AI in Cybersecurity: The What, Why and How
Priya Patel
Oct 29, 2024
Introduction
This comprehensive guide will explore the multifaceted role of AI in enhancing cybersecurity, covering various applications, challenges, and future trends. We’ll delve into how AI technologies are revolutionizing the way we approach digital security, from automating routine tasks to predicting and preventing complex cyber attacks.
In the following sections, we’ll provide an in-depth look at AI in cybersecurity, examining specific use cases, addressing key challenges, and exploring future directions in this rapidly evolving field. Whether you’re a cybersecurity professional, a business leader, or simply interested in the intersection of AI and security, this article will provide valuable insights into AI’s transformative impact on the cybersecurity landscape.
Overview of AI in Cybersecurity
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity refers to using advanced machine learning algorithms, neural networks, and other AI technologies to enhance an organization’s ability to detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats. In this context, AI goes beyond simple rule-based systems, employing sophisticated techniques to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make decisions with minimal human intervention.
The importance of AI in cybersecurity cannot be overstated. As cyber threats become more complex and numerous, traditional security measures need help to keep pace. AI offers the ability to process and analyze enormous volumes of data in real time, identify anomalies that might indicate a threat, and respond faster than any human could. This capability is crucial in an environment where every second counts in preventing or mitigating a cyber attack.
The integration of AI into cybersecurity is not a recent development. The journey began in the late 1980s and early 1990s with the introduction of expert systems and rule-based approaches to security. These early systems laid the groundwork for more advanced AI applications in cybersecurity.
As computing power increased and machine learning algorithms became more sophisticated, the 2000s saw a significant leap in AI capabilities applied to cybersecurity. The advent of big data in the 2010s further accelerated this trend, providing the vast datasets necessary for training advanced AI models.
Today, AI in cybersecurity encompasses a range of technologies, each playing a crucial role in different aspects of digital security:
- Machine Learning (ML): At the heart of many AI cybersecurity solutions, ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies, enabling the detection of known and unknown threats.
- Deep Learning: A subset of machine learning, deep learning uses neural networks with multiple layers to process complex patterns in data. It’s particularly effective in image and speech recognition, which can be applied to biometric authentication and malware detection.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP allows AI systems to understand and analyze human language. Cybersecurity processes and analyzes text-based data, such as emails and social media posts, and detects phishing attempts and social engineering attacks.
- Behavioral Analytics: AI-powered behavioral analytics can learn normal patterns of user and system behavior, allowing for the quick identification of anomalies that may indicate a security breach.
- Automated Reasoning: This AI technology enables systems to make logical deductions and solve problems, crucial for automated threat response and decision-making in security operations.
These AI technologies work together to create robust, adaptive cybersecurity systems capable of defending against various threats. As we move forward, the role of AI in cybersecurity is expected to grow even more significant, with new applications and capabilities emerging to address evolving cyber threats.
Applications of AI in Cybersecurity
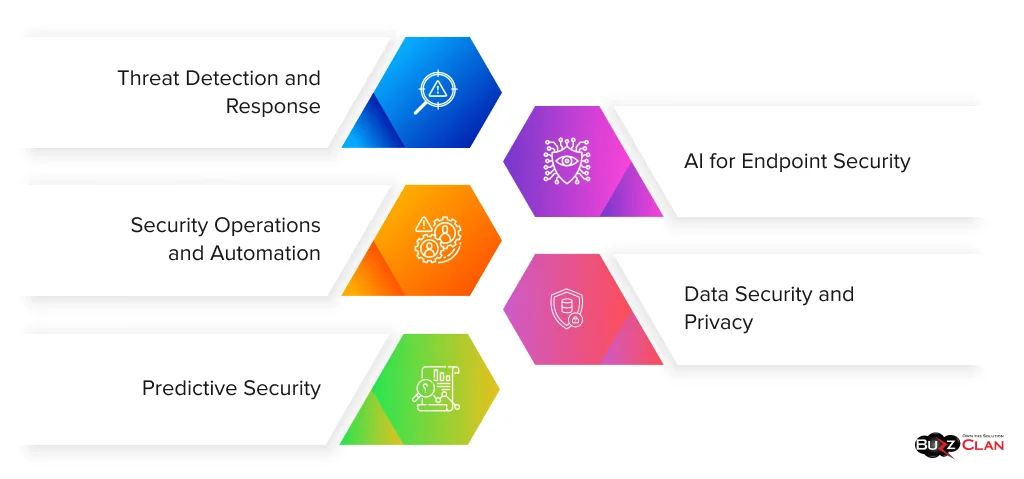
AI has found numerous applications in cybersecurity, revolutionizing how organizations detect, prevent, and respond to threats. Let’s explore some of the key areas where AI is making a significant impact:
Threat Detection and Response
AI excels in threat detection and response, offering capabilities beyond traditional rule-based systems. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, including network traffic, log files, and user behavior, to identify potential threats in real time.
One of AI’s most powerful applications in threat detection is its ability to identify zero-day exploits and previously unknown threats. By learning from historical data and understanding normal behavior patterns, AI systems can flag anomalies that might indicate a new type of attack, even if they don’t match known threat signatures.
AI-powered Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems can correlate events across different network parts, providing a holistic view of the security landscape. This enables faster and more accurate threat detection, reducing the time between initial compromise and detection.
Regarding response, AI systems can automate many aspects of incident response, such as isolating affected systems, blocking malicious IP addresses, or even initiating countermeasures. This rapid response capability is crucial in minimizing the impact of cyber attacks.
AI for Endpoint Security
Endpoint security has become increasingly important as organizations adopt remote work models and bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies. AI plays a crucial role in protecting these endpoints from various threats.
AI-powered endpoint protection platforms use machine learning algorithms to detect and prevent malware infections. Unlike traditional antivirus software that relies on signature-based detection, AI can identify malware based on its behavior, enabling the detection of new and evolving threats.
These systems can also predict potential endpoint vulnerabilities and suggest proactive measures to prevent exploitation. For instance, AI can analyze patterns in software usage and recommend updates or patches before a vulnerability is exploited.
Moreover, AI enhances endpoint detection and response (EDR) capabilities. It can continuously monitor endpoint activity, detect suspicious behavior, and automatically respond to potential threats, such as isolating an infected device from the network.
Security Operations and Automation
AI transforms security operations by automating routine tasks and enhancing security analysts’ capabilities. This automation improves efficiency and allows human experts to focus on more complex, strategic tasks.
AI-powered Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms can automate incident response workflows, reducing response times and ensuring consistent handling of security incidents. These systems can gather information from multiple sources, correlate events, and even initiate predefined response actions without human intervention.
In Security Operations Centers (SOCs), AI assists analysts by prioritizing alerts, reducing false positives, and providing context for faster decision-making. Machine learning algorithms can learn from past incidents and analyst actions to continually improve their recommendations and automate routine responses.
Data Security and Privacy
As data breaches become more frequent and costly, AI plays an increasingly important role in data security and privacy protection. AI systems can monitor data access patterns, detecting and alerting on unusual activities that might indicate a data breach or insider threat.
AI helps organizations comply with data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA. It can automatically classify sensitive data, track its movement, and ensure appropriate access controls are in place. AI-powered data loss prevention (DLP) systems can identify and prevent unauthorized data exfiltration attempts, protecting against malicious actors and accidental data leaks.
Furthermore, AI enhances data encryption techniques. For example, homomorphic encryption, which allows computations on encrypted data without decrypting it, is being advanced through AI research, promising new ways to protect sensitive data while allowing it for analysis.
Predictive Security
One of the most promising applications of AI in cybersecurity is predictive security. By analyzing historical data and current trends, AI systems can forecast potential security incidents and vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to take proactive measures.
AI-powered predictive analytics can identify patterns that might indicate an impending attack, such as increased scanning activity from specific IP ranges or unusual user behavior. This early warning system enables security teams to bolster defenses before an attack occurs.
In addition, AI can predict which systems or applications are most likely to be targeted based on factors like vulnerability data, patch status, and attacker trends. This allows organizations to prioritize their security efforts and allocate resources more effectively.
Predictive security also extends to user behavior. AI systems can learn standard patterns of user activity and predict when a user account might be compromised, enabling preemptive action to prevent unauthorized access.
As these applications demonstrate, AI enhances existing cybersecurity measures and fundamentally changes how we approach digital security. From automated threat detection and response to predictive security, AI enables a more proactive, efficient, and practical approach to cybersecurity.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
To illustrate the practical impact of AI in cybersecurity, let’s examine two detailed case studies and explore notable implementations by significant companies.
Case Study 1: Financial Institution Implements AI-Powered Fraud Detection
A large multinational bank faced increasing challenges in detecting and preventing fraudulent transactions across its global operations. Traditional rule-based systems struggled to keep up with the volume of transactions and the sophistication of modern fraud techniques.
The bank implemented an AI-powered fraud detection system that utilized machine learning and behavioral analytics. The system was trained on historical transaction data, including legitimate and fraudulent transactions, to learn patterns indicative of fraud.
Key features of the AI system included:
- Real-time analysis of transaction data
- Behavioral profiling of account holders
- Anomaly detection based on transaction patterns
- Continuous learning and adaptation to new fraud techniques
Results:
- 60% reduction in false positive alerts
- 85% increase in fraud detection rate
- $50 million in prevented fraudulent transactions in the first year
- Significant reduction in manual review time for security analysts
The AI system’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data in real time and adapt to new fraud patterns proved crucial in staying ahead of sophisticated fraudsters. Moreover, reducing false positives allowed the bank’s security team to focus on genuine threats, improving overall efficiency.
Case Study 2: Manufacturing Company Enhances Industrial Control System Security
A large manufacturing company with multiple facilities worldwide faced increasing cybersecurity risks to its industrial control systems (ICS). The company was concerned about potential disruptions to production processes and the safety implications of a successful cyber attack on its ICS infrastructure.
The company implemented an AI-based anomaly detection system specifically designed for ICS environments. The system combined machine learning with domain-specific knowledge of industrial processes to detect potential security threats and operational anomalies.
Key features of the AI system included:
- Continuous monitoring of ICS network traffic and device behavior
- Baseline modeling of standard operational patterns
- Detection of subtle anomalies that could indicate a cyber attack or system malfunction
- Integration with existing security information and event management (SIEM) systems
Results:
- 75% reduction in time to detect potential security incidents
- Identification of several previously unknown vulnerabilities in ICS devices
- Prevention of a potential significant disruption by early detection of a malware infection
- Improved overall visibility into ICS operations, benefiting both security and operational efficiency
The AI system’s ability to understand the complex interactions within the ICS environment proved invaluable in detecting subtle anomalies that traditional security systems might have missed. This case demonstrates how AI can be effectively applied to secure critical infrastructure and industrial systems.
Notable Implementations by Major Companies
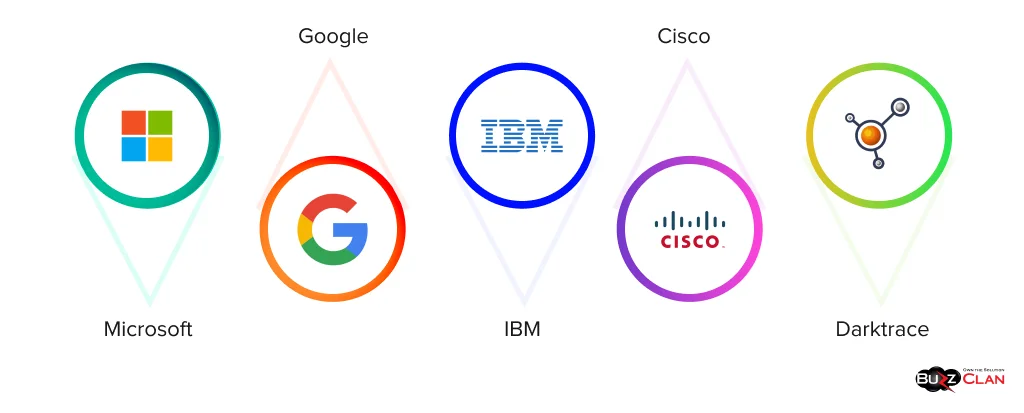
Several major technology companies have made significant strides in implementing AI for cybersecurity:
- Microsoft: Microsoft’s Azure Security Center uses AI to analyze vast amounts of data from various sources to detect threats across cloud workloads. Their AI-powered Advanced Threat Protection service helps organizations investigate and respond to cyber attacks more effectively.
- Google: Google Cloud’s security offerings heavily leverage AI for threat detection and response. Their Chronicle security analytics platform uses machine learning to analyze security telemetry and detect threats at scale.
- IBM: IBM’s Watson for Cyber Security uses natural language processing to analyze vast amounts of unstructured data from research reports, websites, and other sources to provide insights into emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
- Cisco: Cisco’s Stealthwatch uses machine learning algorithms to establish baseline network traffic behavior and detect anomalies that could indicate security threats.
- Darktrace: While not as large as the companies above, Darktrace has made a significant impact with its Enterprise Immune System, which uses AI to learn the ‘pattern of life’ for every user and device on a network to detect and respond to emerging threats in real-time.
These implementations demonstrate how AI is being integrated into cybersecurity solutions at scale, providing enhanced protection against cyber threats. As AI technology advances, we can expect to see even more innovative applications in the cybersecurity field.
Benefits and Challenges of Using AI in Cybersecurity
Integrating AI into cybersecurity brings numerous benefits but presents several challenges that organizations need to navigate. Let’s explore both aspects in detail.
Benefits of AI in Cybersecurity
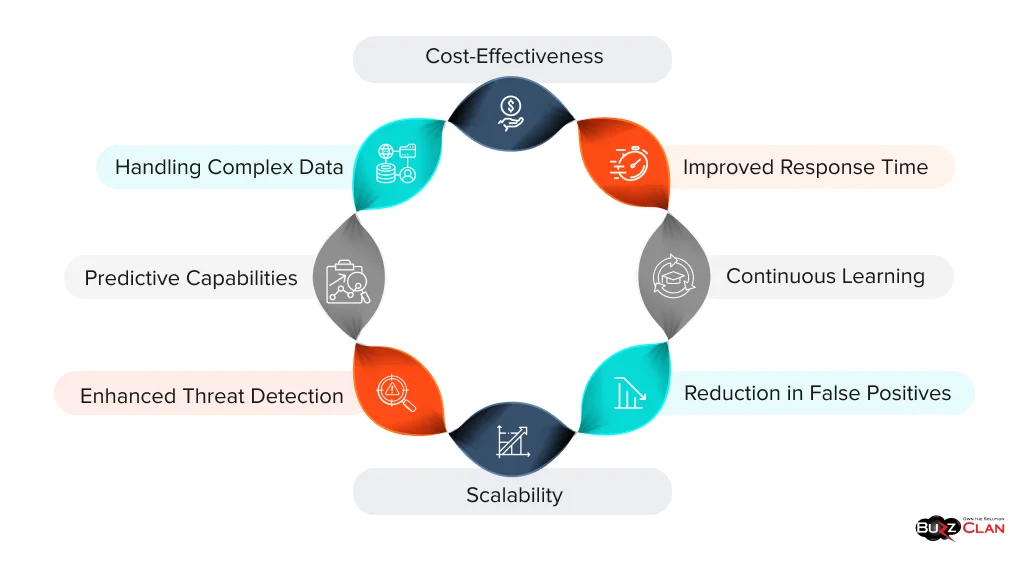
- Enhanced Threat Detection: AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data much faster than humans, enabling the detection of subtle patterns and anomalies that might indicate a security threat. This capability allows for identifying both known and unknown threats in real time.
- Improved Response Time: AI-powered systems can automate many aspects of incident response, significantly reducing the time between threat detection and mitigation. This rapid response capability is crucial in minimizing the impact of cyber attacks.
- Scalability: As data volume and potential threats grow, AI systems can more effectively scale to meet these increasing demands than traditional security measures or human analysts alone.
- Continuous Learning: AI systems can learn from new data and adapt to evolving threats, continuously improving their effectiveness. This adaptability is crucial in the fast-paced world of cybersecurity, where new types of attacks emerge regularly.
- Reduction in False Positives: Advanced AI algorithms can significantly reduce the number of false positive alerts, allowing security teams to focus on genuine threats and improving overall operational efficiency.
- Predictive Capabilities: AI can analyze historical data and current trends to predict potential future threats, enabling organizations to take proactive measures to enhance their security posture.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial investment in AI technology can be significant, it can lead to long-term cost savings by automating routine tasks, improving efficiency, and potentially reducing the impact and frequency of successful cyber attacks.
- Handling Complex Data: AI can process and analyze complex, unstructured data from various sources, providing insights that might be impossible for humans to derive manually.
Challenges of Using AI in Cybersecurity
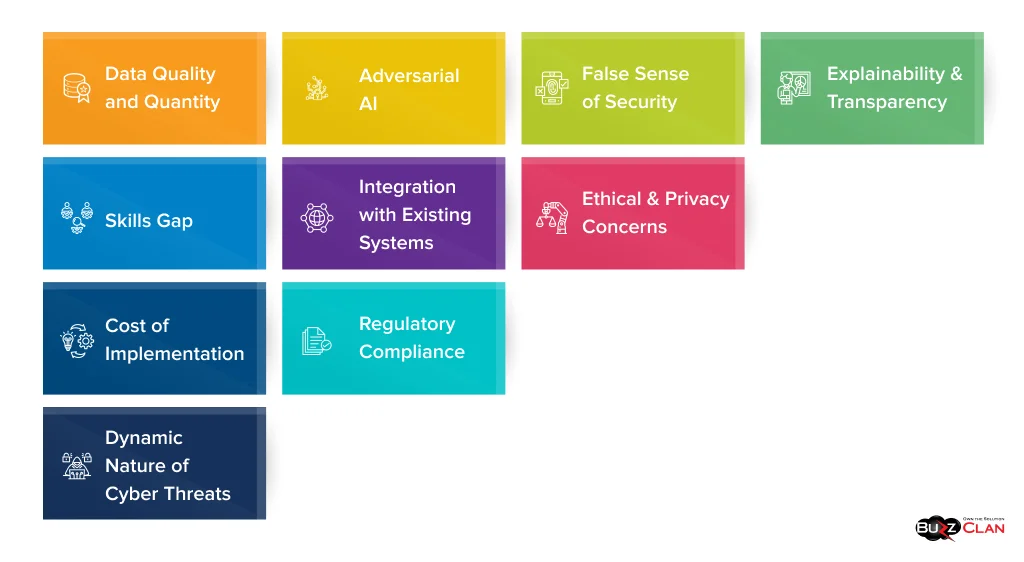
- Data Quality and Quantity: AI systems require large amounts of high-quality data for training. Obtaining sufficient clean, labeled data for training AI models in cybersecurity can be challenging, especially for smaller organizations.
- Adversarial AI: As organizations adopt AI for security, cybercriminals leverage AI to create more sophisticated attacks. This arms race poses ongoing challenges for defensive AI systems.
- False Sense of Security: Over-reliance on AI systems without proper human oversight can lead to a false sense of security. AI should be seen as a tool to augment human expertise, not replace it entirely.
- Explainability and Transparency: Many AI algorithms, particularly deep learning models, operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how they arrive at their decisions. This lack of explainability can be problematic in security contexts where understanding the reasoning behind alerts is crucial.
- Skills Gap: Implementing and maintaining AI-based cybersecurity systems requires specialized skills. More professionals with expertise in both AI and cybersecurity are needed.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating AI-powered security tools with existing cybersecurity infrastructure and workflows can be complex and time-consuming.
- Ethical and Privacy Concerns: The use of AI in security raises ethical questions, particularly around data privacy and the potential for bias in AI decision-making processes.
- Cost of Implementation: While AI can be cost-effective in the long run, the initial investment in AI technology and the expertise required to implement it can be substantial, potentially putting it out of reach for smaller organizations.
- Regulatory Compliance: As AI becomes more prevalent in cybersecurity, organizations must navigate evolving regulations regarding its use, particularly those related to data protection and privacy laws.
- Dynamic Nature of Cyber Threats: The rapidly evolving nature of cyber threats means that AI models must be continuously updated and retrained, which can be resource-intensive.
Navigating these challenges while leveraging AI’s benefits in cybersecurity requires a strategic approach. When implementing AI-based security solutions, organizations must carefully consider their needs, resources, and risk profile. Despite the challenges, AI’s potential benefits in enhancing cybersecurity capabilities make it an increasingly important tool in the fight against cyber threats.
Future of AI in Cybersecurity
As we look towards the future, it’s clear that AI will play an increasingly central role in cybersecurity. The rapid pace of technological advancement and the evolving nature of cyber threats will drive continued innovation in AI-powered security solutions. Let’s explore key emerging trends, ethical considerations, and ongoing research.
Emerging Trends
- AI-Powered Threat Hunting: Future AI systems will become more proactive in seeking out potential threats before they materialize. These systems will combine threat intelligence, behavioral analysis, and predictive analytics to identify and neutralize threats in their earliest stages.
- Autonomous Security Systems: We expect the development of more autonomous AI-driven security systems capable of detecting, analyzing, and responding to threats with minimal human intervention. These systems can make complex real-time decisions, significantly reducing response times.
- AI in Cloud Security: As cloud adoption grows, AI will be crucial in securing cloud environments. Future AI systems will be better equipped to handle the dynamic nature of cloud infrastructure, providing adaptive security that scales with cloud resources.
- AI-Enhanced Encryption: Research on how AI can enhance encryption methods is ongoing. This includes the development of quantum-resistant encryption algorithms and using AI to adjust encryption methods dynamically based on the current threat landscape.
- Cyber-Physical Systems Security: As the Internet of Things (IoT) and industrial control systems become more prevalent, AI will be crucial in securing these cyber-physical systems. Future AI solutions must understand and protect the unique interactions between digital systems and physical processes.
- AI vs. AI: As cybercriminals increasingly leverage AI for attacks, we’ll see the development of more sophisticated AI systems designed to detect and counter AI-powered threats. This will lead to an ongoing arms race between attackers and defenders in AI capabilities.
- Natural Language Processing for Threat Intelligence: Advanced NLP capabilities will enable AI systems to process and analyze vast amounts of unstructured data from threat intelligence sources, providing more comprehensive and timely insights into emerging threats.
Ethical Considerations
As AI becomes more integral to cybersecurity, several ethical considerations come to the forefront:
- Privacy and Data Protection: AI systems often require access to large amounts of data, including potentially sensitive information. Balancing adequate security with individual privacy rights will be an ongoing challenge.
- Algorithmic Bias: AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate or amplify biases in their training data. This could lead to unfair profiling or disproportionate focus on specific threats or user groups in a security context.
- Accountability and Liability: As AI systems become more autonomous in decision-making, questions arise about who is responsible when these systems make errors. Establishing clear lines of accountability will be crucial.
- Transparency and Explainability: Many AI algorithms’ “black box” nature poses challenges where decisions must be explainable and justifiable, such as in legal or regulatory compliance scenarios.
- Dual-Use Concerns: Advanced AI capabilities developed for defensive purposes could be repurposed for malicious use. Managing the dissemination of AI research and technology in cybersecurity will require careful consideration.
- Human Displacement: While AI enhances cybersecurity capabilities, it may also lead to job displacement in certain areas. Addressing the societal impacts of this shift will be important.
Innovations and Research
Ongoing research and innovation in AI for cybersecurity are focused on several key areas:
- Adversarial Machine Learning: Researchers are working on making AI models more robust against adversarial attacks, where malicious actors attempt to manipulate AI systems by exploiting vulnerabilities in their training or input data.
- Federated Learning: This approach allows AI models to be trained across multiple decentralized devices or servers holding local data samples without exchanging them. This could enable more privacy-preserving AI solutions in cybersecurity.
- Explainable AI: Efforts are underway to develop AI models that clearly explain their decisions. This is particularly important in cybersecurity, where understanding the reasoning behind threat detection is crucial.
- Quantum-Safe Cryptography: With the looming threat of quantum computers potentially breaking current encryption methods, research is ongoing into developing quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms, with AI playing a role in this development.
- AI for Insider Threat Detection: Advanced AI models are being developed to detect insider threats by analyzing patterns in user behavior, network activity, and data access.
- Cognitive Security: This emerging field combines AI with human cognition and psychological insights to create more effective security solutions to anticipate and counter human-centric attacks like social engineering.
- AI-Powered Deception Technology: Research explores how AI can enhance deception technologies (like honeypots) to create more convincing decoys and traps for attackers, gathering valuable threat intelligence.
As these trends, ethical considerations and research areas demonstrate, the future of AI in cybersecurity is both exciting and complex. While AI promises to significantly enhance our ability to defend against cyber threats, it also introduces new challenges that will require ongoing attention and innovation to address.
The cybersecurity landscape of the future will likely be characterized by highly sophisticated AI systems engaged in a constant battle of wits, with human experts providing crucial oversight, strategic direction, and ethical guidance. As we move forward, the successful integration of AI into cybersecurity will depend on technological advancements and our ability to navigate the ethical, legal, and societal implications of these powerful technologies.
Implementing AI in Cybersecurity
Many want to implement these technologies as organizations recognize AI’s potential to enhance their cybersecurity posture. However, integrating AI into existing security frameworks can be a complex process. Here’s a guide to help organizations get started, with best practices and an overview of popular tools and platforms.
Getting Started
- Assess Your Current Security Posture: Before implementing AI, conduct a thorough assessment of your current cybersecurity infrastructure, processes, and capabilities. Identify areas where AI could have the most significant impact.
- Define Clear Objectives: Determine what you want to achieve with AI in your cybersecurity strategy. This could include improving threat detection, reducing false positives, automating incident response, or enhancing overall security operations efficiency.
- Data Readiness: AI systems require high-quality, relevant data for training and operation. Evaluate your data collection and management practices to ensure you have the necessary data to support AI implementation.
- Start Small: Begin with a pilot project or proof of concept in a specific area, such as email security or network anomaly detection. This allows you to gain experience and demonstrate value before scaling up.
- Build a Cross-Functional Team: Successful AI implementation requires collaboration between cybersecurity experts, data scientists, and IT professionals. Form a team that combines these skill sets.
- Choose the Right Solution: Based on your objectives and resources, select an AI solution that fits your needs. This could be a commercial off-the-shelf product, a custom-developed solution, or a combination of both.
- Plan for Integration: Develop a strategy for integrating the AI solution with your existing security tools and workflows. Consider how it will interact with your SIEM, firewalls, endpoint protection, and other security systems.
- Invest in Training: Ensure your team has the skills to work with AI systems. This may involve training existing staff or hiring new talent with AI expertise.
Best Practices for Integrating AI in Cybersecurity
| Best Practices | Description |
|---|---|
| Maintain Human Oversight | While AI can automate many tasks, human expertise remains crucial. Establish clear human oversight and decision-making processes, especially for critical security actions. |
| Continuously Monitor and Tune | AI models need ongoing monitoring and tuning to maintain effectiveness. Regularly review the performance of your AI systems and adjust as necessary. |
| Keep AI Models Updated | Cyber threats evolve rapidly. Ensure your AI models are regularly updated with the latest threat intelligence and retrained on new data to stay effective against emerging threats. |
| Prioritize Explainability | Use AI models that explain their decisions where possible. This is crucial for building trust in the system and for compliance purposes. |
| Implement Strong Data Governance | Ensure you have robust data governance practices to protect the data used by your AI systems, including data used for training and operation. |
| Balance Automation and Human Intervention | While AI can automate many tasks, define clear thresholds for when human intervention is required, especially for high-impact decisions. |
| Consider Ethical Implications | Consider the ethical considerations of using AI in cybersecurity, particularly regarding privacy and potential biases. Develop guidelines for ethical AI use in your organization. |
| Stay Informed | AI in cybersecurity is rapidly evolving. Stay informed about the latest developments, best practices, and regulatory requirements. |
Top AI Tools and Platforms for Cybersecurity Integration
Several tools and platforms are available for organizations looking to implement AI in their cybersecurity strategies:
- IBM QRadar: This SIEM solution uses AI to analyze log data and network flows to detect threats and anomalies.
- Darktrace: Offers an AI-powered “Enterprise Immune System” that learns normal behavior patterns to detect anomalies and potential threats.
- Cylance: Provides AI-based endpoint protection, using machine learning to predict and prevent malware and advanced threats.
- Vectra Cognito: Uses AI to automate threat detection and response in cloud and data center workloads.
- Splunk: Incorporates machine learning into its data analysis platform for security monitoring and anomaly detection.
- Microsoft Azure Security Center: Leverages AI for threat protection across hybrid cloud workloads.
- Crowdstrike Falcon: Uses AI and machine learning for endpoint protection and threat intelligence.
- LogRhythm NextGen SIEM: Incorporates AI for advanced analytics and automated response in its SIEM platform.
- Exabeam: Offers a security management platform that uses machine learning for user and entity behavior analytics.
- Recorded Future: Utilizes machine learning and natural language processing for threat intelligence and analysis.
When selecting tools, consider integration capabilities with your existing infrastructure, scalability, customization options, and the vendor’s track record in AI and cybersecurity.
Implementing AI in cybersecurity is a journey that requires careful planning, ongoing effort, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By following these guidelines and best practices, organizations can harness the power of AI to significantly enhance their cybersecurity capabilities, staying ahead of evolving threats in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
Conclusion
The benefits of AI in cybersecurity are clear: improved threat detection accuracy, faster response times, enhanced scalability, and the ability to handle complex, high-volume data analysis. These capabilities are crucial in an era where cyber threats constantly evolve and grow in number and complexity.
However, integrating AI into cybersecurity has its challenges. Data quality, the potential for adversarial AI, the need for explainability, and ethical considerations must be carefully navigated. Moreover, the successful implementation of AI in cybersecurity requires not just technological solutions but also strategic planning, skilled personnel, and a commitment to ongoing learning and adaptation.
Looking to the future, we can expect AI to play an even more central role in cybersecurity. Emerging trends such as AI-powered threat hunting, autonomous security systems, and the use of AI in securing cyber-physical systems promise to enhance our defensive capabilities further. At the same time, ongoing research in areas like adversarial machine learning, explainable AI, and quantum-safe cryptography will help address current limitations and challenges.
For organizations considering implementing AI in their cybersecurity strategies, it’s crucial to approach this journey with careful planning and a clear understanding of both the potential benefits and the challenges involved. Starting with a clear assessment of current capabilities, defining specific objectives, and beginning with focused pilot projects can pave the way for successful AI integration.
Ultimately, while AI represents a powerful tool in the fight against cyber threats, it’s important to remember that it’s not a silver bullet. The most effective cybersecurity strategies will continue to combine AI’s analytical power and speed with human expertise, creativity, and ethical judgment.
As we progress in this AI-enhanced cybersecurity landscape, ongoing collaboration between technologists, security professionals, policymakers, and ethicists will be crucial. By working together, we can harness AI’s full potential to create a safer digital world while addressing these powerful technologies’ complex challenges and ethical considerations.
Integrating AI into cybersecurity represents a technological shift and a fundamental change in how we approach digital security. As cyber threats continue to evolve, so too must our defenses. With its ability to learn, adapt, and operate at machine speed, AI offers a promising path forward in this ongoing battle. By embracing these technologies responsibly and thoughtfully, we can build more resilient, responsive, and effective cybersecurity systems better equipped to protect our digital assets and infrastructure in an increasingly connected world.
FAQs

Get In Touch
