Navigating the Clouds: An In-depth Guide to Cloud Storage
Priyanshu Raj
Apr 7, 2025
What is Cloud Storage?
Did you know that the global cloud storage market is slated to hit a whopping $639.40 billion by 2032? And what is driving this trend? Remote work, increased adoption, and big data are just a few factors. So, what exactly is cloud-based storage, and why is it a must? It is a service that lets you manage, store, and access data remotely over the Internet. The first benefit of cloud storage is that you can reduce IT costs and the need for on-premise servers. However, what is the need to invest in cloud storage?
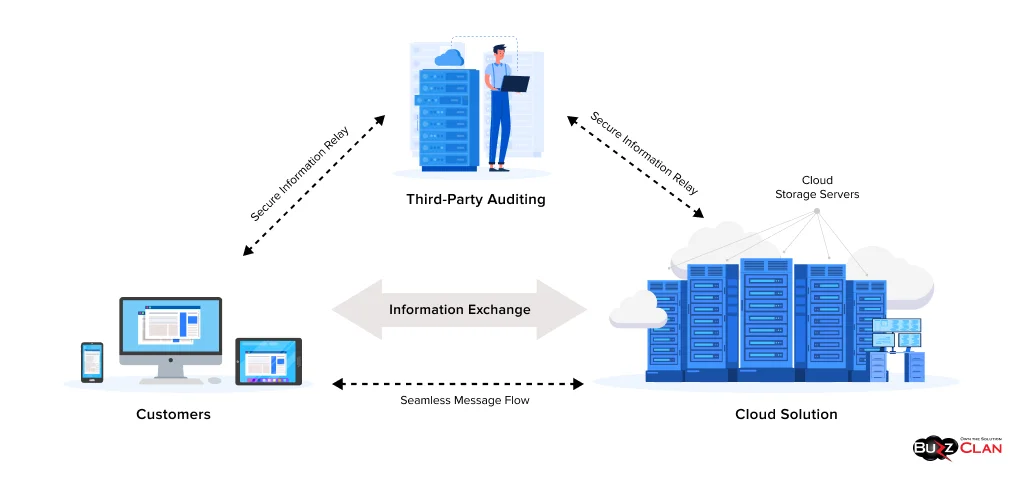
Regarding SMBs, cloud storage options are excellent for boosting scalability and cost efficiency. The best part is that Dropbox, OneDrive, and Google Drive offer plans starting at $6 per month, whereas enterprises require high-performance solutions. The reason is that enterprises require storage solutions that offer advanced security, top-notch scalability, and eliminate compliance concerns. Luckily, the benefits of cloud storage don’t just end here. This blog will detail all aspects of cloud storage for your business.
Industry-Specific Examples of Cloud Storage
Before jumping onto cloud storage architecture, let us look at some industry-specific examples of cloud storage.
| Industry | How Do They Use Cloud Storage? | Popular Cloud Services |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Healthcare firms use cloud storage to secure their electronic health records (EHRs) | AWS HealthLake, Google Cloud Healthcare API |
| Finance | Fintech institutions depend on cloud storage to take backups and archive financial transactions. | Azure Blob Storage, IBM Cloud Object Storage |
| Education | Cloud-based learning management systems use this storage option to store study material and secure their knowledge base. | Google Drive for Education, Dropbox EDU |
| Retail | Cloud storage is used to store customer data and e-commerce transactions. | AWS S3, Shopify Cloud Storage |
| Manufacturing | Cloud storage is used to store IoT and supply chain data | Microsoft Azure IoT Hub, Siemens MindSphere |
| Telecom | Cloud storage is used for network and call data | Verizon Cloud, IBM Cloud Storage |
| Gaming | Used for storing game assets and player progress | Google Cloud Game Servers, AWS GameLift |
Cloud Storage Architecture
Learning about the basic architecture is essential before we understand the nuances of cloud storage. The primary purpose of designing this architecture is to ensure smooth storage management and data retrieval over the Internet. Let’s know its multiple layers and components one by one.
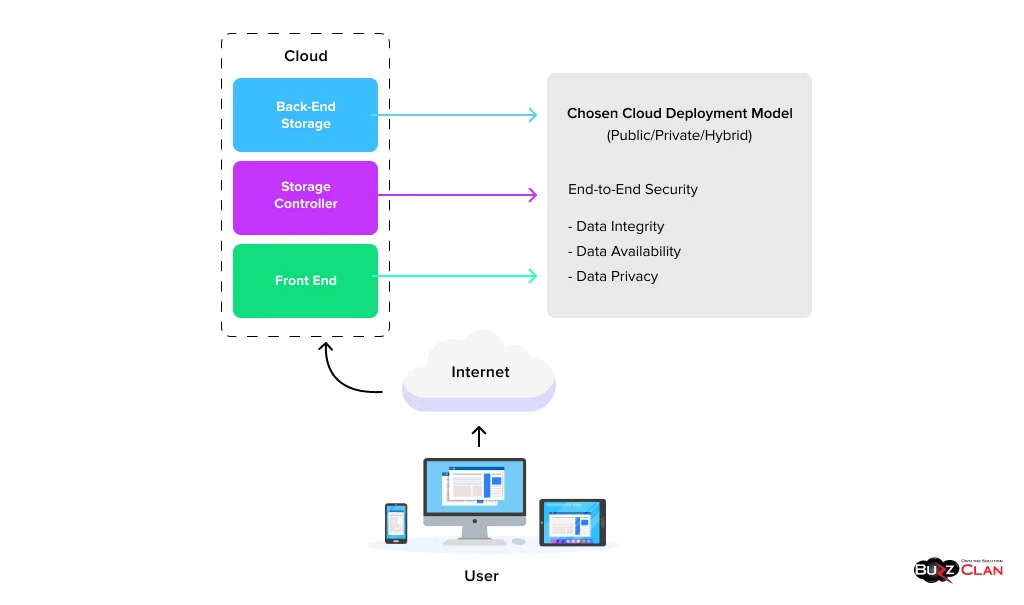
Front-End Interface
As the name suggests, the front-end interface deals with clients and is an entry point for users and applications. But what exactly are these interfaces? They could be dashboards or APIs (Application Program Interface) that let you access, store, retrieve, and manage data according to your business needs. The best part is that cloud storage solutions support protocols and APIs, including HTTP and HTTPS. This further makes it easier for businesses to integrate their existing systems with cloud storage services.
Middleware Layer
Let’s go deeper into cloud storage and explore the middleware layer. Well, this layer is responsible for coordinating storage operations. All cloud storage-related policies, including data replication, encryption, compression, and deduplication, are handled in this layer. We will be exploring them in the later sections of the blog. Also, the middleware layer handles metadata management. But what does that mean? It includes information about the location of the data, users who can access it, and the version of the data stored. As a result, middleware plays a key role in ensuring consistency and reliability across distributed storage environments. Cloud storage often involves storing data in multiple locations depending on the sensitivity of the data.
Back-End Storage Layer
Coming to the jackpot layer! Jokes apart, this layer stores the data. Cloud service providers use multiple storage models to ensure your data is stored appropriately. Object storage is the most common, and it is used for backups, images, and videos. At the same time, block storage goes a notch higher and handles structured workloads. These include virtual machines and databases. Next is the file storage, which is ideal for applications that need a defined hierarchy. We will discuss the role of all these in detail in the following sections.
Network Infrastructure
While the components mentioned above perform their role, the network infrastructure helps establish coordination between them. This is why software-defined networking and content delivery networks (CDN) are used in cloud storage to minimize lags and boost performance and data access. Security is also essential to this layer: access control, encryption, and authentication are enforced by network infrastructure to protect your business from cyber threats. Cloud storage architecture also uses advanced technologies like AI-driven automation and edge computing to boost efficiency. While AI helps predict failures and strengthen security, edge computing helps process data closer to the user.
Importance and Benefits of Cloud Storage
Now that you have understood how the cloud storage architecture works, it is time to explore why it is necessary. Simply put, reliability, consistency, and scalability are the reasons. You will be surprised to know that data growth is expected to hit 175 zettabytes by 2025. Traditional storage solutions are not built to keep up with the changing demands. At the same time, cloud storage helps you eliminate the need for on-premise solutions and works on demand. This is why top-cloud providers use distributed storage to ensure your data has multiple copies across locations for higher availability and prompt data recovery.
Scalability
Scalability continues to be a prominent advantage of cloud storage. Cloud storage offers horizontal scaling (workload distribution) instead of traditional data centers, which require physical upgrades to boost capacity. And this is possible with the help of distributed storage networks. Have you ever wondered how giants like Amazon handle millions and trillions of objects and never run out of storage space? Well, scaling ease with the cloud is the only reason.
Durability
Hardware failures never come announced. Thus, it helps to be prepared in advance. Luckily, cloud storage providers leverage erasure coding and data replication to help you keep your data intact. While the former breaks data into sectors and encodes it to add redundancy, the latter involves creating multiple copies and backups. This is why businesses trust Google Cloud Storage, as it automates data distribution across regions and reduces the risk of data loss. Banking systems and healthcare organizations increasingly depend on cloud storage to maintain data integrity.
Cost-Efficiency
Cloud computing is all about leveraging pay-as-you-go models. Cloud storage helps you do that and much more. Not only do you reduce your capital expenditure (CapEx) on hardware, but you can also cut your IT costs by 30-50%. Don’t believe us? Netflix even abides by the principles of cloud storage, as it streams 250 million hours plus of content daily! Let’s see what our expert has to say.
Data Accessibility and Security
Cloud storage and solutions ensure seamless remote work. Dropbox and Google Drive let you and your employees access files anytime and anywhere, boosting productivity and collaboration. By 2028, cloud will not be a hyped technology but a must-have to gain competitive edge and achieve top-notch operational abilities. So, if you have not yet hopped on the train, let us remind you that time is slipping through the cracks. Make the best use of it!
Security and Encryption
We know that cloud security is paramount. This is why cloud storage services provide end-to-end encryption. However, only encryption is not enough. Cloud storage services enforce identity and access management (IAM) policies and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure that only authorized personnel can access data. However, you will still need to be cautious about insider threats. You must train your employees properly and educate them about the importance of vigilance. Lastly, compliance with industry standards further adds a security layer. So, ensure you are fulfilling all guidelines, or if you find yourself confused, rope in a consultant.
Seamless Integration with Applications
Cloud storage is designed to integrate easily with DevOps pipelines and AI/ML workloads. Cloud providers provide APIs and SDKs ( Software Development Kits) to make this possible. This is why services like Google Cloud Functions and AWS Lambda make provisions for serverless computing, where stored data can be easily accessed and processed without needing dedicated servers. We will discuss how integrating cloud storage solutions with digital tools can help you boost performance in the later sections of the blog.

Types of Cloud Storage
It is time we understand the different types of cloud storage models. Each type serves a different purpose and can be optimized for various workloads.
Object Storage
As the name suggests, this cloud storage type stores data as objects, not in a defined hierarchy. So, what can be stored here? It is ideal for backups, multimedia content, and cloud-native applications. Storing data as objects helps you quickly retrieve and scale data conveniently. The benefits don’t end here! This storage type is one of the most durable options. If you are looking for viable options for your business, Amazon S3 and Azure Blob Storage are ideal choices.
Block Storage
If you wonder how block storage helps you, it is ideal for high-performance applications such as virtual machines and databases. In this cloud storage type, files are broken down into fixed-size blocks. Once broken into blocks, a unique identifier is allotted to them—this way, they can be easily stored across multiple locations. All these aspects make it highly efficient for applications that need high throughput and low latency. Amazon Elastic Block Store is one of the best options for block storage.
File Storage
The most organized storage option, file storage, stores data in designated directories and subdirectories. This storage type is best suited for content management systems and web-hosting environments. When it comes to handling structured data, you must choose this option. Moreover, you can easily access it from multiple devices over a network, making it the best choice for collaborative storage. A good choice for business would be Azure Files and Google Filestore.
Cold Storage (Archival Storage)
Cold storage is the perfect option if you have hardly used data that needs to be accessed for legal, compliance, and backup purposes. The catch is that you must trade off access speed for lower costs. Moreover, retrieving data can take minutes or even hours. This is why cold storage is often used for regulatory archives. Google Archive Storage is an excellent option for your business.
Types of Cloud Storage Models
Now that you understand the cloud storage types, it is time to explore cloud storage models. Each model serves a specific business use case. Take a look and decide for yourself.
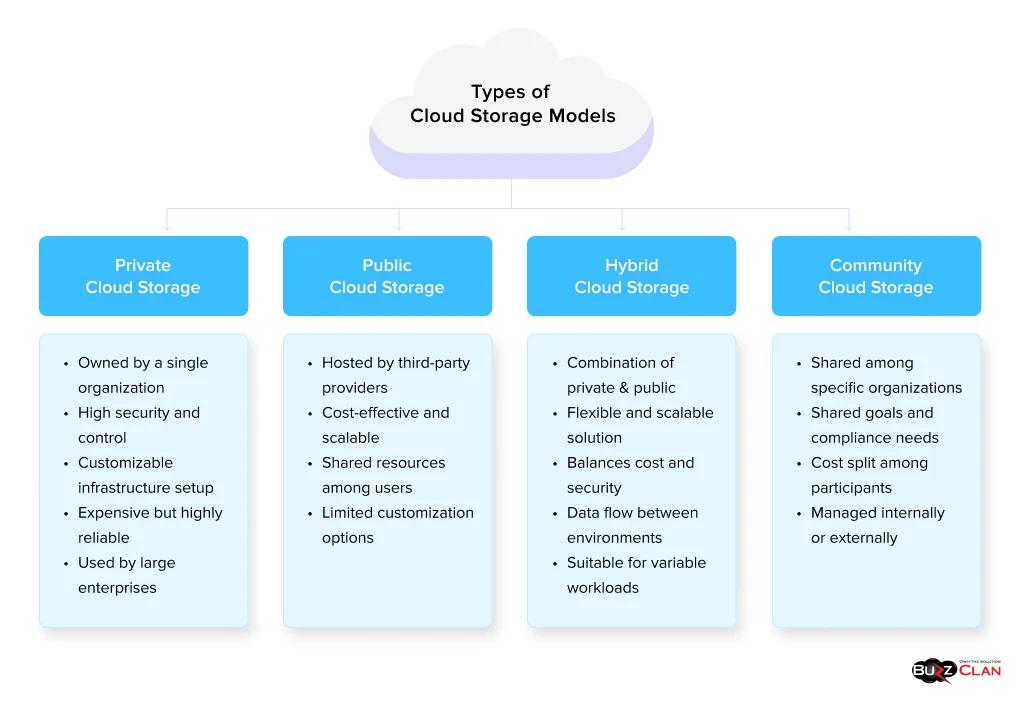
Public Cloud Storage
In the public cloud model, third-party providers offer storage options over the Internet. You can easily rent storage capacity and do away with the need to invest in physical infrastructure. The best part about this model is that it is highly accessible, scalable, and offers excellent redundancy. Businesses often use this model as it is cost-efficient and suited for all types. Even if you are new to the cloud, you can not go wrong with public storage. However, don’t store your sensitive data on the public cloud. One of the best public cloud storage options for businesses is Microsoft Azure Blob Storage, which supports various workloads, including big data analytics.
Private Cloud Storage
These cloud storage models are designed for a single organization. From top-notch security, greater control, and customization capabilities, private cloud storage offers this and much more! You can choose to host this model on-premise or in a data center. While costly, the benefits of this model far outweigh the price rise. Government agencies, financial institutions, and healthcare organizations leverage private cloud storage to secure sensitive data. OpenStack Swift and IBM Cloud Object Storage are excellent choices if you are looking for robust and powerful private cloud storage.
Hybrid Cloud Storage
A hybrid cloud storage model offers the best of both worlds. While sensitive data can be stored on a private cloud, the public cloud provides cost optimization and scalability. This model is ideal for handling dynamic workloads or having special disaster recovery needs. If you are looking for an effective solution for hybrid cloud storage, AWS Storage Gateway is a good choice.
Multi-Cloud Storage
As business needs evolve, so do cloud storage options. Multi-cloud storage is one such model that helps you boost performance, improve resilience, and avoid instances of vendor lock-in. Businesses around the globe distribute their workloads across multiple cloud environments to improve performance and keep costs in check. A combination of Amazon S3 and Google Cloud Filestore is ideal for handling file-based applications and analytic workloads.
How Does Cloud Storage Work?
Having understood the multiple cloud storage options, it is time to know how cloud storage works.
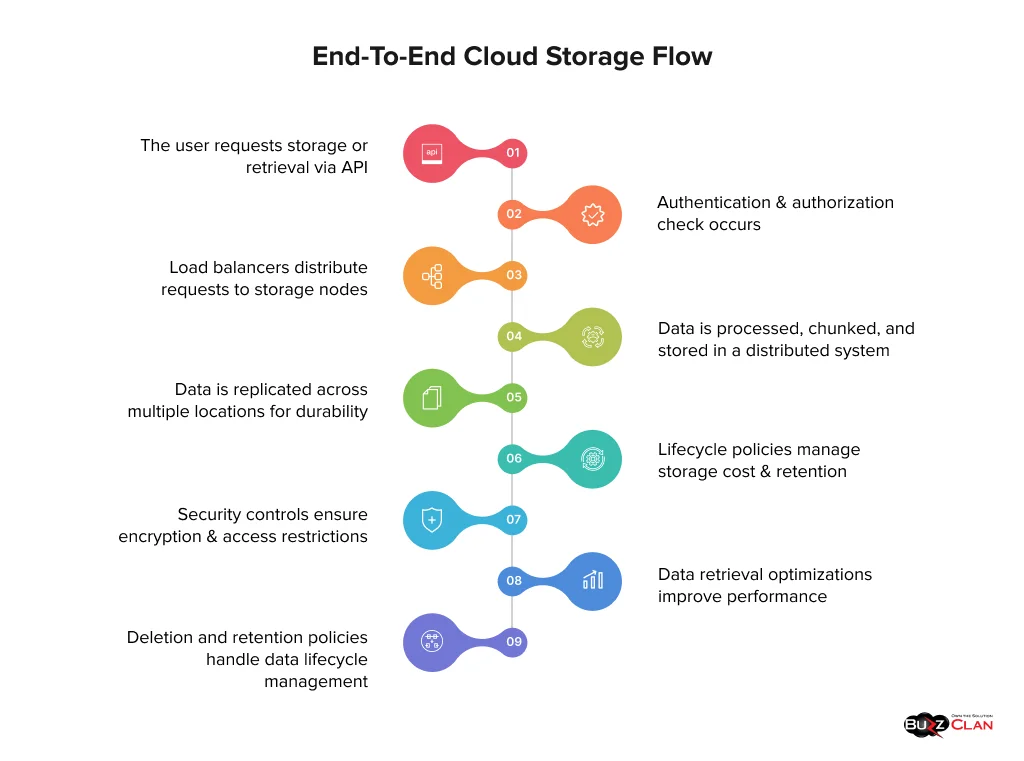
Data Ingestion and Upload
In the first step, you or an application upload data to a cloud storage solution. Once uploaded, it is processed on the edge of your cloud provider’s network. This processing involves compressing, deduplicating (ensuring no redundant copies are on cloud storage), and encrypting data. Content delivery networks (CDNs) are often used to reduce lags and optimize the upload process before data is stored in the primary storage cluster.
Breaking Down Data
In this step, the data is broken into smaller chunks, and this is done to boost reliability and scalability. These data chunks are distributed carefully across multiple storage nodes in different data centers or availability zones. But what is the whole purpose of this? It ensures that numerous copies of your data are stored in different locations. However, they are compressed, encrypted, and encoded to ensure minimal space is taken while maintaining top-notch security.
Assigning Metadata Tags
In this stage, each file or object is tagged as metadata. This includes details, file size, types, permissions, and the exact location in the distributed network. Cloud storage systems maintain a complete index of metadata to help you locate and retrieve data in real-time.
Storage Layering and Data Distribution
You will have a data set; not all will be required simultaneously. So, storing them in different tiers for specific use cases is best. While hot storage is ideal for data accessed frequently, cold storage takes longer to retrieve but is cost-effective. Glacier or archival storage is designed for long-term retention, and you can only access it in hours. Furthermore, the data is distributed using hashing algorithms. This is done to ensure loads are balanced across storage nodes, and there is minimal data movement if scaling needs to be done.
Retrieving Data and Access Control
When you request stored data, the cloud storage system will locate the required chunks, recreate them, and deliver the file. When we talk about the role of access control, it helps cloud providers ensure that only authorized personnel are seeking access. Stringent mechanisms are implemented to ensure that no third party can misuse the data.
Advanced Topics in Cloud Storage
Cloud storage has become more complex over the years. This is due to advanced techniques used in the cloud ecosystem to boost scalability, security, and reliability. Let’s explore the key advanced topics in cloud storage.
Erasure Coding
Data loss prevention is a must. This is why cloud providers use mechanisms like replication and erasure coding (EC). While the former is about creating multiple copies of data, it takes up more storage space. At the same time, the latter breaks down the data into smaller fragments. After that, the data is split into smaller fragments encoded with additional parity fragments and distributed across multiple storage nodes. This approach boosts storage efficiency and helps maintain fault tolerance. And why do we say that? Let’s say a 10+4 erasure coding scheme is followed. Even if you lose four parts or fragments, you can create the original data as it has been distributed.
Distributed File Systems and Metadata Scaling
Efficient metadata management is necessary since millions of files or objects are stored across different locations. Have you ever wondered how enterprises handle the same? Well, distributed file systems have a huge role to play in them. Popular cloud storage systems like the Google File System (GFS) leverage the power of decentralized metadata architectures to prevent any bottlenecks in the workflow. In these mechanisms, algorithms distribute metadata, and thus, there is no need for a central metadata repository. As a result, you can look forward to improved scalability and performance. Techniques like metadata sharding and dynamic partitioning (dynamic memory space allocation) are gradually gaining momentum.
Data Deduplication and Compression for Storage Optimization
Data deduplication is as valid as data redundancy in cloud storage. This is why cloud providers use block-level and file-level deduplication techniques. These techniques help them identify similar chunks and ensure no redundant file uploads. Cloud providers like Google Drive and Dropbox also use these techniques combined with similarity hashing (near-duplicate detection) for superlative performance. Additionally, compressing data allows for efficient encoding. However, you must ensure that you only use those encryption algorithms that ensure data integrity.
Storage Tiering and Lifecycle Management
Not all data is sensitive and needs to be accessed at all times. Cloud storage services offer multiple storage classes to optimize cost and performance. While hot storage is apt for frequently accessed data and offers low latency, cold storage is more suited for archival data. But what supports all these storage classes, and how can you manage them? It is possible with lifecycle management policies. They help move data between tiers, access patterns, and compliance requirements. This way, you can quickly reduce storage costs without manual intervention.
Encryption, Zero Trust, and Confidential Computing
While most of us know the benefits of end-to-end encryption, cloud storage goes beyond that by offering homomorphic encryption that allows computation on encrypted data without decryption. This way, you can act on your data while saving it from the eyes of hackers who prey on it. Also, cloud storage solutions worldwide have adopted zero-trust architectures (ZTA) to enforce least-privilege access and ensure nothing slips through the cracks. Lastly, confidential computing helps you enable secure enclaves (protected and isolated environments) to keep your data safe and encrypted even during processing.
Kubernetes and Docker
How do you store containerized applications? With Kubernetes and Docker by your side, you need not worry! They not only help you fully utilize storage resources, but they also help you ensure scalability and availability. If you talk about Kubernetes, it enables you to manage persistent volumes and storage classes and allows seamless integration with cloud storage solutions. Both technologies are ideal for reliable storage, high availability, and automated scaling for cloud-native applications.
Cloud Storage Performance Optimization
Cloud storage performance depends on throughput, network latency, and IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second). Most providers use caching mechanisms to reduce latency and content delivery networks (CDNs) to improve load times for distributed applications. Wait, there is more to it! You can also optimize storage access patterns, such as sequential reads/writes, rather than being random in your approach to boost performance for specific workloads.
Importance of Data Redundancy in Cloud Storage
Did you know that cloud storage is one of the areas where redundancy is not frowned upon but celebrated? All bad jokes on us! Data redundancy is a must to ensure accurate data, high availability, and fault tolerance. As discussed in previous sections, cloud environments store data across multiple physical and virtual locations to reduce data loss due to accidental deletions. An example is Amazon S3, which offers cross-region replication (CRR) to ensure data remains accessible even if one region experiences downtime.
As mentioned before, Erasure coding plays a significant role in ensuring high data availability and fault tolerance. Besides these technologies, redundancy must be coupled with data deduplication and compression measures to ensure zero storage wastage. You need to be very careful when storing your assets on the cloud. If you are not monitoring them closely, the costs can run high. Thus, establish a tandem between all the aspects and leverage the essence of redundancy to ensure that cloud providers can provide 99.99% uptime and help you build a resilient organizational framework.
Cloud Storage vs. Traditional Storage
Let’s understand the difference between cloud and traditional storage.
| Aspect | Cloud Storage | Traditional Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Uses remote servers managed by a cloud provider | On-premises data centers managed internally |
| Deployment Model | Hosted on cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP | Hosted on local storage devices like HDDs, SSDs, NAS, SAN |
| Scalability | Highly scalable and elastic expansion on demand | Limited scalability options and requires hardware upgrades |
| Performance | Varies based on network speed and storage tier. | High-speed access within LAN is limited by local hardware |
| Latency | Higher due to network dependency | Lower latency within a local environment |
| Data Accessibility | Accessible from anywhere via the internet. | Limited to local network or VPN |
| Redundancy & Availability | High availability with multi-region redundancy | Depends on RAID setups and backup strategies |
| Security | Managed security with encryption, IAM, and compliance policies | Full control over security requires manual configurations |
| Cost Structure | Pay-as-you-go model (storage + data transfer fees) | High upfront cost for hardware & maintenance |
| Backup and Recovery | Automated backup and disaster recovery options | Requires manual setup and maintenance |
| Data Durability | 99.99% durability in cloud platforms | Requires internal audits and regulatory adherence |
| Compliance and Governance | Limited control over hardware and configurations | Full customization of hardware and storage architecture |
| Customization | Limited control over hardware and configurations | Full customization of hardware and storage architecture |
| Maintenance | Managed by the cloud provider, and no hardware upkeep is required | Requires IT team for hardware maintenance and upgrades |
| Data Transfer Speed | Dependent on internet bandwidth and provider’s limits | Direct, high-speed transfer within a LAN environment |
| Disaster Recovery | Multi-region replication and automated failover | Manual recovery and may require offsite backups |
| Integration | Integrates with cloud-native applications and services (AI, analytics, etc.) | Limited integrations, mainly local applications |
| Control | Less control over storage infrastructure | Complete control over hardware, software, and configurations |
| Use Case | Ideal for dynamic workloads, remote access, and scalability | Ideal for high-performance, low-latency local storage needs |
The Role of AI and ML in Cloud Storage Optimization
AI and ML can help businesses optimize cloud storage, reduce costs, and improve scalability. And how does that happen? MLOps enables you to predict usage trends effectively, allocate resources, and move data to tiers as needed. With the global AI cloud market expected to reach USD 327.15 billion by 2029, you should consider integrating it with your storage systems.
AI-driven deduplication and compression techniques will not only help you reduce bandwidth consumption, but they will also help you boost performance in the cloud environments. Wait, there is more to it! Security is another area where AI and ML play a significant role. Now, hackers are using AI to advance their threats. However, AI is also helping to strengthen cloud infrastructure. Here is what our expert, Vishal Vaid, has to say.

How to Migrate Your Data to the Cloud?
Let’s look at the process you must follow for cloud migration.
- Knowing your system inside out is the key to a successful cloud migration. To ensure the process proceeds smoothly, ensure you have all your requirements, including dependencies, security policies, storage formats, and compliance needs.
- Choose between public, private, hybrid, or multi-cloud solutions based on your workload requirements. We suggest using the hybrid cloud model to leverage cost optimization features and keep your data safe.
- You must follow the 7Rs of cloud migration to build a migration strategy. Some standard methods include re-platforming, refactoring, repurchasing, rehosting, and retiring.
- Decide whether to transfer your data over the internet using cloud-native tools, use physical devices for large-scale transfers, or use a hybrid approach for staged migration. Choose the process that best meets your business requirements. Before you kickstart the process, make sure your team is in sync.
- Ensure you encrypt data in transit and at rest. This will help you ensure compliance with industry standards and enforce role-based access for selective privilege.
- Once you have migrated your data, check for data integrity and test system compatibility. You can test migration on a data subset before implementing it fully, allowing you to establish rollback procedures in case of failure.
- The last step is to optimize storage costs by selecting appropriate storage tiers. Make sure you implement monitoring tools to track performance and security anomalies.
How Can Businesses Deal With Cloud Storage Security Threats?
Here is a list of cloud storage security threats you must know.
Data Breaches
Data breaches can often occur due to weak authentication and encryption methods. You must protect your cloud environments from insecure APIs and social engineering attacks.
- Solution: To ensure your cloud storage stays safe from all these threats, you must first enable multi-factor authentication (MFA). Encrypting your data at rest and in transit is a must. You will also need to perform security audits to fix any misconfigurations. API penetration testing and implementing OAuth 2.0 and API gateways should be a part of your cybersecurity strategy to ensure security across the organizational spectrum.
Data Losses
Ransomware, accidental deletions, or outages can lead to permanent data loss. This can harm your organizational reputation and even result in financial loss.
- Solution: Having automated and versioned backups is a must to prevent such instances. You will also need to implement immutable storage policies to make sure no data is deleted accidentally
Insider Threats
Your employees may expose cloud data unintentionally or with malicious intent. Detecting these threats can be challenging, as users already have access.
- Solution: Make sure only authorized users should have access to sensitive data. You should also monitor user activity logs using SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) tools and implement behavioral analytics to detect anomalies faster.
Compliance and Legal Issues
Not complying with industry standards can lead to unnecessary penalties, fines, and lost opportunities with potential clients.
- Solution: Implement data residency policies to ensure you are following regional regulations. Compliance audits are a must to detect issues related to cloud storage. You can also use cloud access security brokers (CASBs) to enforce security policies across all services. Following these measures will help you stay on top of your compliance needs.
DDoS Attacks
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks can overwhelm cloud storage systems with excessive traffic, causing downtime and potential data access issues.
- Solution: Deploying cloud-based DDoS protection services like AWS Shield is a simple way to protect your cloud storage from these attacks. You can also distribute traffic efficiently using web application firewalls and CDNs.
Mitigating Cloud Storage Cost Surprises
Cloud storage costs can quickly add up due to a combination of factors, including changes in API requests, data retrieval fees, and storage tier mismatch. A common misconception is that businesses think data storage costs are limited to the per-gigabyte rate. However, hidden expenses can throw you off track when you receive the cloud bill. Thus, make sure to follow these measures to avoid cost surprises.
Analyze Usage Patterns
Recheck your storage usage patterns and select the classes to prevent cost overrun. For the same, you need to carefully address your data needs and then align them as per the data lifecycle. Let’s say you are not frequently using a data type; it must be stored in archival tiers to use lower per-GB storage costs best. On the other hand, the data you need to access frequently must be stored in standard tiers to avoid paying extra fees.
Keep A Check on Egress and API Costs
Are you downloading frequently from your cloud storage to external locations? It is time to keep a check on this, as cloud providers charge for transferring data (egress costs) out of their networks. A potent solution for avoiding this fee is to leverage data localization strategies. Edge caching and content delivery networks can help you curb unnecessary data movement. Another thing to remember is that API costs can add up faster than the speed of light. If your applications require a higher frequency of reads and writes or need to retrieve metadata, you must handle batch requests. This will help you index effectively, reduce redundant operations, and cut costs.
Implement Automation and Monitoring Tools
The best way to ensure your cloud costs are checked is to partner with cloud providers offering alerting tools and cost analysis. This way, you can track spending trends and set up budget alerts. You can automate data transitions between storage classes using a set of criteria. This way, your data can easily be moved to cost-effective storage tiers without manual intervention. Lastly, deleting redundant data with scheduled cleanups will help you reduce storage costs.
Here is a list of the factors you must consider when dealing with cloud storage costs.
| Cost Factor | Reason for Impact |
|---|---|
| Storage Capacity | Additional storage capacity will increase costs, as cloud providers charge based on the volume of data stored. |
| Storage Class/Tier | Not all data can be a high priority, so different storage classes have been assigned in cloud storage. The costs will vary depending on your access frequency. |
| Data Transfer (Ingress/Egress) | Cloud providers charge for transferring data out of the cloud, but data ingress is often cheaper or even free. |
| Read/Write Operations | If you are dealing with frequent read-and-write requests, it will increase costs for transactional storage solutions. |
| Data Redundancy & Replication | Multi-region replication and high-availability setups increase costs due to additional storage and network usage. |
| Backup & Snapshots | Snapshots and backups need extra storage, adding to cloud storage costs. |
| Compliance & Security Features | Regular audits, advanced security, and ensuring compliance with industry standards add to overhead costs. |
| Retention Policies | You need to be very careful about the data you retain as it will add to storage costs and, if not appropriately managed, can lead to legal and compliance issues. |
| Cloud Provider & Region | Pricing varies across cloud providers and geographic regions due to infrastructure and operational costs. |
| APIs & Requests | Some providers charge based on API calls for retrieving or managing stored data. |
Integrating Cloud Storage with Other Digital Tools
It is time to understand why undertaking these initiatives is a must.
Centralizing Data Storage
What if you could centralize data storage while looking forward to secure file sharing and real-time data processing? Well, consider your wish fulfilled by doing a simple integration. Integrating your cloud storage solutions with data lakes lets you easily handle large-scale analytics and machine learning workloads. This means you can free your IT team from tasks requiring their expertise. Use ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools like Google Dataflow to streamline data ingestion and transformation processes further. This way, you can reduce lags and improve employee and user experiences.
Integration With DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines
Did you know you can simplify your development process when connecting DevOps and CI/CD pipelines? Cloud storage can easily store customers’ build outputs (ready-to-use code) and configuration files. When you integrate them with these techniques, you will notice a sharp increase in speed and efficiency. This is because you can access and deploy resources from cloud storage buckets. When automated deployments and simplified version management become a reality, you can look forward to groundbreaking innovations for your business. Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) tools like Terraform are the icing on the cake. Use them to ensure seamless scalability and consistency across environments.
Workflow Automation and Collaboration
We all use cloud productivity suites to back up, share, and edit files with team support. But what makes this possible? These tools enhance collaboration and simplify workflows so employees or leaders can access data faster and experience zero bottlenecks. As you explore the integrations further, you can take advantage of multiple aspects, which, in turn, will increase productivity and operational efficiency.
Compliance and Cloud Storage
Compliance plays a massive role in cloud computing as different regions have defined rules for handling data. Let’s look at how the various compliance standards impact cloud storage.
| Compliance Standard | Impact on Cloud Storage | How To Ensure Compliance? |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation - EU) | Data localization encryption and user consent are musts. | Cloud service providers must ensure top-notch compliance, ensure only authorized personnel can access data, and conduct regular audits and document them to ensure compliance. |
| HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act - US) | The chosen cloud storage model must protect healthcare data, manage access control, and maintain audit logs. | A safe way to ensure compliance is to only partner with HIPAA-compliant cloud services. Ensure you encrypt PHI (Protected Health Information) and have robust backup policies and audit logs. |
| ISO 27001 (International Security Standard) | The focus lies on SIEM and ensuring consistency across all locations. | Without saying, audits and employee training are your weapons of success. You will also need to implement risk assessment and mitigation strategies. Lastly, make sure you have secure access and provision for 24/7 monitoring. |
| SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2 - US) | Requires security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy controls | Partner with cloud providers who are SOC 2 certified and implement advanced monitoring tools for data security and integrity. |
| CCPA(California Consumer Privacy Act - US) | It is similar to GDPR and requires data access, deletion, and opt-out of data selling. | Ensure you provide user opt-out mechanisms and implement data mapping to track personal data. You will also need to update privacy policies regularly to ensure seamless compliance. |
| PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) | It focuses on securing payment card information | Regular vulnerability scans and network penetration testing are essential. Additionally, restricted access to cardholder data must be ensured. |
| FedRAMP (Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program - US) | Governs cloud security for federal agencies | Only work with FedRAMP-authorized cloud providers, maintain continuous monitoring and compliance reporting, and implement role-based access control (RBAC). |
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Cloud Storage
Now that you know how compliance affects cloud storage, it is time to understand the essentials when choosing a cloud storage provider and picking the right option among the top choices.
Assessing Storage Performance
A host of technical factors is involved when you have to assess the performance of a cloud storage solution. For that, you need to develop an understanding of your read/write requirements and latency sensitivity. High-performance applications encompass real-time analytics, and they also require low-latency storage solutions. At the same time, if you are dealing with archival workloads, you will need to deal with cold storage tiers and pave the way for higher latency. Additionally, some cloud storage solutions are adept for block storage solutions, which can be customized for high IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) and can be used to handle databases and virtual machines. Before selecting a cloud storage solution, thoroughly assess your needs and then proceed to invest.
Scalability and Durability
Nearly all cloud providers offer a promise of 99.99% uptime. However, in the case of scalability, things differ based on storage type. While object storage solutions are designed for unlimited scalability, the same is not the case with file storage options. You will need to deal with performance constraints and size limitations. So, you must decide what storage best suits your business needs. We suggest using a solution that offers multi-region replication and can boost data availability and disaster recovery capabilities. This will help you prevent data loss and regional outages.
Security and Compliance Options
Security and compliance are essential when choosing a cloud storage solution. Not only do you need to evaluate encryption options, but you will also need to check how stringent their entity and Access Management (IAM) policies are. If you plan to work with a cloud provider that doesn’t offer compliance certifications, you are setting yourself up for trouble. Make sure they offer compliance with SOC 2, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR to ensure you don’t end up paying hefty fines and penalties. Lastly, check if they offer audit logging and anomaly detection tools. This will help you track access and detect potential security threats.
Cost Efficiency
While most providers offer dynamic pricing, they charge for data retrieval, API requests, and outbound data transfer. This can quickly add to the total cost of ownership. As a result, you need to evaluate pricing models and leverage lifecycle policies to ensure less-frequently accessed data stays in lower-cost tiers. You also need to select storage options that offer built-in redundancy, as they will reduce the need for costly backup solutions. Additionally, monitoring tool support is a must to keep track of expenses and avoid unexpected charges.
User Interface, Customer Support, and Integration Options
Is your cloud storage provider offering poor-quality user interfaces? Well, it is time to bid them goodbye! Another thing to consider is how is their customer support. Are they available at odd hours if you encounter an issue? Do they have a dedicated knowledge base to help you or at least automated chatbot support? If yes, you are in good hands; otherwise, you must reconsider your choices. Last but not least, can you integrate your chosen cloud storage option with your existing systems? Ensure all these aspects align with your business expectations for a perfect choice.
Now that you know the factors to consider when selecting a cloud storage provider, it is time to examine the popular services and what makes them suitable for your organization.
Popular Cloud Storage Services
Let’s understand the multiple aspects of the popular cloud storage services.
| Service | Free Storage | Paid Plans | Why Choose Them? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Drive | 15 GB |
|
You can choose this option to make the best of the Google Ecosystem. Seamless collaboration opportunities and generous free storage will help you a lot. |
| OneDrive | 5 GB |
Best suited for users within the Microsoft environment. You get access to all Microsoft 365 applications, which can easily be integrated with existing systems. |
|
| Dropbox | 2 GB |
|
It is a boon for businesses working on collaborative projects. The best part about Dropbox is its simplicity and robust third-party integrations. |
| IDrive | 10 GB |
|
Idrive offers competitive pricing for significant storage needs, emphasizing security and real-time syncing. |
| pCloud | 10 GB |
|
It attracts users seeking lifetime plans and strong security features like zero-knowledge encryption. |
| MEGA | 20 GB |
|
It provides substantial free storage and end-to-end encryption and is ideal for businesses keen on high-end security. |
| Box | 10 GB |
|
Tailored for business and enterprise users, offering advanced collaboration tools and AI assistance. |
| iCloud | 5 GB |
|
Optimal for Apple users. It ensures seamless integration across Apple devices with automatic backups. |
| Koofr | 10 GB |
|
It offers customized plans with integration capabilities that are ideal for businesses looking to consolidate multiple cloud accounts. |
The Future of Cloud Storage
Cloud computing trends impact every aspect of cloud architecture. The same is the case with cloud storage. Let’s analyze what the future of cloud storage looks like.
Steep Increase In Storage Capacity and Cost Efficiency
As we have read before, global data storage is set to hit 200+ zettabytes by 2025, so it is time to switch gears if you have not done so yet. Experts believe more than 60% of the data will reside in the cloud. In the upcoming years, cloud storage costs will be slashed further using hyperscale data centers. While the cost per terabyte started at $0.10/GB in 2010, it is currently under $0.02/GB. You will also witness fierce competition among cloud providers to offer the best options at discounted rates.
Advancements in Storage Technologies
DNA data, quantum, and holographic storage will redefine the future of cloud storage. And why do we say that? Well, they offer excellent improvements in data density. DNA storage can theoretically store 215 petabytes per gram, far outweighing traditional storage options. Moreover, these technologies are long-lasting and will help you scale better in the long run. While quantum storage has yet to reach its full potential, the promise of unbreakable encryption and ultra-fast processing is fascinating. Lastly, holographic storage will allow faster-than-light retrievals and phenomenal capacity.
AI-Driven Storage Optimization
What if you could predict failures before they happen? Well, you would be able to avert them and minimize downtime. Advanced AI capability will help you do that and much more. Moreover, with improved predictive caching capabilities, you will be able to reduce latency to a great extent and speed up access.
Edge Computing and Decentralized Cloud Storage
Increased 5G and IoT usage has shifted storage closer than ever to users. Companies worldwide are using it to reduce latency for real-time applications. Many providers use blockchain-based storage models for top-notch security and offer distributed alternatives to centralized data centers.
Unlock Enterprise-Grade Cloud Storage With BuzzClan
If you are looking forward to meeting diverse business requirements, then our cloud storage solutions are just what you need. Our team of experts is adept at multi-cloud strategy, which enables you to reduce failure risks and ensure continuous access. We use the best tools and technologies to ensure optimal performance and resource utilization so your business stays ahead of the competition. We first understand your requirements and then create a detailed roadmap to ensure all key stakeholders are aligned with the process. Our work doesn’t end just there! We also offer post-monitoring and logging support to help you entirely focus on your business needs. Here is why you should partner with us.
- Reduce cloud spend by up to 40%
- Real-time cost monitoring and predictive scaling
- Reduce deployment time by up to 60%
- Seamless application modernization
- ROI-focused implementation
- Cloud-native development expertise
- Industry-specific compliance expertise
Conclusion
Cloud storage has evolved from a simple data repository to a sophisticated, AI-enabled ecosystem that is the backbone of modern digital transformation. As we’ve explored throughout this article, the technology offers unparalleled advantages in scalability, cost-efficiency, security, and accessibility that traditional storage solutions simply cannot match.
Organizations across industries—from healthcare and finance to manufacturing and entertainment—are leveraging cloud storage to safeguard their data and transform it into actionable intelligence. With multi-region replication, advanced encryption, and automated lifecycle management, today’s cloud storage solutions provide enterprises with the resilience and compliance capabilities to operate in increasingly regulated environments.
The future of cloud storage promises even greater innovation with quantum storage technologies, AI-driven optimization, edge computing integration, and blockchain-based security. These advancements will further reduce costs while dramatically increasing storage density and performance. The question is no longer whether to adopt cloud storage but how to optimize your implementation for maximum business value.
By carefully selecting the right cloud storage models, implementing proper security measures, and following cost optimization strategies outlined in this guide, organizations can build a flexible, efficient storage infrastructure that scales with their needs while controlling costs.
FAQs

Get In Touch
Follow Us
Table of Contents
- What is Cloud Storage?
- Industry-Specific Examples of Cloud Storage
- Cloud Storage Architecture
- Importance and Benefits of Cloud Storage
- Types of Cloud Storage
- Types of Cloud Storage Models
- How Does Cloud Storage Work?
- Advanced Topics in Cloud Storage
- Importance of Data Redundancy in Cloud Storage
- Cloud Storage vs. Traditional Storage
- The Role of AI and ML in Cloud Storage Optimization
- How to Migrate Your Data to the Cloud?
- How Can Businesses Deal With Cloud Storage Security Threats?
- Mitigating Cloud Storage Cost Surprises
- Integrating Cloud Storage with Other Digital Tools
- Compliance and Cloud Storage
- Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Cloud Storage
- Popular Cloud Storage Services
- The Future of Cloud Storage
- Unlock Enterprise-Grade Cloud Storage With BuzzClan
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Get In Touch