Mastering SAFe: Your Roadmap to Scaling Agile for Enterprise Success
Vishal Sharma
Dec 10, 2024
Introduction
As complex projects grow and teams expand, traditional Agile methodologies may struggle to keep pace. This is where the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) comes into play. SAFe is a comprehensive framework designed to help large enterprises scale Agile practices across multiple teams and departments, enabling them to deliver value faster and more efficiently.
Implementing SAFe offers numerous benefits, including improved alignment between business and IT, faster time-to-market, enhanced product quality, and increased employee engagement. By adopting SAFe, organizations can achieve the agility and adaptability needed to thrive in today's competitive landscape.
In this blog post, we will dive deep into the world of SAFe. We will start by understanding the framework's definition, purpose, and evolution. Next, we will explore its core values, principles, key components, and configurations. We will also provide a roadmap for implementing SAFe, discuss certification and training options, and share real-world case studies. Additionally, we will cover advanced topics, compare SAFe with other frameworks, and look at the future trends shaping the world of scaled Agile. By the end of this post, you will have a comprehensive understanding of SAFe and how it can benefit your organization.
Understanding the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe)
The Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) is a knowledge base of proven, integrated principles, practices, and competencies for achieving business agility using Lean, Agile, and DevOps. It provides a structured approach to scaling Agile practices beyond individual teams, enabling organizations to deliver value on a larger scale.
The primary objective of SAFe is to align and synchronize the efforts of multiple Agile teams, ensuring that they work towards a common goal and deliver value incrementally. By providing a shared language, common processes, and a clear roadmap, SAFe helps organizations overcome the challenges of scaling Agile, such as coordination, communication, and dependencies.
SAFe's creator, Dean Leffingwell, began exploring ways to scale Agile practices in the early 2000s. The first official version of SAFe was released in 2011, and since then, it has undergone several updates and iterations. The current version, SAFe 5.0, was released in 2020 and introduces new concepts, such as the Continuous Learning Culture and Organizational Agility.
Core Values and Principles
SAFe is built upon four core values that guide decision-making and behavior within the framework:
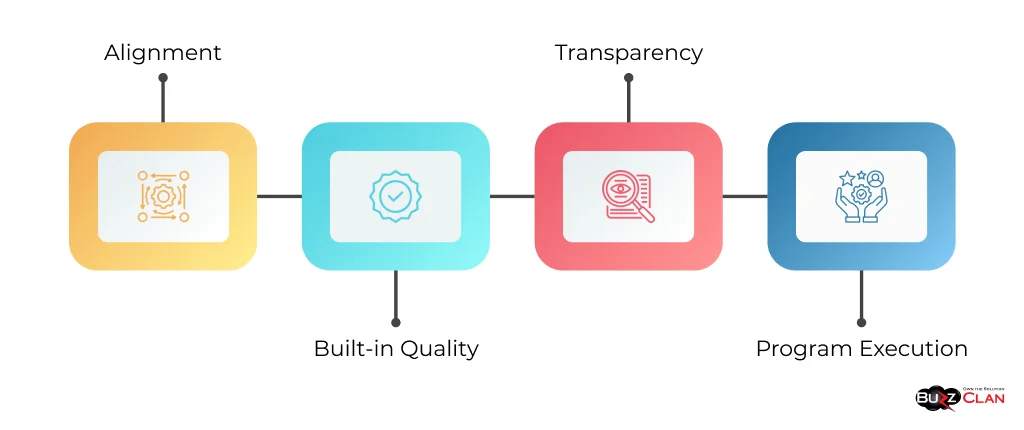
- Alignment: Ensuring that everyone in the organization works towards a common goal and understands how their work contributes to the bigger picture.
- Built-in Quality: Integrating quality practices throughout development emphasizes the importance of delivering high-quality products and services.
- Transparency: Promoting open communication, visibility, and trust among teams and stakeholders.
- Program Execution: Focusing on delivering value incrementally and continuously while adapting to changing market conditions and customer needs.
In addition to the core values, SAFe is guided by ten principles that provide a foundation for successful implementation. These principles include:
- Take an economic view
- Apply systems thinking
- Assume variability; preserve options
- Build incrementally with fast, integrated learning cycles
- Base milestones on an objective evaluation of working systems
- Visualize and limit work-in-progress, reduce batch sizes, and manage queue lengths
- Apply cadence, synchronize with cross-domain planning
- Unlock the intrinsic motivation of knowledge workers
- Decentralize decision-making
- Organize around value
Each principle guides teams and organizations toward achieving business agility and consistently delivering value.
Key Components of SAFe
SAFe consists of several key components that work together to enable scaling Agile practices across the organization:
Roles and Responsibilities:
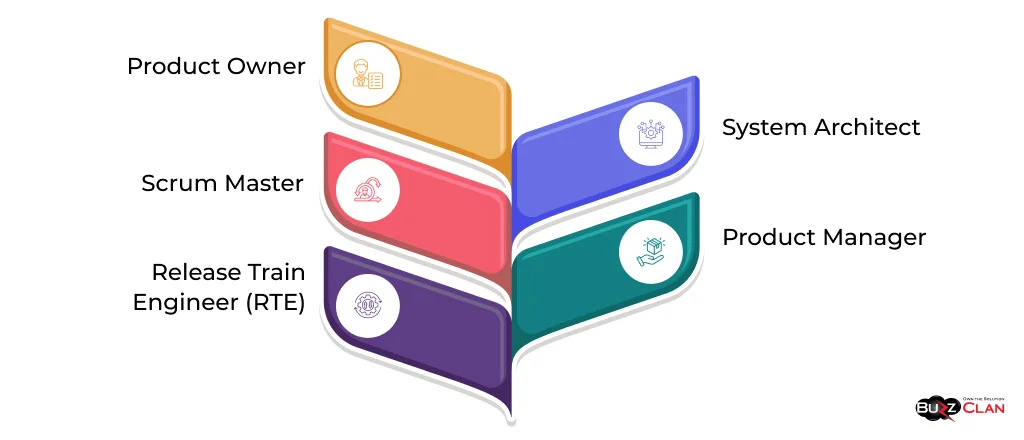
- Product Owner: This person is responsible for defining and prioritizing the product backlog and ensuring the team delivers value to the customer.
- Scrum Master: Facilitates the Agile process, removes impediments, and coaches the team on Agile practices.
- Release Train Engineer (RTE): This person facilitates the Agile Release Train (ART), ensuring the teams are aligned and working towards a common goal.
- System Architect: Defines the solution's overall architecture and technical direction.
- Product Manager: This person owns the product vision and roadmap and works closely with the Product Owner to define and prioritize features.
Artifacts and Events:
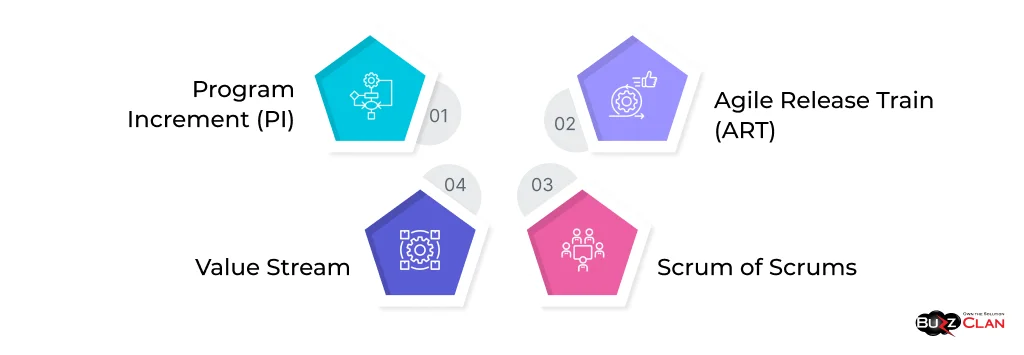
- Program Increment (PI): Planning is a periodic event in which multiple teams come together to plan and synchronize their work for the upcoming increment.
- Agile Release Train (ART): A virtual organization consisting of multiple Agile teams that work together to deliver a common solution.
- Scrum of Scrums: A coordination meeting where representatives from each team meet to discuss progress, impediments, and cross-team dependencies.
- Value Stream: An organization's sequence of steps to deliver value to the customer, from concept to cash.
These components form the foundation of SAFe and enable organizations to scale Agile practices across multiple teams and departments.
SAFe Configurations
SAFe offers four configurations to suit the needs of different organizations:
Essential SAFe is the most basic configuration, suitable for organizations starting their Agile journey. It focuses on the core elements of SAFe, such as the Agile Release Train (ART), Program Increment (PI) Planning, and Scrum of Scrums.
- Large Solution SAFe: Designed for organizations building large, complex solutions that require coordination across multiple ARTs. It introduces additional roles and practices, such as Solution Management and Solution Train.
- Portfolio SAFe: Aligns the organization's strategy with execution by providing a framework for managing multiple value streams and solutions. It includes Lean Portfolio Management and Epics to ensure the organization invests in the right initiatives.
- Full SAFe: The most comprehensive configuration, suitable for large enterprises looking to achieve business agility across the entire organization. It includes all the elements of Essential, Large Solution, and Portfolio SAFe, along with additional practices for Lean-Agile leadership and continuous learning.
Organizations can choose the configuration that best fits their needs and gradually scale up as they mature in their Agile journey.
Implementation Roadmap
Implementing SAFe is a significant undertaking that requires careful planning and execution. The SAFe implementation roadmap provides a structured approach to help organizations navigate the process:
Steps to Implement SAFe:
- Train and educate the team: Provide SAFe training to key stakeholders, including executives, managers, and team members.
- Identify value streams and ARTs: Map out the organization's value streams and identify the ARTs needed to deliver value.
- Launch ARTs: Conduct PI Planning to synchronize the work of multiple teams and launch the ARTs.
- Establish Lean Portfolio Management: Implement Lean Portfolio Management to align strategy with execution and ensure that the organization invests in the right initiatives.
- Implement Continuous Delivery: Establish a pipeline for frequent releases and faster time-to-market.
- Sustain and improve: Continuously assess and improve the SAFe implementation, using metrics and feedback loops to drive performance.
Common Challenges and Solutions:
- Resistance to change: Address resistance by communicating the benefits of SAFe, involving stakeholders in the process, and celebrating successes.
- Lack of leadership buy-in: Engage leaders by demonstrating the business value of SAFe and providing them with the necessary training and support.
- Inadequate training: Invest in comprehensive training programs to ensure everyone understands their roles and responsibilities within the SAFe framework.
- Silos and lack of collaboration: Break down silos by fostering cross-functional collaboration, encouraging open communication, and aligning teams around common goals.
Best practices for successful SAFe implementation include starting small, securing leadership support, investing in training and coaching, and continuously assessing and improving the process.
Certification and Training
SAFe certification is essential for individuals and organizations looking to demonstrate their expertise in the framework and drive successful implementations. The Scaled Agile Academy offers several certification paths, including:
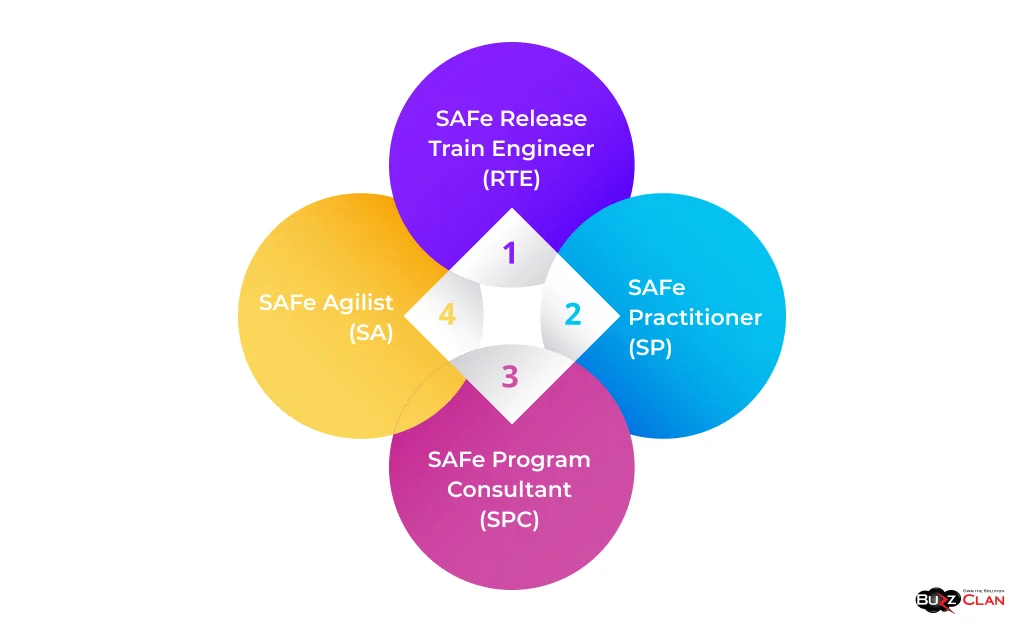
- SAFe Agilist (SA): This is an entry-level certification for individuals who want to understand the basics of SAFe and how to apply it in their organization.
- SAFe Practitioner (SP): This is an intermediate-level certification for individuals who want to deepen their understanding of SAFe and learn how to implement it in their teams and programs.
- SAFe Program Consultant (SPC): Advanced-level certification for individuals who want to lead SAFe implementations and provide coaching and guidance to organizations.
- SAFe Release Train Engineer (RTE): This certification is for individuals who want to serve as RTEs and facilitate the execution of ARTs.
In addition to certification, the Scaled Agile Academy offers a range of training courses, including Leading SAFe, Implementing SAFe, and SAFe for Teams. These courses provide hands-on experience and practical guidance on how to apply SAFe in various roles and contexts.
Investing in SAFe certification and training can be a significant cost, but it offers substantial value in improved agility, faster time to market, and enhanced product quality. Organizations prioritizing SAFe training and certification are better equipped to drive successful implementations and achieve their business goals.
Case Studies and Examples
Many organizations have successfully implemented SAFe and achieved significant benefits as a result. Here are a few real-world examples:
- Bosch: The global engineering and technology company implemented SAFe to improve collaboration and alignment across its hundreds of teams. As a result, they reduced time-to-market by 50%, increased productivity by 30%, and improved quality by 20%.
- Philips: The healthcare technology company adopted SAFe to scale Agile across its product development organization. They achieved a 50% reduction in time-to-market, a 25% increase in productivity, and improved customer satisfaction.
- LEGO: The toymaker used SAFe to align its business and IT teams and deliver value faster. They reduced time-to-market by 20%, increased productivity by 30%, and improved employee engagement.
Key lessons from these case studies include the importance of leadership buy-in, the need for comprehensive training and coaching, and the value of starting small and scaling gradually. By studying these examples, organizations can gain valuable insights into implementing SAFe and achieving similar benefits.
Advanced Topics in SAFe
As organizations mature in their SAFe journey, they may explore advanced topics to optimize their processes further and drive continuous improvement:

- SAFe and DevOps: Integrating DevOps practices into the SAFe framework can help organizations accelerate delivery, improve quality, and foster a culture of collaboration and continuous learning. SAFe 5.0 introduces the Continuous Delivery Pipeline, which provides a framework for implementing DevOps practices at scale.
- Lean Portfolio Management: SAFe's Lean Portfolio Management (LPM) approach helps organizations align strategy with execution and ensure they invest in the right initiatives. LPM includes practices such as value stream identification, portfolio backlog management, and Lean budgeting.
- Weighted Shortest Job First (WSJF):WSJF is a prioritization technique used in SAFe to sequence epics and features based on their relative cost of delay. By considering factors such as business value, time criticality, risk reduction, and opportunity enablement, WSJF helps organizations make informed decisions about what to build and when.
Exploring these advanced topics can help organizations optimize their SAFe implementations and achieve greater agility and business value.
Comparison with Other Frameworks
While SAFe is a popular framework for scaling Agile, it is not the only option available. Other frameworks and methodologies include:
- Traditional Agile: Traditional Agile methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, are designed for small, co-located teams and may not be suitable for large, complex organizations. SAFe builds upon the principles of traditional Agile and provides a structured approach to scaling these practices across multiple teams and departments.
- Scrum@Scale: Scrum@Scale is a framework for scaling Scrum across multiple teams. While it shares some similarities with SAFe, such as using Scrum of Scrums, it does not provide the same level of guidance on organizational structure, Lean Portfolio Management, and DevOps.
- Large-Scale Scrum (LeSS): LeSS is another framework for scaling Scrum. It focuses on simplifying organizational structure and minimizing management overhead. Unlike SAFe, LeSS does not prescribe specific roles or events and instead emphasizes the need for continuous improvement and adaptation.
- Spotify Model: The Spotify Model is a people-driven approach to scaling Agile, emphasizing autonomy, collaboration, and innovation. While not a formal framework like SAFe, it has been adopted by many organizations to foster a culture of agility and continuous learning.
Ultimately, the choice of framework depends on the specific needs and goals of the organization. SAFe's comprehensive approach and structured guidance make it a popular choice for large enterprises looking to achieve business agility at scale.
Future of SAFe
Future of SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework)
The Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) is evolving rapidly, and its future looks promising as more organizations embrace agile practices on a larger scale. With the introduction of SAFe 6.0, several exciting trends and improvements are shaping its development. Let’s break down what we can expect:
- Wider Adoption Across All Departments:
SAFe 6.0 aims to extend its reach beyond just IT teams to include various business areas like finance, marketing, and operations. This broader approach will help organizations respond faster to market changes and customer needs, ensuring that agility is a company-wide effort.
- Focus on Lean Principles:
Lean thinking will become a key part of SAFe, emphasizing the importance of streamlining processes, cutting waste, and boosting efficiency. This shift encourages a culture of continuous improvement throughout the organization, helping teams work smarter.
- Integration of Automation and AI:
Expect to see more automation and artificial intelligence (AI) integrated into agile practices. SAFe 6.0 will utilize AI to improve decision-making, automate repetitive tasks, and provide valuable insights for ongoing enhancements. This means teams can focus more on strategic work rather than mundane tasks.
- Support for Remote Work:
As remote work becomes the norm, SAFe will adapt to ensure smooth collaboration among distributed teams. This support is crucial for maintaining productivity and effective communication in diverse work environments.
- Stronger DevOps Integration:
SAFe 6.0 will continue to enhance the connection between agile practices and DevOps. This integration will create a more cohesive process for software development and delivery, enabling organizations to release updates faster and with greater reliability.
By staying attuned to these trends and continuously evolving the framework, SAFe will remain a valuable tool for organizations seeking to achieve agility and thrive in an increasingly complex and uncertain world.
Conclusion
Throughout this blog post, we have explored SAFe's key elements, including its core values and principles, implementation roadmap, certification and training options, and advanced topics. We have also examined real-world case studies and compared SAFe with other scaling frameworks.
As organizations continue to adapt to new challenges and opportunities, the need for frameworks like SAFe will only grow. By embracing SAFe and continuously improving their Agile practices, organizations can position themselves for success in an increasingly complex and uncertain world.
If you consider implementing SAFe in your organization, we encourage you to take the first step today. Whether you are just starting your Agile journey or looking to scale your existing practices, SAFe provides a proven path forward. Investing in training, certification, and continuous improvement can unlock your organization's full potential and achieve your most ambitious goals.
FAQs

Get In Touch
