Certifications serve as important indicators of a cloud provider’s commitment to regulatory compliance, but organizations must understand that certifications alone do not guarantee compliance for specific implementations. Provider certifications demonstrate platform capabilities while customer implementations determine actual compliance outcomes.
Major cloud providers typically maintain certifications for SOC 2, ISO 27001, PCI DSS, HIPAA, and FedRAMP, among others. However, maintaining compliance requires ongoing collaboration between cloud providers and customers to ensure that platform capabilities are correctly configured and utilized.
- BuzzClan’s Partnership Strategy focuses on selecting cloud providers that offer robust compliance capabilities while providing flexibility for implementing custom compliance requirements. Our partnerships with leading cloud providers enable clients to leverage native platform security features while implementing additional compliance controls as needed.
- Multi-Cloud Compliance Considerations require careful evaluation of how compliance controls operate across different cloud platforms. Successful multi-cloud compliance strategies must account for varying provider capabilities, different regulatory certifications, and platform-specific security features.
The BuzzClan Framework includes provider evaluation criteria that assess compliance capabilities, regulatory alignment, and operational compatibility. This evaluation process ensures that selected cloud providers can support long-term compliance objectives while providing the flexibility needed for evolving regulatory requirements.
- Due Diligence and Ongoing Assessment processes ensure that cloud provider compliance capabilities remain aligned with organizational requirements over time. Regular provider assessments, compliance capability reviews, and regulatory alignment evaluations help maintain effective partnerships that support ongoing compliance objectives.
The Role of Cloud Providers in Compliance
- Shared Responsibility Models define the boundaries between cloud provider and customer compliance responsibilities, but these boundaries vary significantly across different service models and providers. Understanding these boundaries is crucial for implementing effective compliance strategies that avoid gaps in coverage.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) models typically assign physical security, network infrastructure, and hypervisor security to cloud providers. At the same time, customers retain responsibility for operating system security, application security, and data protection. Platform as a Service (PaaS) models shift additional responsibilities to providers, while Software as a Service (SaaS) models transfer most technical compliance responsibilities to the provider.
- Provider Compliance Services extend beyond basic platform security to include specialized compliance management tools, automated monitoring capabilities, and regulatory reporting features. Leading cloud providers offer compliance-focused services that can significantly reduce the operational overhead associated with maintaining regulatory compliance.
AWS offers services like Config, CloudTrail, and Security Hub that provide comprehensive compliance monitoring and reporting capabilities. Microsoft Azure includes Azure Policy, Security Center, and Compliance Manager that help organizations maintain compliance across complex cloud environments. Google Cloud Platform provides Security Command Center, Cloud Asset Inventory, and Cloud Security Scanner that support ongoing compliance management.
- Third-party compliance Tools integrate with cloud provider platforms to provide additional compliance capabilities that may not be available through native provider services. These tools often specialize in specific regulatory frameworks or provide multi-cloud compliance management capabilities.
- Vendor Management and Due Diligence processes must include ongoing assessment of cloud provider compliance capabilities and regulatory alignment. Organizations should establish regular review cycles that assess provider compliance postures, evaluate new compliance services, and ensure continued alignment with organizational regulatory requirements.
Continuous Monitoring and Auditing for Ongoing Compliance
- Real-Time Compliance Monitoring transforms compliance from a periodic assessment activity into an ongoing operational capability. Traditional compliance approaches create significant blind spots between audit cycles, while continuous monitoring provides immediate visibility into compliance status and enables proactive issue resolution.
Effective continuous monitoring systems track configuration changes, access patterns, security events, and operational activities that may impact compliance status. These systems provide automated alerting when potential compliance violations are detected while maintaining comprehensive audit trails that support regulatory reporting requirements.
- Automated Audit Trail Generation ensures that all network activities are captured in formats suitable for regulatory reporting and audit requirements. Automated systems eliminate the manual effort associated with preparing audit documentation while ensuring that audit trails are comprehensive, accurate, and tamper-proof.
Modern cloud environments generate enormous volumes of audit data that must be collected, processed, and analyzed to support compliance requirements. Automated systems can filter relevant events, correlate related activities, and generate reports that demonstrate compliance with specific regulatory requirements.
- Compliance Dashboard and Reporting capabilities provide stakeholders with real-time visibility into compliance status across all network components. These dashboards must present complex compliance information in formats that are useful for different audiences, from technical operations teams to executive leadership and regulatory auditors.
Effective compliance dashboards include trend analysis, risk identification, and predictive analytics that help organizations understand not just current compliance status but also potential future compliance risks. These capabilities enable proactive compliance management that prevents violations rather than merely detecting them after they occur.
- Integration with Business Processes ensures that compliance monitoring is embedded into ongoing operational activities rather than existing as a separate, parallel process. This integration reduces the operational overhead associated with compliance while ensuring that compliance considerations are included in all relevant business decisions.
- Regulatory Reporting Automation generates required compliance reports automatically, reducing the time and effort needed for regulatory submissions while improving report accuracy and consistency. Automated reporting systems can produce reports in formats required by different regulatory bodies while ensuring that all the necessary information is included and properly formatted.
Future-Proofing Cloud Networks with Compliance at the Core
- Emerging Regulatory Trends indicate that compliance requirements will continue to evolve in response to technological advances, changing threat landscapes, and growing awareness of privacy and security issues. Organizations must design cloud networks that can adapt to these evolving requirements without requiring complete architectural overhauls.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are creating new regulatory requirements around algorithmic transparency, bias detection, and automated decision-making. Cloud networks supporting AI/ML workloads must implement monitoring and auditing capabilities that can demonstrate compliance with emerging AI governance regulations.
- Privacy-Enhancing Technologies such as differential privacy, homomorphic encryption, and secure multi-party computation are becoming increasingly important for maintaining compliance while enabling advanced data analytics capabilities. Cloud networks must be designed to support these technologies as they become standard components of privacy-compliant architectures.
- Quantum Computing Implications for cryptographic security and compliance are becoming increasingly relevant as quantum computing technologies advance. Organizations must prepare for post-quantum cryptographic requirements while maintaining current compliance obligations during the transition period.
- Zero Trust Architecture Evolution represents a fundamental shift in network security models that aligns well with many regulatory requirements. Compliance-driven networks will likely assume zero trust principles by default, requiring authentication and authorization for every network interaction regardless of location or previous trust relationships.
- Compliance Automation and AI capabilities will continue to evolve, providing more sophisticated tools for managing complex compliance requirements across dynamic cloud environments. Machine learning algorithms will become increasingly capable of predicting compliance risks, optimizing compliance controls, and automating complex compliance decision-making processes.
- Global Regulatory Harmonization efforts may reduce the complexity associated with multi-jurisdictional compliance. Still, organizations must prepare for the possibility that regulatory divergence may continue or even increase in some areas. Cloud network architectures must maintain flexibility to support varying regulatory requirements across different geographic regions and industry sectors.
- BuzzClan’s Innovation Roadmap includes ongoing research and development in emerging compliance technologies, regulatory requirement analysis, and automated compliance management capabilities. Our commitment to staying ahead of regulatory trends ensures that clients can implement future-ready compliance strategies that adapt to evolving regulatory landscapes.
Conclusion
The integration of compliance and cloud networking represents more than a technical evolution—it’s a fundamental shift toward treating regulatory requirements as architectural advantages rather than operational constraints. Organizations that embrace compliance-driven cloud networking gain competitive advantages through superior risk management, operational efficiency, and strategic agility.
The BuzzClan Framework transforms compliance from a reactive burden into a proactive enabler of business innovation. By embedding regulatory requirements directly into network architecture, organizations create self-governing infrastructure that maintains compliance automatically while supporting business growth and technological advancement.
The future belongs to organizations that view compliance as a strategic capability rather than a necessary evil. Those who implement integrated compliance-driven cloud networking today will be positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities while maintaining the trust and regulatory alignment essential for long-term success.
Success in the modern regulatory landscape requires more than meeting current compliance requirements—it demands building adaptive capabilities that can evolve with changing regulatory expectations while delivering superior business outcomes. The BuzzClan Framework provides the foundation for achieving these objectives through intelligent, automated, and future-ready compliance-driven cloud networking.
FAQs

Get In Touch
Follow Us
Table of Contents
- Understanding Integrated Compliance-Driven Cloud Networking
- Pro-Tips for Navigating Cloud Compliance
- Types of Cloud Networking
- Building Regulatory Controls Into Cloud Infrastructure
- The BuzzClan Framework: A Unified Approach to Cloud Networking and Compliance
- Automation and Compliance Tools
- Widely Used Cloud Compliance Standards
- Overcoming Challenges with the BuzzClan Framework
- Real-World Implementation Examples
- Selecting the Right Cloud Providers for Compliance Success
- The Role of Cloud Providers in Compliance
- Continuous Monitoring and Auditing for Ongoing Compliance
- Future-Proofing Cloud Networks with Compliance at the Core
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Get In Touch