Building an Inclusive Workplace: A Guide to ADA Compliance for Employers
Nidhi Rani
Jun 13, 2024
Introduction
The American Disabilities Act (ADA) is a crucial piece of legislation that has transformed the landscape of employment rights for individuals with disabilities. As an employer, understanding and complying with the ADA is a legal and moral obligation. By ensuring equal opportunities and accommodations for employees with disabilities, organizations can foster a diverse, inclusive, and productive workforce.
In this comprehensive blog post, we will delve into the key aspects of the ADA, focusing on employer requirements and the rights of individuals with disabilities. We will provide an overview of the ADA’s history and purpose, outline the specific obligations for employers, and discuss strategies for ensuring compliance. Additionally, we will explore best practices for creating an inclusive workplace culture and highlight real-world case studies that demonstrate successful ADA implementation.
Whether you are a small business owner, an HR professional, or a manager, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the complexities of the ADA and create a welcoming environment for all employees, regardless of their disabilities. By the end of this post, you will have a solid understanding of your responsibilities under the ADA and be well-prepared to foster a compliant and inclusive workplace.
Overview of the American Disabilities Act (ADA)
The American Disabilities Act (ADA) is a comprehensive civil rights law that prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities in various aspects of life, including employment, public accommodations, transportation, and telecommunications. The ADA was signed into law in 1990 and has undergone several amendments and expansions over the years to protect the rights of persons with disabilities further.
The primary purpose of the ADA is to ensure that individuals with disabilities have equal opportunities and access to employment, goods, services, and facilities. The law defines disability as a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities, such as walking, seeing, hearing, or working. The ADA also extends protection to individuals with a history of a disability and those who are perceived as having a disability.
The ADA has had a profound impact on the lives of millions of Americans with disabilities, breaking down barriers and promoting inclusion in the workplace and society at large. The law has evolved to keep pace with changing societal norms and technological advancements, ensuring that individuals with disabilities can fully participate in all aspects of life.
Employer Requirements Under the ADA
The ADA imposes several key requirements on employers to ensure equal employment opportunities for individuals with disabilities. These requirements apply to private employers with 15 or more employees and state and local governments.
Reasonable Accommodations:
One of the most significant obligations under the ADA is to provide reasonable accommodations to qualified employees or job applicants with disabilities. Reasonable accommodations are modifications or adjustments to the work environment, job duties, or the application process that enable individuals with disabilities to perform essential job functions or enjoy equal employment opportunities.
Examples of reasonable accommodations include:
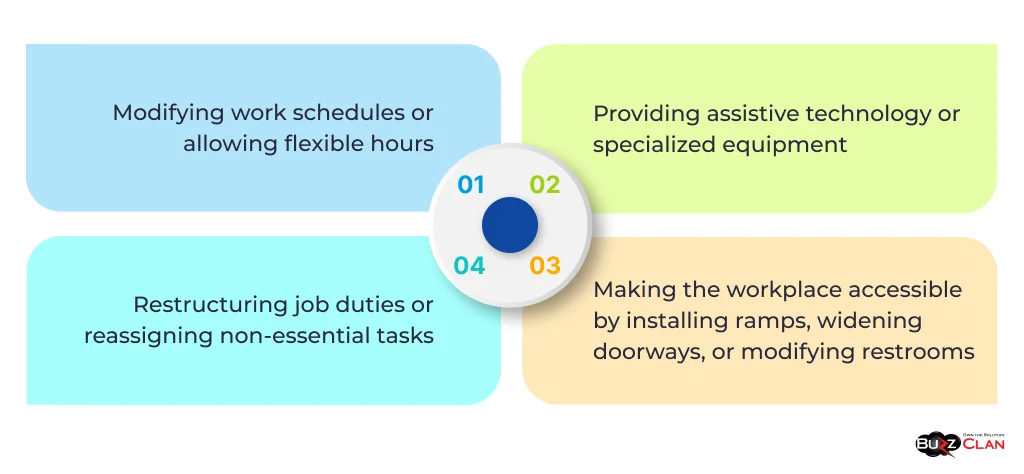
- Modifying work schedules or allowing flexible hours
- Providing assistive technology or specialized equipment
- Restructuring job duties or reassigning non-essential tasks
- Making the workplace accessible by installing ramps, widening doorways, or modifying restrooms
Employers must interact with employees to determine appropriate accommodations on a case-by-case basis. However, employers are not obligated to provide accommodations that would impose an undue hardship on the business, such as those that are excessively costly or disruptive.
Non-Discrimination Policies:
The ADA prohibits discrimination against qualified individuals with disabilities in all employment aspects, including hiring, promotion, termination, compensation, and training. Employers must develop and implement non-discrimination policies that clearly state their commitment to equal employment opportunities for individuals with disabilities.
These policies should be communicated to all employees and included in employee handbooks and training materials. Employers must also ensure that their hiring practices, job descriptions, and performance evaluations are free from discrimination and do not screen out individuals with disabilities who are otherwise qualified for the position.
Accessible Work Environment:
Employers are required to ensure that their workplace is accessible to employees with disabilities. This includes the physical workspace and the digital environment, such as websites and software applications. Employers should conduct accessibility audits to identify and remove barriers that may prevent individuals with disabilities from fully participating in the workplace.
Examples of accessibility measures include:
- Ensuring that entrances, hallways, and common areas are wheelchair accessible
- Providing accessible parking spaces and restrooms
- Ensuring that digital content, such as websites and documents, is compatible with assistive technologies like screen readers
- Providing closed captioning or sign language interpretation for meetings and events
Confidentiality:
The ADA requires employers to maintain the confidentiality of employees’ medical information and disability status. Employers may only share this information on a need-to-know basis and must keep medical records separate from general personnel files. Employers should also train managers and supervisors on maintaining confidentiality and appropriately handling disability-related information.
Rights of Individuals Under the ADA

The ADA grants several important rights to employees and job applicants with disabilities, ensuring their protection from discrimination and enabling them to request necessary accommodations.
Protection from Discrimination:
Individuals with disabilities have the right to be free from discrimination in all aspects of employment, including hiring, promotion, termination, compensation, and training. The ADA prohibits employers from making employment decisions based on an individual’s disability as long as the person is qualified for the position and can perform the essential job functions with or without reasonable accommodations.
Employees and job applicants with disabilities also have the right to be free from harassment or retaliation based on their disability. Employers must promptly address any instances of disability-based harassment or discrimination in the workplace.
Right to Reasonable Accommodation:
Qualified individuals with disabilities have the right to request and receive reasonable accommodations that enable them to perform the essential functions of their jobs or enjoy equal employment opportunities. Employees can request accommodations at any stage of the employment process, including during the application process, after a job offer, or during employment.
Employees should initiate the accommodation request and interact with their employer to determine an appropriate accommodation. Employers may request medical documentation to substantiate the need for an accommodation. Still, they cannot request information unrelated to the specific accommodation or the employee’s ability to perform the job.
Individuals with disabilities also have the right to decline an accommodation if they believe it is unnecessary or if it would pose a direct threat to their health or safety. However, if an employee refuses reasonable accommodation and cannot perform the essential job functions, the employer may not be required to provide alternative accommodations.
Compliance Strategies for Employers
Employers should implement several key strategies and best practices to ensure compliance with the ADA and create an inclusive workplace.
ADA Training:
Providing comprehensive training on the ADA to managers, supervisors, and employees is crucial for ensuring compliance and fostering an inclusive workplace culture. Training should such as:
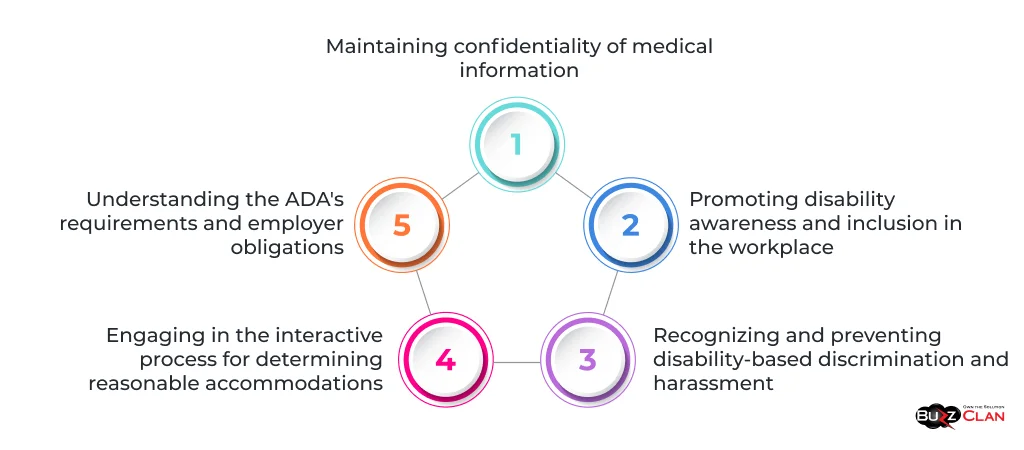
- Understanding the ADA’s requirements and employer obligations
- Recognizing and preventing disability-based discrimination and harassment
- Engaging in the interactive process for determining reasonable accommodations
- Maintaining confidentiality of medical information
- Promoting disability awareness and inclusion in the workplace
Training should be conducted regularly and updated to reflect changes in the law or best practices. Employers should also ensure that new hires receive ADA training during onboarding.
Interactive Process:
Engaging in an interactive process with employees who request accommodations is a key component of ADA compliance. The interactive process is a collaborative dialogue between the employer and employee to identify their specific limitations and determine an appropriate accommodation that enables them to perform the essential job functions.
During the interactive process, employers should:
- Listen to the employee’s request and engage in a good-faith discussion
- Request medical documentation, if necessary, to substantiate the need for an accommodation
- Explore various accommodation options and their feasibility
- Consider the employee’s preferences and the effectiveness of each option
- Select an accommodation that is reasonable and does not impose an undue hardship on the business
- Monitor the effectiveness of the accommodation and make adjustments as needed
Documenting the interactive process, including the accommodations considered and the final decision, is essential for demonstrating compliance and protecting the organization from legal challenges.
Documentation and Record-Keeping:
Maintaining accurate and comprehensive records is crucial for demonstrating compliance with the ADA. Employers should document all aspects of the accommodation process, including:
- Accommodation requests and the interactive process
- Medical documentation related to the accommodation
- Accommodations provided and their effectiveness
- Any denials of accommodation requests and the reasons for the denial
Employers should also maintain records of ADA training, non-discrimination policies, and disability-related complaints or incidents. These records should be kept separate from general personnel files and maintained in a secure location with limited access.
Regular Audits:
Regular audits of the organization’s ADA compliance are essential for identifying and addressing potential issues. Audits should review:
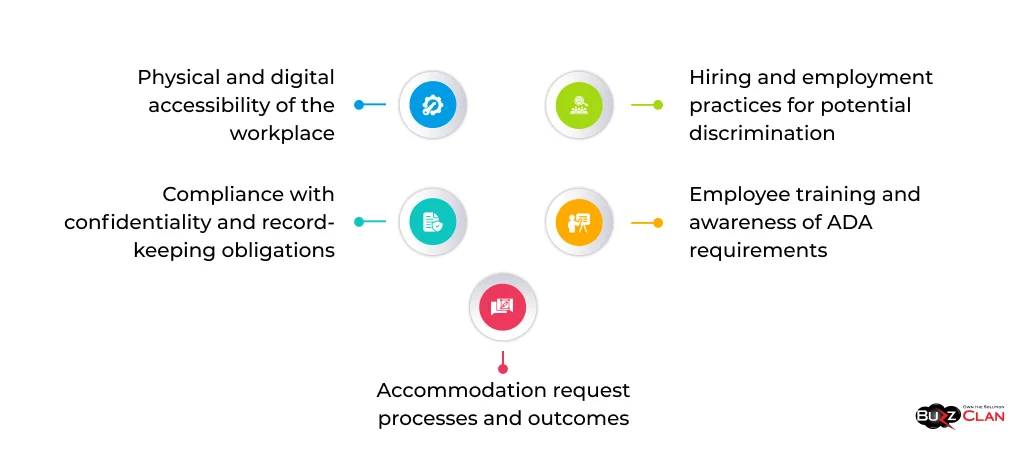
- Physical and digital accessibility of the workplace
- Hiring and employment practices for potential discrimination
- Accommodation request processes and outcomes
- Employee training and awareness of ADA requirements
- Compliance with confidentiality and record-keeping obligations
Audits can be conducted internally by HR or compliance teams or by external consultants specializing in ADA compliance. Regular audits help organizations proactively identify and address compliance gaps, reducing the risk of legal challenges and promoting an inclusive workplace.
Best Practices for ADA Compliance
Beyond the specific compliance strategies outlined above, employers should also implement several best practices to create a truly inclusive workplace that supports employees with disabilities.
Inclusive Hiring Practices:
Developing inclusive hiring practices is essential for attracting and retaining a diverse workforce that includes individuals with disabilities. Some best practices for inclusive hiring include:
- Ensuring that job descriptions focus on essential functions and do not unnecessarily screen out individuals with disabilities
- Making the application and interview process accessible, such as providing alternative formats for applications or conducting interviews in accessible locations
- Training hiring managers and interviewers on avoiding bias and discrimination in the selection process
- Actively recruiting candidates with disabilities through targeted outreach and partnerships with disability organizations
- Highlighting the organization’s commitment to diversity and inclusion in job postings and recruitment materials
Creating an Inclusive Culture:
Fostering an inclusive workplace culture is critical for ensuring that employees with disabilities feel valued, supported, and able to contribute to the organization’s success. Some best practices for creating an inclusive culture include:
- Promoting disability awareness and understanding through training, workshops, and educational resources
- Encouraging open communication and dialogue about disability-related issues
- Celebrating diversity and recognizing the contributions of employees with disabilities
- Providing mentorship and career development opportunities for employees with disabilities
- Involving employees with disabilities in decision-making processes and soliciting their feedback on workplace policies and practices
Accessibility Initiatives:
Implementing proactive accessibility initiatives demonstrates the organization’s commitment to inclusion and ensures all employees can fully participate in the workplace. Some examples of accessibility initiatives include:
- Conducting regular accessibility audits of physical and digital spaces
- Investing in assistive technologies and ensuring compatibility with existing systems
- Providing accessible transportation options for work-related events and travel
- Partnering with disability organizations to identify and implement best practices for accessibility
- Establishing an accessibility committee to oversee and prioritize accessibility efforts
Feedback Mechanisms:
Establishing clear and accessible feedback mechanisms is essential for ensuring that employees with disabilities can voice their concerns, report any issues, and suggest improvements to the workplace. Some best practices for feedback mechanisms include:
- Providing multiple channels for feedback, such as anonymous surveys, suggestion boxes, or designated HR representatives
- Ensuring that feedback processes are accessible and inclusive, such as providing alternative formats for surveys or offering sign language interpretation for in-person meetings
- Training managers and supervisors on how to actively listen and respond to feedback from employees with disabilities
- Regularly reviewing and acting upon feedback to demonstrate the organization’s commitment to continuous improvement
Case Studies and Examples
To illustrate the impact and benefits of effective ADA compliance, let’s explore two real-world case studies.
Case Study 1: Microsoft’s Inclusive Hiring Program
Microsoft, a global technology leader, has implemented a comprehensive, inclusive hiring program to attract and retain employees with disabilities. The program includes:
- Partnerships with disability organizations and universities to reach a diverse pool of candidates
- Accessible job postings and application processes, including alternative formats and assistive technologies
- Training for hiring managers and interviewers on inclusive hiring practices and avoiding bias
- Mentorship and career development opportunities for employees with disabilities
- Accessibility initiatives, such as ensuring that all products and services are designed with accessibility in mind
As a result of this program, Microsoft has significantly increased the representation of employees with disabilities in its workforce and has been recognized as a leader in disability inclusion. The company has also reported increased innovation and productivity as diverse teams bring new perspectives and ideas.
Case Study 2: Starbucks’ Accessible Workplace Initiative
Starbucks, a global coffee chain, has implemented an accessible workplace initiative to ensure that all employees, including those with disabilities, can fully contribute to the company’s success. The initiative includes:
- Conducting regular accessibility audits of stores and facilities
- Providing accessible equipment and assistive technologies, such as adjustable workstations and visual alerts for timers
- Training managers and employees on disability awareness and inclusive customer service
- Partnering with disability organizations to identify and implement best practices for accessibility
- Establishing an accessibility feedback process for employees and customers to report any issues or suggest improvements
Through this initiative, Starbucks has created a more inclusive and welcoming environment for employees and customers with disabilities. The company has reported increased employee engagement, customer satisfaction, and positive brand recognition for its commitment to accessibility.
Lessons Learned:
These case studies highlight several key lessons for successful ADA compliance and disability inclusion:
- Proactive and comprehensive initiatives, such as inclusive hiring programs and accessible workplace initiatives, can have a significant impact on attracting and retaining employees with disabilities
- Partnerships with disability organizations and other experts can provide valuable guidance and resources for implementing best practices
- Training and education for managers and employees is critical for fostering an inclusive culture and ensuring compliance with the ADA
- Accessible feedback mechanisms and regular audits are essential for identifying and addressing any issues or barriers to inclusion
- Investing in accessibility and inclusion can lead to tangible business benefits, such as increased innovation, productivity, and customer satisfaction
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and complying with the American Disabilities Act is a critical responsibility for every employer. By implementing the strategies and best practices outlined in this blog post, organizations can create a more inclusive and welcoming workplace for employees with disabilities while reducing the risk of legal challenges and reputational damage.
From providing reasonable accommodations and ensuring an accessible work environment to fostering an inclusive culture and investing in proactive initiatives, there are many steps employers can take to demonstrate their commitment to disability inclusion. By engaging in an interactive process with employees, maintaining accurate records, and conducting regular audits, organizations can ensure ongoing compliance with the ADA and identify opportunities for improvement.
Microsoft and Starbucks’ real-world case studies illustrate the tangible benefits of investing in disability inclusion, such as increased innovation, productivity, and customer satisfaction. By learning from these examples and implementing similar initiatives tailored to their specific needs, organizations can create a workplace where all employees, regardless of their disabilities, can thrive and contribute to the company’s success.
Ultimately, complying with the ADA is not just a legal obligation but a moral imperative. By embracing disability inclusion and creating a workplace that values diversity, employers can tap into a wider talent pool, foster a more engaged and productive workforce, and contribute to a more just and equitable society. It is up to each organization to take proactive steps towards ADA compliance and disability inclusion and to continuously strive for improvement in creating a truly accessible and inclusive workplace.
FAQs

Get In Touch
Follow Us

Get In Touch