The Ultimate Guide to Optimizing Your Staffing Process: 8 Steps to Success
Ety Garg
Jun 12, 2024
Introduction
An effective staffing process is the backbone of any successful organization. It ensures that people with the right skills are in the right positions at the right time. A well-designed staffing process helps attract and retain top talent and aligns the workforce with the organization’s strategic goals. In today’s competitive business landscape, having a robust staffing process is more critical than ever.
This comprehensive blog post will explore the world of staffing, its definition, the eight essential steps, best practices, and specific considerations for IT staffing. Whether you are an HR professional, a hiring manager, or a business owner, this guide will provide valuable insights and practical tips to optimize your staffing process and build a high-performing workforce.
Throughout this blog, we will cover the key aspects of the staffing process, from workforce planning and job analysis to recruitment, selection, and onboarding. We will also discuss the unique challenges and strategies specific to IT staffing, recognizing the crucial role of technology professionals in driving business success. By the end of this post, you will have a solid understanding of how to design and implement an effective staffing process that aligns with your organizational objectives.
What is the Staffing Process?
The staffing process is a systematic approach to finding, selecting, and onboarding the most qualified candidates for an organization. It encompasses a series of steps designed to ensure that the right people are hired for the right positions at the right time and in the right quantities. The staffing process is a critical component of human resources management, as it directly impacts an organization’s ability to achieve its goals and maintain a competitive edge.
An effective staffing process aims to:
- Identify and assess the organization’s current and future workforce needs
- Attract a diverse pool of qualified candidates
- Select the most suitable candidates based on job requirements and organizational fit
- Onboard and train new hires to ensure their success in their roles
- Continuously evaluate and improve the staffing process to adapt to changing business needs
The 8 Steps of the Staffing Process
The staffing process has eight essential steps, each crucial to building a high-performing workforce. Let’s explore each step in detail.
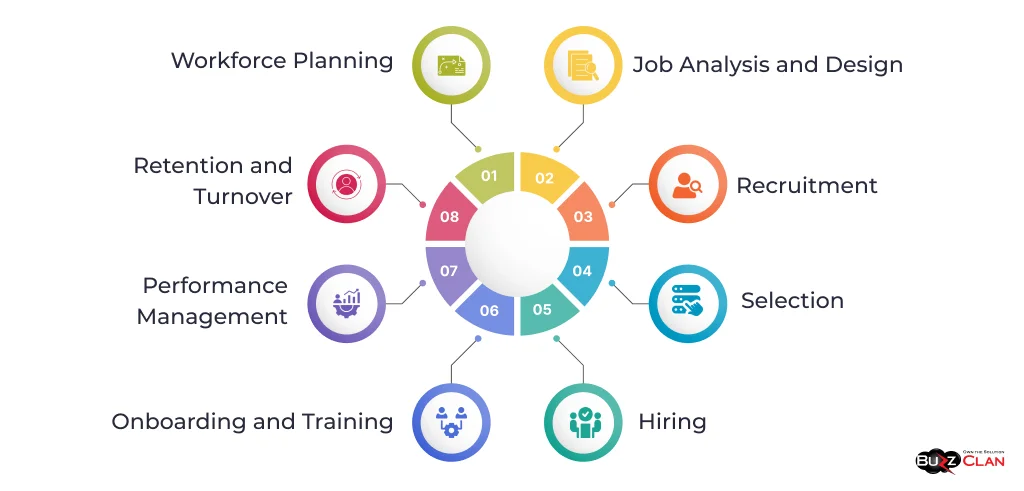
Step 1: Workforce Planning
Workforce planning is the foundation of the staffing process. It involves assessing the organization’s current workforce, identifying future staffing needs, and developing strategies to bridge gaps. This step requires a thorough understanding of the organization’s strategic goals, industry trends, and anticipated changes in the business environment.
Key activities in workforce planning include:
- Analyzing the current workforce composition and skills inventory
- Forecasting future staffing requirements based on business objectives and growth projections
- Identifying potential skill gaps and talent shortages
- Developing strategies to address staffing needs, such as recruitment, training, or succession planning
Step 2: Job Analysis and Design
Once the workforce planning is complete, the next step is to analyze and design the job roles that need to be filled. Job analysis involves gathering information about a job’s duties, responsibilities, and requirements. This information is used to create job descriptions and specifications, the foundation for recruitment and selection.
Key activities in job analysis and design include:
- Conducting job analysis through interviews, questionnaires, and observations
- Defining the essential functions, tasks, and responsibilities of each job
- Identifying the knowledge, skills, and abilities required for successful job performance
- Creating detailed job descriptions and specifications
Step 3: Recruitment
Recruitment is the process of attracting a pool of qualified candidates for the job openings identified in the workforce planning stage. It involves creating job postings, advertising open positions, and actively seeking out potential candidates through various channels.
Key activities in recruitment include:
- Developing a recruitment strategy based on the job requirements and target candidate profile
- Creating compelling job postings and advertisements
- Leveraging various recruitment channels, such as job boards, social media, employee referrals, and recruitment agencies
- Building a strong employer brand to attract top talent
Step 4: Selection
The selection step involves evaluating the pool of candidates generated during the recruitment phase and choosing the most suitable individuals for the job. This step typically includes several stages: resume screening, interviews, assessments, and reference checks.
Key activities in selection include:
- Screening resumes and applications to identify candidates who meet the minimum job requirements
- Conducting interviews to assess candidates’ skills, experience, and fit with the organization’s culture
- Administering job-related assessments or tests to evaluate candidates’ abilities and potential
- Conducting reference checks and background investigations to verify candidates’ information and suitability
Step 5: Hiring
Once the most suitable candidate is identified, the hiring step involves making a job offer and completing the necessary paperwork. This step also includes negotiating compensation and benefits and meeting all legal and regulatory requirements.
Key activities in hiring include:
- Extending a job offer to the selected candidate
- Negotiating compensation, benefits, and other terms of employment
- Conducting pre-employment screenings, such as drug tests or medical examinations, if required
- Completing the necessary paperwork, such as employment contracts and tax forms
Step 6: Onboarding and Training
Onboarding and training are critical in helping new hires integrate into the organization and become productive team members. Onboarding involves orienting new employees to the company’s culture, policies, and procedures, while training provides them with the skills and knowledge necessary to perform their jobs effectively.
Key activities in onboarding and training include:
- Develop a comprehensive onboarding program that covers the company’s history, mission, values, and policies
- Assigning mentors or buddies to help new hires navigate the organization and build relationships
- Providing job-specific training to ensure new employees have the necessary skills and knowledge to succeed
- Setting clear expectations and goals for new hires’ performance and development
Step 7: Performance Management
Performance management is an ongoing process that involves setting goals, providing feedback, and evaluating employees’ contributions to the organization. This step ensures employees meet expectations and continuously improve their skills and performance.
Key activities in performance management include:
- Setting clear, measurable goals and objectives for each employee
- Providing regular feedback and coaching to help employees improve their performance
- Conducting periodic performance evaluations to assess employees’ progress and identify areas for development
- Recognizing and rewarding high-performing employees to boost motivation and retention
Step 8: Retention and Turnover
The final step in the staffing process is managing retention and turnover. While some turnover is inevitable, high turnover rates can be costly and disruptive to the organization. Effective retention strategies help keep top talent engaged and committed to the organization.
Key activities in retention and turnover management include:
- Identifying the root causes of turnover through exit interviews and surveys
- Developing retention strategies, such as competitive compensation, career development opportunities, and work-life balance initiatives
- Creating a positive work environment that fosters engagement, collaboration, and recognition
- Continuously monitoring and analyzing turnover rates to identify trends and areas for improvement
Recruitment and Selection in the Staffing Process
Recruitment and selection are two critical steps in the staffing process that directly impact the quality of new hires. Let’s examine these steps and the strategies involved.
Recruitment Strategies
Effective recruitment strategies are essential for attracting a diverse pool of qualified candidates. Some common recruitment strategies include:

- Employee referrals: Encouraging current employees to refer candidates from their professional networks
- Job boards and online platforms: Posting job openings on popular job search websites and industry-specific platforms
- Social media recruiting: Leveraging social media platforms, such as LinkedIn, to reach out to potential candidates and promote job openings
- Campus recruiting: Partnering with universities and colleges to attract fresh talent
- Recruitment events: Participating in job fairs, industry conferences, and other events to meet potential candidates in person
Selection Methods
Once a pool of candidates has been generated through recruitment efforts, the next step is to evaluate and select the most suitable individuals for the job. Some common selection methods include:
- Resume screening: Reviewing resumes and applications to identify candidates who meet the minimum job requirements
- Interviews: Conducting structured or unstructured interviews to assess candidates’ skills, experience, and fit with the organization’s culture
- Assessments and tests: Administering job-related assessments, such as personality tests, cognitive ability tests, or technical skill tests, to evaluate candidates’ potential
- Reference checks: Contacting candidates’ references to verify their work history, skills, and character
- Background checks: Conducting background investigations, such as criminal record checks or credit checks, to ensure candidates’ suitability for the position
IT Staffing Process
The IT staffing process presents unique challenges and considerations due to the rapidly evolving nature of technology and the high demand for skilled IT professionals.
Unique Challenges
Some of the unique challenges faced in the IT staffing process include:
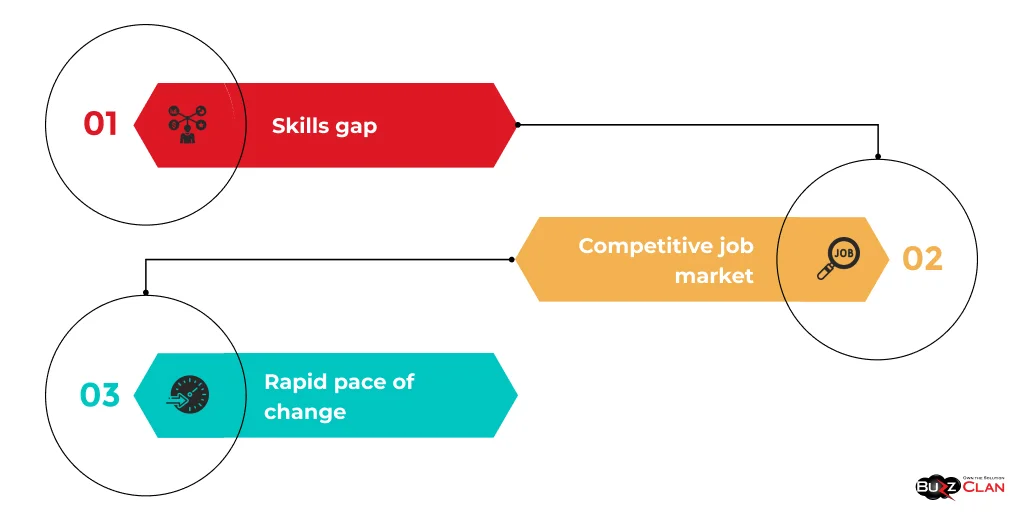
- Skills gap: The technology landscape is constantly changing, making it difficult to find candidates with the latest skills and expertise
- Competitive job market: High demand for IT professionals leads to intense competition for top talent
- Rapid pace of change: IT roles and requirements can change quickly, requiring a flexible and adaptable staffing process
Specialized Skills
IT staffing often requires identifying and recruiting candidates with specialized skills, such as:
- Programming languages and frameworks
- Cloud computing and infrastructure
- Cybersecurity and data protection
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning
- DevOps and agile methodologies
IT Recruitment Strategies
To overcome these challenges and attract top IT talent, organizations can employ specific recruitment strategies, such as:
- Emphasizing the organization’s technology stack and innovative projects in job postings
- Partnering with technology schools and boot camps to identify promising candidates
- Offering competitive compensation packages and benefits, such as flexible work arrangements or professional development opportunities
- Building a strong employer brand that showcases the organization’s technology culture and values
Best Practices for an Effective Staffing Process
Organizations should follow best practices that promote fairness, efficiency, and continuous improvement to ensure a successful staffing process.
Diversity and Inclusion
Promoting diversity and inclusion in staffing is a legal and ethical imperative and a business advantage. Diverse teams bring a wider range of perspectives and experiences, leading to better decision-making and innovation.
Best practices for promoting diversity and inclusion in staffing include:
- Using inclusive language in job postings and eliminating bias in job requirements
- Conducting blind resume screening to minimize unconscious bias
- Providing diversity and inclusion training for hiring managers and interviewers
- Setting diversity goals and regularly monitoring and reporting on progress
Continuous Improvement
The staffing process should be continuously evaluated and improved to adapt to changing business needs and candidate expectations. Regular feedback from hiring managers, new hires, and other stakeholders can provide valuable insights into areas for improvement.
Best practices for continuous improvement in staffing include:
- Establishing metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of the staffing process
- Conducting surveys and interviews to gather feedback from candidates and new hires
- Regularly reviewing and updating job descriptions and requirements to ensure they remain relevant
- Investing in technology and tools to streamline and automate parts of the staffing process
Technology and Tools
Technology is increasingly important in staffing, from applicant tracking systems (ATS) to video interviewing platforms. These tools can help organizations manage large volumes of candidates, reduce time-to-hire, and improve the overall candidate experience.
Best practices for leveraging technology in staffing include:
- Implementing an ATS to streamline candidate management and communication
- Using video interviewing platforms to screen candidates remotely and efficiently
- Leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning tools to automate resume screening and candidate matching
- Investing in data analytics to gain insights into the staffing process and make data-driven decisions
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The staffing process is subject to various legal and ethical considerations, such as equal employment opportunity laws, data privacy regulations, and fair hiring practices. Organizations must ensure compliance with these requirements to avoid legal risks and maintain a positive reputation.
Best practices for legal and ethical staffing include:
- Ensuring that all hiring practices comply with equal employment opportunity laws and regulations
- Protecting candidate and employee data by data privacy regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA
- Providing training on legal and ethical hiring practices for all individuals involved in the staffing process
- Conducting regular audits to ensure compliance and identify potential risks
Conclusion
Throughout this blog post, we have explored the key aspects of the staffing process, including recruitment and selection strategies, best practices for IT staffing, and the importance of diversity, continuous improvement, technology, and legal compliance. Organizations can gain a competitive edge in today’s rapidly changing business landscape by implementing these best practices and continuously evaluating and improving their staffing process.
FAQs

Get In Touch